Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with BPI-W3"
(→LED) |
(→NPU usage) |
||
| Line 238: | Line 238: | ||
==NPU usage== | ==NPU usage== | ||
| + | |||
| + | DEMO video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y7mYxn3rq0U | ||
| + | |||
Prepare tools | Prepare tools | ||
| + | |||
1. Use the Ubuntu18.04 / Ubuntu20.04 operating system (OS). | 1. Use the Ubuntu18.04 / Ubuntu20.04 operating system (OS). | ||
| Line 244: | Line 248: | ||
Preparation procedure | Preparation procedure | ||
| + | |||
First make sure you have docker installed on your Ubuntu system,If not, refer to the Internet installation tutorial | First make sure you have docker installed on your Ubuntu system,If not, refer to the Internet installation tutorial | ||
| Line 250: | Line 255: | ||
Create a rknpu folder on the PC server and copy the firmware to the folder | Create a rknpu folder on the PC server and copy the firmware to the folder | ||
| − | rknpu/rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0/docker$ ls | + | rknpu/rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0/docker$ ls |
| − | md5sum.txt rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0-cp36-docker.tar.gz rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0-cp38-docker.tar.gz | + | md5sum.txt rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0-cp36-docker.tar.gz rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0-cp38-docker.tar.gz |
| + | |||
Run the following command to run the docker image. After the Docker image is run, the bash environment of the image is displayed | Run the following command to run the docker image. After the Docker image is run, the bash environment of the image is displayed | ||
| − | docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb rknn-toolkit2:1.4.0-cp38 /bin/bash | + | docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb rknn-toolkit2:1.4.0-cp38 /bin/bash |
| + | |||
Map examples code into a Docker environment by attaching "-v <host src folder>:<image dst folder>"Parameters, such as: | Map examples code into a Docker environment by attaching "-v <host src folder>:<image dst folder>"Parameters, such as: | ||
| − | docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb -v /your/rknn-toolkit2-1.x.x/examples:/examples rknn-toolkit2:1.x.x /bin/bash | + | docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb -v /your/rknn-toolkit2-1.x.x/examples:/examples rknn-toolkit2:1.x.x /bin/bash |
| + | |||
The code is synchronized after mapping | The code is synchronized after mapping | ||
| Line 264: | Line 272: | ||
BOARD ARCH corresponds to the aarch64 directory on 64-bit Linux systems and to the armhf directory on 32-bit systems | BOARD ARCH corresponds to the aarch64 directory on 64-bit Linux systems and to the armhf directory on 32-bit systems | ||
| − | 1. adb push all files in Linux/rknn server/${B0ARD_ ARCH}/usr/bin/ to /usr/bin | + | 1. adb push all files in Linux/rknn server/${B0ARD_ ARCH}/usr/bin/ to /usr/bin |
| − | 2. adb push Linux/librknn api/${BOARD ARCH}/ librknrnt. so to /usr/1ib | + | 2. adb push Linux/librknn api/${BOARD ARCH}/ librknrnt. so to /usr/1ib |
| − | 3. Access the serial port terminal of the board and run the following command | + | 3. Access the serial port terminal of the board and run the following command |
chmod +x /usr/bin/rknn server | chmod +x /usr/bin/rknn server | ||
chmod +X /usr/bin/start_ rknn.sh | chmod +X /usr/bin/start_ rknn.sh | ||
chmod +X /usr/bin/restart rknn.sh | chmod +X /usr/bin/restart rknn.sh | ||
restart_ rknn. sh | restart_ rknn. sh | ||
| + | |||
run program | run program | ||
| + | |||
Execute adb devices in the docker image first, remembering the adb ID number | Execute adb devices in the docker image first, remembering the adb ID number | ||
Go to /examples/onnx/yolov5 and change test.py | Go to /examples/onnx/yolov5 and change test.py | ||
| − | ret = rknn.init_runtime(target='rk3588', device_id=DEVICE_ID, perf_debug=True,eval_mem=True) | + | ret = rknn.init_runtime(target='rk3588', device_id=DEVICE_ID, perf_debug=True,eval_mem=True) |
| − | outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[img]) | + | outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[img]) |
| − | ret = rknn.eval_perf(inputs=[img], is_print=True) | + | ret = rknn.eval_perf(inputs=[img], is_print=True) |
| − | cv2.imwrite("result.jpg", img_1) | + | cv2.imwrite("result.jpg", img_1) |
| + | |||
The above four functions are not added | The above four functions are not added | ||
Revision as of 22:37, 6 September 2023
Contents
Introduction









Before starting to use your ArmSoM-W3 get the following items ready
- PI-W3
- power supply(choose one of three)
- 12 volt @2/3A via DC Power
- USB C PD Charger (15W & above)
- 12 volt PoE
- If you wish to boot from sd card:MicroSD Card/TF Card: Class 10 or Above, minimum 8GB SDHC
specifications
Linux
The below steps is to flash linux release image into BPI-W3
Prepare
- 1. Good Type-C data cable for image download into EMMC
- 2. Usb to ttl cable if you need debug, default baudrate is 1500000.
- 3. Windows or Linux PC.
- 4. Download the Linux Release Image Release Linux Release Image, and confirm that the md5 checksum is correct before flashing.
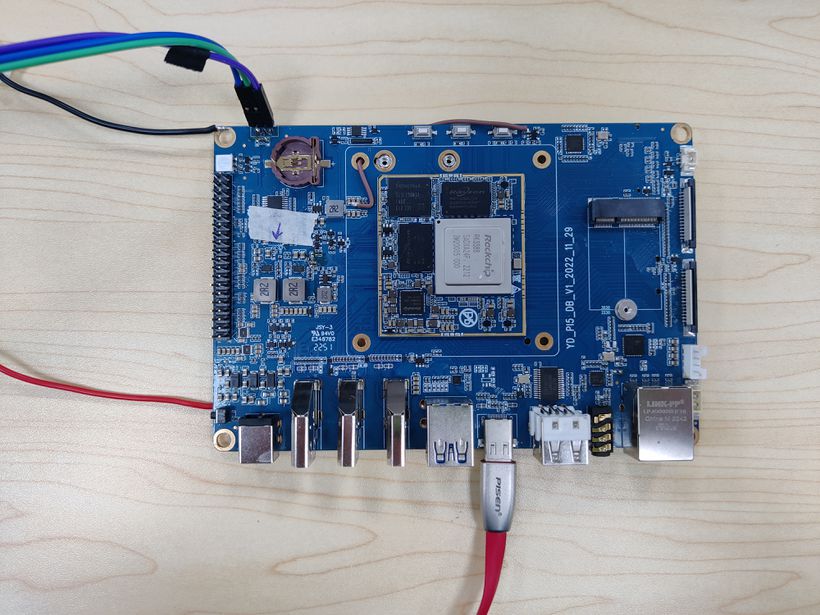
Note: The below picture is for BPI-W3's Debug Connecting, the red usb cable is Type-C data cable for image download, the three colors usb to ttl cable is linux serial console, please install CH340E's USB convert serial driver.
Starting the board for the first time
BPI-W3 can be started with eMMC Module or μSD Card..
Install Whole Image with Usb Download Tool
Windows Driver install
1. Download and install Rockchip USB driver
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
2. Download Rockchip USB Download Tool for EMMC upgrade
- This tool defaults language is Chinese. you can change it to English after extract the package. Open RKDevTool_Release_v2.84/config.ini with an text editor (like notepad). The starting lines are:
#Language Selection: Selected=1(Chinese); Selected=2(English) [Language] Kinds=2 Selected=2 LangPath=Language\
3. Open RKDevTool.exe, Switch to the “upgrade firmware” page. Press the “firmware” button to open the image file to be upgraded. The upgrade tool displays detailed firmware information.
Note: Because Linux's release image is very large, So you need wait for a long time when Software open and analysis the image file.
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
4. Disconnect power adapter, connect dual male usb cable from the top usb host port to PC.Use the Type-C data cable to connect one end to the PC and the other end to the BPI-W3 board.
5. There have two usb download mode for image upgrade.
- Uboot Usb Download Mode (loader mode)
- It's supposed to use this way if board already flashed a bootable uboot before.
- Maskrom Usb Download Mode
- Press the Recovery button or Maskrom button beside 3pin uart header and hold, connect the power adapter or press the RST button if power adapter already connected, about two seconds later, release the button. PC will Identify the device if RK usb driver installed correctly.
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
- The download tool also show the download mode if device connected.
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
6. Press the “upgrade” button to start the upgrade.
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
7: If the upgrade fails, you can try to erase the Emmc by pressing the EraseFlash button first, and then upgrade image again.
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Install Separate Images with Usb Download Tool
1. Download Rockchip USB Download Tool for EMMC upgrade 2. Open RKDevTool.exe, Switch to the “Download Image” page. The upgrade tool displays detailed all firmware image information. Then all image file is ready, you may push "run", the upgrade process begin.
Note: Because Linux's release package, Example: Ubuntu-22.04-Desktop-EMMCBoot-rockdev-MT7531SW-DSA.zip, unzip it into the same folder "Update-EMMC-Tools" inside.
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Install Image with SDcard
1. Download Rockchip SDDiskTool.
2. Insert microSD card to Windows PC, 8GB sdcard size at least.
3. Run SD_Firmware_Tool, check the “Upgrade Firmware” box and select the correct removable disk device, Choose firmware image, then Click Create button to make it and wait until it is finshed
- Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
4. Safely remove the microSD card, insert it into the R2pro board, power on the board, it will start Linux System.
Build Linux BSP Source Code
- 1. Get Linux source code
$ git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-W3-BSP
- 2. Build the Linux BSP Source code
Dual Display
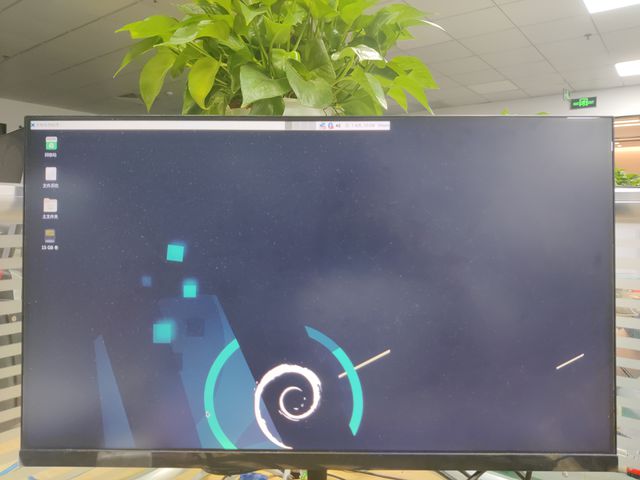
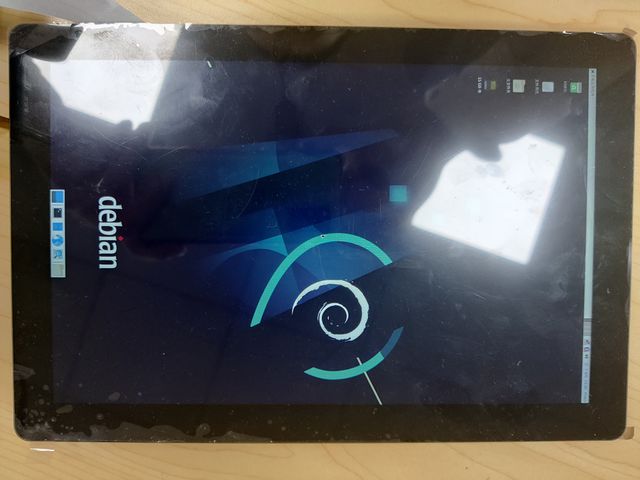
Note: All linux Image suuport dual display HDMI and MIPI-DSI together, MIPI-DSI only support 1200x1920. Note: HDMI Display
Note: MIPI-DSI panel Display
Wlan&BT
- J14 M.2 KEY E Slot is used for connect Wlan&BT adapter, default image support RTL8822CE(PCIE+USB) and RTL8822CS(SDIO+UART).
Ethernet
ArmSoM-w3 is configured with one 2.5G Ethernet interface. You can connect ArmSoM-w3 to the network using a network cable (one end is connected to an external network port or a route). The ArmSoM-w3 automatically configures the network for your Internet access.
Check that the Ethernet is working by using the ifconfig command, which displays network card eth0 or enP4p65s0, along with the Ethernet IP address. In addition, you can use the ping tool to test network connectivity.
ifconfig ping www.google.com
If the network cable is connected, no IP address is assigned to the node.
dhclient eth0 or dhclient enP4p65s0
HDMI RX
The ArmSoM-w3 uses an hdmi_in port built into the rk3588 chip,You can use the v4l2 command to test the hdmi in interface.
View all video nodes
ls /dev/video*
Look for the rk hdmirx device
Run the v4l2-ctl -d command to specify the vidoe node. Run the -D command to view the node information. Check the rk_hdmirx device using the Driver name.
# v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 -D Driver Info: Driver name : rk_hdmirx Card type : rk_hdmirx Bus info : fdee0000.hdmirx-controller Driver version : 5.10.66 Capabilities : 0x84201000 Video Capture Multiplanar Streaming Extended Pix Format Device Capabilities Device Caps : 0x04201000 Video Capture Multiplanar Streaming Extended Pix Format
Query resolution and image format
To query the current resolution and image format:
# v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video17 --get-fmt-video Format Video Capture Multiplanar: Width/Height : 3840/2160 Pixel Format : 'NV16' Field : None Number of planes : 1 Flags : premultiplied-alpha, 000000fe Colorspace : Unknown (1025fcdc) Transfer Function : Unknown (00000020) YCbCr Encoding : Unknown (000000ff) Quantization : Default Plane 0 : Bytes per Line : 3840 Size Image : 16588800
Grab image file
Save the image file to the device, adb pull to the PC, and view it through 7yuv and other tools:
v4l2-ctl --verbose -d /dev/video17 \ --set-fmt-video=width=3840,height=2160,pixelformat='NV16' \ --stream-mmap=4 --stream-skip=3 \ --stream-to=/data/4k60_nv16.yuv \ --stream-count=5 --stream-poll
Querying the HDMI RX status
Query the current status of HDMI RX, including signal locking, image format, Timings information, Pixl Clk, etc.
# cat /d/hdmirx/status status: plugin Clk-Ch:Lock Ch0:Lock Ch1:Lock Ch2:Lock Ch0-Err:0 Ch1-Err:0 Ch2-Err:0 Color Format: YUV422 Store Format: YUV422 (8 bit) Mode: 3840x2160p60 (4400x2250) hfp:172 hs:92 hbp:296 vfp:8 vs:10 vbp:72 Pixel Clk: 594024000
Camera
1. MIPI-CSI The camera uses the IMX415 module,After the camera module is connected and powered on, you can view the startup log.
root@linaro-alip:/# dmesg | grep imx415 [ 2.547754] imx415 3-001a: driver version: 00.01.08 [ 2.547767] imx415 3-001a: Get hdr mode failed! no hdr default [ 2.547819] imx415 3-001a: Failed to get power-gpios [ 2.547826] imx415 3-001a: could not get default pinstate [ 2.547831] imx415 3-001a: could not get sleep pinstate [ 2.547850] imx415 3-001a: supply dvdd not found, using dummy regulator [ 2.547918] imx415 3-001a: supply dovdd not found, using dummy regulator [ 2.547945] imx415 3-001a: supply avdd not found, using dummy regulator [ 2.613843] imx415 3-001a: Detected imx415 id 0000e0 [ 2.613890] rockchip-csi2-dphy csi2-dphy0: dphy0 matches m00_b_imx415 3-001a:bus type 5 [ 18.386174] imx415 3-001a: set fmt: cur_mode: 3864x2192, hdr: 0 [ 18.389067] imx415 3-001a: set exposure(shr0) 2047 = cur_vts(2250) - val(203)
The kernel assigns device information description files to the camera.
grep "" /sys/class/video4linux/v*/name | grep mainpath /sys/class/video4linux/video11/name:rkisp_mainpath Verify the functions of the camera
Grab a picture
# v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video11 --set-fmt-video=width=3840,height=2160,pixelformat=NV12 --stream-mmap=3 --stream-skip=60 --stream-to=/tmp/cif73.out --stream-count=3 --stream-poll
Display on desktop using gst-launch-1.0
# gst-launch-1.0 v4l2src device=/dev/video11 ! video/x-raw,format=NV12,width=3840,height=2160, framerate=30/1 ! xvimagesink
2. USB3.0 Camera
After connecting the usb3.0 camera, open the Qt V4L2 test Utility application for testing
Then open the video node: video21:
Then click the camera button, you will see the camera screen:
NPU usage
DEMO video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y7mYxn3rq0U
Prepare tools
1. Use the Ubuntu18.04 / Ubuntu20.04 operating system (OS).
2. An W3-PRO board
Preparation procedure
First make sure you have docker installed on your Ubuntu system,If not, refer to the Internet installation tutorial
We provide the source code and the docker image of the installed environment:docker image
Create a rknpu folder on the PC server and copy the firmware to the folder
rknpu/rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0/docker$ ls md5sum.txt rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0-cp36-docker.tar.gz rknn-toolkit2-1.4.0-cp38-docker.tar.gz
Run the following command to run the docker image. After the Docker image is run, the bash environment of the image is displayed
docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb rknn-toolkit2:1.4.0-cp38 /bin/bash
Map examples code into a Docker environment by attaching "-v <host src folder>:<image dst folder>"Parameters, such as:
docker run -t -i --privileged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb -v /your/rknn-toolkit2-1.x.x/examples:/examples rknn-toolkit2:1.x.x /bin/bash
The code is synchronized after mapping
The rknn service needs to run on the development board
BOARD ARCH corresponds to the aarch64 directory on 64-bit Linux systems and to the armhf directory on 32-bit systems
1. adb push all files in Linux/rknn server/${B0ARD_ ARCH}/usr/bin/ to /usr/bin
2. adb push Linux/librknn api/${BOARD ARCH}/ librknrnt. so to /usr/1ib
3. Access the serial port terminal of the board and run the following command
chmod +x /usr/bin/rknn server
chmod +X /usr/bin/start_ rknn.sh
chmod +X /usr/bin/restart rknn.sh
restart_ rknn. sh
run program
Execute adb devices in the docker image first, remembering the adb ID number
Go to /examples/onnx/yolov5 and change test.py
ret = rknn.init_runtime(target='rk3588', device_id=DEVICE_ID, perf_debug=True,eval_mem=True)
outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[img])
ret = rknn.eval_perf(inputs=[img], is_print=True)
cv2.imwrite("result.jpg", img_1)
The above four functions are not added
Run python3 test.py
LED
On BPI-W3 three-color LED is configured as LED class device. When the blue LED is not active a green LED will show to indicate the board has power. You can control the behavior mode of the blue LED by writing to /sys/class/leds/blue:status/trigger. By default only root users can write to the device. The default mode of the blue LED is heartbeat.
linaro@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# sudo su // linaro password root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# echo timer > /sys/class/leds/blue:status/trigger root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# echo activity > /sys/class/leds/blue:status/trigger
You can use cat on the trigger property to list all the available LED modes. The value in brackets is the currently active mode.
root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# cat /sys/class/leds/blue:status/trigger none rfkill-any rfkill-none kbd-scrolllock kbd-numlock kbd-capslock kbd-kanalock kbd-shiftlock kbd-altgrlock kbd-ctrllock kbd-altlock kbd-shiftllock kbd-shiftrlock kbd-ctrlllock kbd-ctrlrlock tcpm-source-psy-4-0022-online mmc2 mmc1 timer oneshot disk-activity disk-read disk-write ide-disk mtd nand-disk heartbeat backlight gpio cpu cpu0 cpu1 cpu2 cpu3 cpu4 cpu5 cpu6 cpu7 mmc0 [activity] default-on transient flash torch panic netdev rfkill0
In the None mode, writing to /sys/class/leds/blue:status/brightness can manually control the status of the blue LED.
root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# echo none > /sys/class/leds/blue:status/trigger root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# echo 1 > /sys/class/leds/blue:status/brightness root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# echo 0 > /sys/class/leds/blue:status/brightness
red light is the same, class device /sys/class/leds/red:status/trigger
RTC Device
BPI-W3 is equipped with one RTC IC hym8563
Firstly, plug in RTC battery to give power to RTC IC. Please note that we should keep the RTC battery in the RTC connector.
Secondly,Check whether the driver is successfully loaded.
root@linaro-alip:~# dmesg | grep rtc [ 3.149263] rtc-hym8563 6-0051: rtc information is valid [ 3.154624] rtc-hym8563 6-0051: registered as rtc0 [ 3.155646] rtc-hym8563 6-0051: setting system clock to 2021-01-01T12:00:05 UTC (1609502405)
Finally, check whether you can view and set the time.
root@linaro-alip:~# hwclock -r 2022-08-07 13:38:24.370866+00:00 root@linaro-alip:~# date 2022年 08月 07日 星期日 13:38:41 UTC root@linaro-alip:~# hwclock -w
Audio
View sound cards in the system.
root@linaro-alip:/# aplay -l **** List of PLAYBACK Hardware Devices **** card 0: rockchipdp0 [rockchip,dp0], device 0: rockchip,dp0 spdif-hifi-0 [rockchip,dp0 spdif-hifi-0] Subdevices: 1/1 Subdevice #0: subdevice #0 card 1: rockchipes8316 [rockchip-es8316], device 0: fe470000.i2s-ES8316 HiFi es8316.7-0011-0 [fe470000.i2s-ES8316 HiFi es8316.7-0011-0] Subdevices: 1/1 Subdevice #0: subdevice #0 card 3: rockchiphdmi0 [rockchip-hdmi0], device 0: rockchip-hdmi0 i2s-hifi-0 [rockchip-hdmi0 i2s-hifi-0] Subdevices: 1/1 Subdevice #0: subdevice #0 card 4: rockchiphdmi1 [rockchip-hdmi1], device 0: rockchip-hdmi1 i2s-hifi-0 [rockchip-hdmi1 i2s-hifi-0] Subdevices: 1/1 Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
Specify the sound card to play audio fiile.
aplay -D hw:0,0 /mnt/test.wav
MIC
root@linaro-alip:/root# arecord -D hw:1,0 -f S16_LE -t wav -c2 -r 16000 -d 3 t.wav Recording WAVE 't.wav' : Signed 16 bit Little Endian, Rate 16000 Hz, Stereo root@linaro-alip:/root# aplay t.wav Playing WAVE 't.wav' : Signed 16 bit Little Endian, Rate 16000 Hz, Stereo
Storage device
Supports three types of storage devices
microSD card
/dev/mmcblk1
eMMC
/dev/mmcblk0
NVME M.2 SDD
root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# mkdir temp root@linaro-alip:/home/linaro# mount /dev/nvme0n1 temp
FAN
echo 0 > /sys/devices/platform/fd8b0010.pwm/pwm/pwmchip*/export echo 10000 > /sys/devices/platform/fd8b0010.pwm/pwm/pwmchip*/pwm0/period echo 5000 > /sys/devices/platform/fd8b0010.pwm/pwm/pwmchip*/pwm0/duty_cycle echo inversed > /sys/devices/platform/fd8b0010.pwm/pwm/pwmchip*/pwm0/polarity echo 1 > /sys/devices/platform/fd8b0010.pwm/pwm/pwmchip*/pwm0/enable #echo 0 > /sys/devices/platform/fd8b0010.pwm/pwm/pwmchip*/pwm0/enable