BPI-5202 Loongson 2K1000LA Embedded single board industrial computer
Contents
Embedded industrial computer overview
Definition and application scenarios of embedded industrial computer
Industrial Personal Computer (IPC for short) is a reinforced and enhanced microcomputer that appeared in the 1990s and is widely used in industrial field monitoring and control. Industrial personal computers often operate in harsh environments. Data security requirements are also higher, so industrial computers are usually specially designed for reinforcement, dust-proof, moisture-proof, corrosion-proof, radiation-proof, etc. Up to now, the X86+Windows (Wintel) architecture is still the mainstream solution for industrial computers. It can be defined as a traditional industrial computer. Generally speaking
While the traditional industrial computer plays an important role in the automation and informatization of the industrial control field, its inherent weakness has always plagued manufacturers, integrators and users. Everyone is looking for a better solution
In the past ten years, the embedded system has developed rapidly. With its low power consumption, low cost and continuously improved high performance, it has become the only solution for mobile devices (mobile phones, PADs); The ideal choice for data acquisition and processing in various industries. The embedded system of ARM architecture has the characteristics of flexible and efficient customization of software and hardware solutions. At present, a complete industrial chain ecosystem has been formed, which can provide users with solutions that meet their actual needs and have certain advances. Products with extended margins and more competitive prices; when user needs gradually exceed the capabilities of current products, they can continuously provide new products that meet user requirements through rapid program design and iteration, and can realize "needs— —Technology—Scheme—Product—Market—User—Demand” a virtuous circle of rising
Compared with the traditional industrial computer, the specially designed system based on the embedded computer architecture is called the embedded industrial computer.
The main features of traditional industrial computer and embedded industrial computer are compared as follows:
| Nomber | Key elements | Traditional industrial computer (Windows+X86) | Embedded industrial computer (Linux+LoongArch/ARM) |
| 1 | performance | Commercial-grade Celeron or commercial/industrial-grade Core i3~I5 | Industrial grade, higher performance than Celeron, weaker than I3 |
| 2 | safety | Vulnerable, vulnerable to viruses and hackers | Stable system, few upgrades, high security |
| 3 | real-time | Poor real-time responsiveness | Real-time responsiveness can meet the requirements |
| 4 | reliability | High power consumption requires strong heat dissipation and low reliability | Low power consumption does not need to consider heat dissipation, high reliability |
| 5 | Scalability | It is complicated to expand various interfaces on the motherboard | It is more convenient to expand various interfaces on the core board/development board |
| 6 | industrial grade | It is more difficult to realize real industrial grade products | It is easier to realize real industrial grade products |
| 7 | Customization | Customization efficiency is low and cost is high | Application-oriented fast and efficient customization and iteration |
| 8 | performance | Insufficient or excess performance for industrial applications | Application-specific solutions with the best performance |
| 9 | overall price | higher | Application-specific, price advantage |
| 10 | Operation and maintenance cost | High power consumption and high operation and maintenance costs | Low power consumption and low cost, green and environmental protection |
| 11 | life cycle | Frequent replacement, difficult to guarantee inventory | Long CPU life cycle, guaranteed inventory |
Embedded industrial computer has become a strong competitor of traditional industrial computer. In the future, the former will form an overwhelming advantage over the latter, there is no suspense
Application Scenarios of Embedded Industrial Computers
The rapid development of the industrial Internet and the Internet of Things is not only a battle for many computer software and hardware manufacturers (including communication solutions and product manufacturers, which are essentially computer systems, even embedded system software and hardware manufacturers) trying to enter the relatively high-profit industry. It is a successive attempt to monitor the industry market; it is also an enlightenment movement to open up "people's awareness of people's wisdom" and popularize professional knowledge. This big storm, which has lasted for more than ten years, has expanded the general public's demand and imagination for monitoring and control applications to every corner of all walks of life
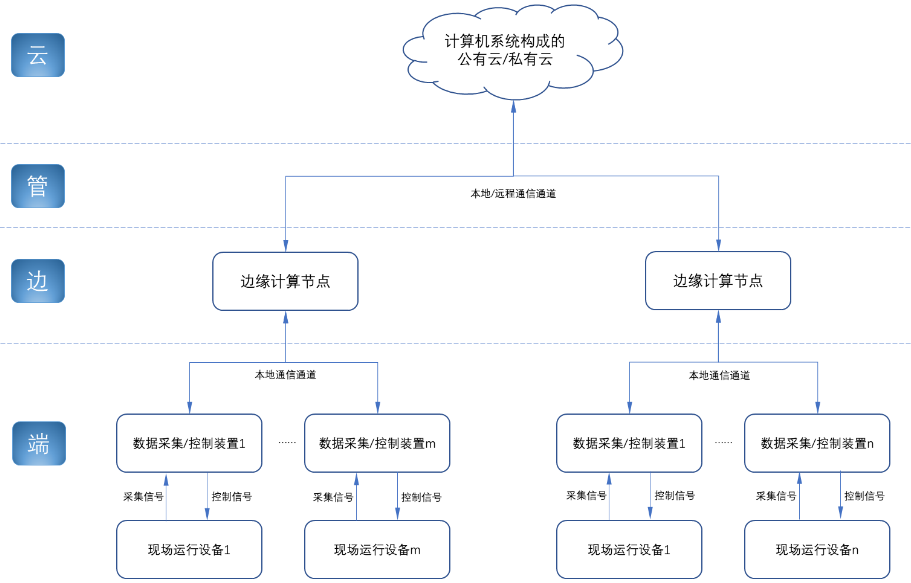
The concept of "cloud-pipe-edge-end" is a classic summary and induction of the principles of surveillance and control based on Internet thinking and terms; The mainstream model and architecture adopted by monitoring applications in various industries for decades
- Cloud: The computer system that implements the monitoring center system and more advanced application software and algorithms. The "cloud" here includes both the "public cloud" on the Internet and the "private cloud" on the enterprise LAN. Build "cloud" computer systems, currently mainly high-end X86+Windows/Linux servers, and their clusters
- Tube: Provide various efficient, reliable, convenient and cost-effective wired/wireless channels for both sides of the equipment. There are not only "pipes" between the "cloud" and "edge", such as wide area Ethernet, 4G/5G, etc.; between the "edge" and "end" of the application site, there are also pipes suitable for on-site application scenarios. The existence of wired/wireless "pipes", such as local Ethernet, serial port, high-speed power line carrier (HPLC), LoRa, ZigBee, WIFI, etc.
- Edge: A computer system used to perform on-site computing tasks. The main role of "edge" was assumed by traditional industrial computers in the early days, or by general desktops and servers when the requirements were not so strict; now there is a trend of building embedded industrial computers with mid-to-high-end ARM architecture embedded systems
- Terminal: The device (secondary device) used to monitor and control the main device (primary device) in industrial applications, and the device (secondary device) to monitor various main devices in the Internet of Things environment. The main role of "end" was realized by low-end embedded single-chip microcomputer system in the early stage; at present, it is gradually transitioning to low-end embedded system (main frequency below 1GMHz) as the mainstream solution
From the above analysis, it is not difficult to see that the application of industrial computer is mainly located at the "edge" level. As a specific application of "edge", the embedded industrial computer mainly carries the following two types of functions:
- Automatic operations, such as gateways, NVRs, routers, firewalls, etc., are realized through specially designed industrial-grade low-end embedded computer systems. Some have simple character/bitmap-based display and special button parameter configuration and status display functions
- Interactive operation class, complete monitoring and system (including HMI human-computer interaction interface) and other functions, realized through a specially designed industrial-grade mid-to-high-end embedded computer system, with the interactive ability of vector graphics system
Typical Application Scenarios of Embedded Industrial Computers
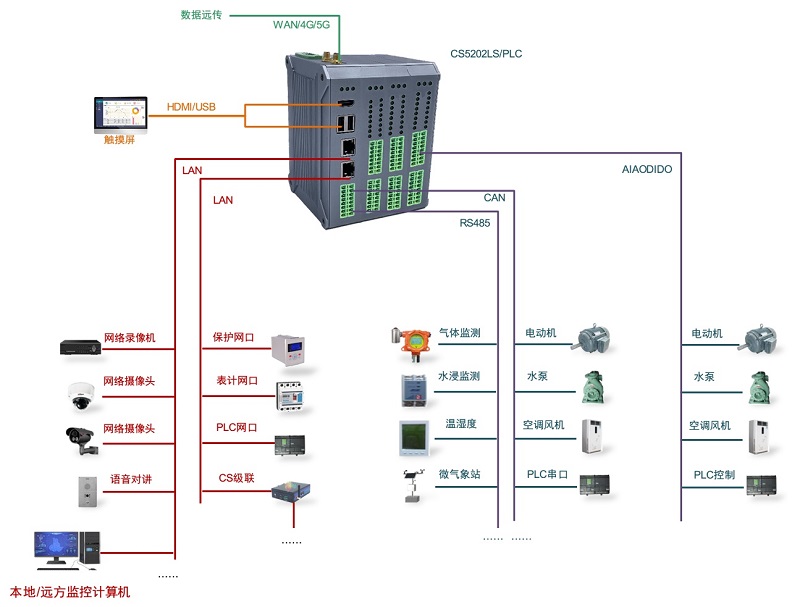
- The edge "brain" of intelligent power distribution room, computer room power environment, pumping station, intelligent park, intelligent campus, intelligent manufacturing, etc., realizes the connection with on-site data acquisition unit, measurement and control device, protection equipment, PLC equipment, CNC equipment, and robot equipment Access, protocol analysis, alarm processing, conversion, integrated transmission and control
- Embedded SCADA system (C/S, B/S mode)
- 100ms level soft PLC
- Industrial control/IoT field small data server
- Enterprise workshop-level industrial kanban/OEE kanban, lightweight MES front-end data acquisition and display that meet the requirements of "intelligent transformation and digital transformation"
- Development and operation platform for third-party algorithms and models based on industry applications
- Access and push of video front-end equipment, video recording and linkage, video AI analysis interface and comprehensive linkage of analysis results
- On-site network security and audit