Difference between pages "Getting Started with BPI-W3" and "Banana Pi BPI-M6"
(→Wlan&BT) |
(→Armbian) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[zh:香蕉派 BPI-M6]] | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-M6_1.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M6]] with Synaptics VS680]] | |
| + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-M6_2.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M6]] with Synaptics VS680]] | ||
| + | [[File:BPI-M2_Pro_2.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M2 Pro]] S905x3 design]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-M5_1.JPG|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M5 ]]Amlogic S905X3 Processor]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-M4_1.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M4]] Realtek RTD1395]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_pi_BPI-M64_1.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M64]] Allwinner A64]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_pi_BPI-M2+_2.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M2+]] Allwinner H3/H5/H2+]3]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-M6_banner.jpg]] | ||
| − | + | Banana Pi BPI-M6 is the next generation single board computer from Banana Pi in 2022,It is powered by Synaptics VS680 quad-core Cortex-A73 (2.1GHz) and One Cortex-M3 processor,Imagination GE9920 GPU.and NPU Up to 6 .75Tops. Onboard 4GB LPDDR4 memory and 16GB EMMC storage, and supports 4 USB 3.0 interface, a gigabit network port.onboard 1 HDMI-rx port and 1 Hdmi-tx port. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | ==About VideoSmart VS680== |
| + | VideoSmart™ VS680 solution, an industry-first edge computing SoC that combines a CPU, NPU, and GPU. This new multimodal platform with integrated neural network accelerator is purpose built with perceptive intelligence for applications including smart displays, smart cameras, set-top-boxes and media streamers.The Synaptics VideoSmart VS680 is a multimedia powerhouse that combines a Qdeo 4K-video engine, an audio processor capable of far-field keyword detection and voice recognition, and a proprietary SyNap deep-learning accelerator (DLA). it also integrates a higher-performance Imagination PowerVR Series9 GPU. Another new feature is an ISP with HDR capabilities that can handle two 4K cameras. Previous VideoSmart products target the streaming-video set-top-box (STB) market, but the VS680 aims for a broader range of smart-home devices. It s well suited to the Facebook Portal and other smart displays, which enable video calling. The audio processor can drive a smart speaker or sound bar, but when coupled with the DLA, it handles on-device voice-UI functions in addition to providing the front end to a cloud-based digital assistant. The DLA works with the dual ISP to run neural networks on video streams from front and rear cameras, enabling face ID, object recognition, and security monitoring, among other tasks. The Qdeo engine can drive two displays, allowing the device to power a 1080p touchscreen panel in an STB while simultaneously streaming to a 4K TV. | ||
| − | + | VS680 chip official Developer Center: https://developer.senarytech.com/index.html | |
| − | |||
| − | : | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Key Features== | ||
| + | * Synaptics VideoSmart VS680 quad-core Cortex-A73 (2.1GHz) and One Cortex-M3 processor | ||
| + | * Imagination GE9920 GPU | ||
| + | * NPU for AI up to 6 .75Tops | ||
| + | * 4GB LPDDR4 | ||
| + | * 16GB eMMC flash | ||
| + | * M.2 Key E(PCIe + MIPI CSI) | ||
| + | * 4 USB 3.0 | ||
| + | * 1 GbE ethernet | ||
| + | * 1 HDMIin and 1 HDMIout | ||
| − | == | + | ==Getting Start== |
| − | + | *[[Getting Started with BPI-M6]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | =Hardware= | |
| − | |||
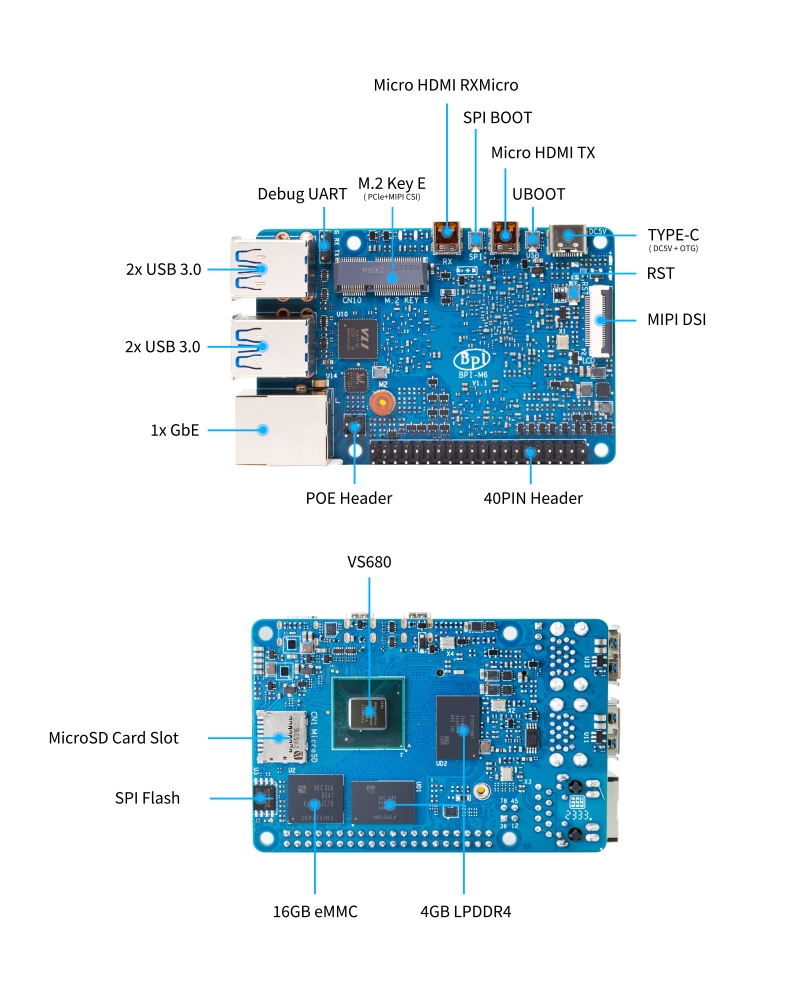
| − | + | ==Hardware interface== | |
| − | + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-M6_interface.jpg]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Hardware spec== | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" colspan="4"| '''HardWare Specification of Banana pi BPI-M6''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CPU|| Synaptics VS680 quad-core Cortex-A73 (2.1GHz) and One Cortex-M3 processor | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | GPU||Imagination GE9920 GPU | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NPU for AI|| Up to 6 .75Tops | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Memory|| 4 GB LPDDR4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Storage|| MicroSD slot with support for up to 256GB expansion and 16G eMMC flash with support for up to 64GB | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Network|| 10/100/1000 Mbit/s Ethernet ,Optional WiFi USB dongle | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Video || 1 x HDMI 2.1 (up to 4K@60Hz with HDR, CEC, EDID) out, and 1 HDMI in Port | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Audio Output(s)|| 1 x HDMI digital output | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Display||MIPI DSI interface | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |M.2 interface||M.2 Key E(PCIe + MIPI CSI) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | USB ports|| USB 3.0 PORT (x4) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO|| 40 Pin Header : GPIO (x28) and Power (+5V, +3.3V and GND). GPIO pins can be used for UART, I2C, SPI or PWM | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Switches|| SPI boot and U-boot | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | LED|| Power Status and Activity status | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Power Source|| 5 volt @3A TYPE C | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Size & Weight|| 92x60mm, 48g | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |OS|| Android and Linux | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | 4 | + | ==GPIO PIN define == |
| + | ===40PIN Header(CON3)=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" colspan="4"| ''' BPI-M6 40PIN Header(CON3)''' | ||
| − | 5 | + | |- |
| + | |BPI-M6-CON3 ||PIN ||PIN ||BPI-M6-CON3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PWR_3V3_CTL ||1 ||2 ||PWR_5V | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO46/TW0_SDA ||3 ||4 ||PWR_5V | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO47/TW0_SCL ||5 ||6 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO53/PWM1 ||7 ||8 ||SM_GPIO15/UART2_TXD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||9 ||10 ||SM_GPIO14/UART2_RXD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO36/PWM3 ||11 ||12 ||GPIO20/I2S1_BCLK | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO37/PWM2 ||13 ||14 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_4 ||15 || 16 ||EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PWR_3V3_CTL ||17 ||18 ||EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SM_GPIO13/SPI2_SDO/URT2_RTS/SM_STRAP1 ||19 ||20 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SM_GPIO12/SPI2_SDI/URT2_CTS ||21 ||22 ||GPIO4/SPDIF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SM_GPIO11/SPI2_SCK ||23 ||24 ||SM_GPIO17/SPI2_SS0/SM_STRAP2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||25 ||26 ||SM_GPIO16/SPI2_SS1/SM_STRAP3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO15/I2S1_DO3 ||27 ||28 ||GPIO16/I2S1_DO2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_7 ||29 ||30 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_6 ||31 ||32 ||EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_5 ||33 ||34 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO21/I2S1_LRCK ||35 ||36 ||EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GPIO18/I2S1_MCLK ||37 ||38 ||GPIO17/I2S1_DO1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||39 ||40 ||GPIO19/I2S1_DO0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ===M.2 E-KEY(CN10)=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | : | + | |- |
| + | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" colspan="4"| ''' BPI-M6 M.2 E-KEY(CN10)''' | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | ||PIN || ||PIN | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||1 ||2 ||VCC-NGFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NGFF_KEYE_DP ||3 ||4 ||VCC-NGFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NGFF_KEYE_DM ||5 ||6 ||WiFi-LED | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||7 ||8 ||SM_GPIO10/TW3_SDA | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD0p ||9 ||10 ||SM_GPIO9/TW3_SCL | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD0n ||11 ||12 ||NI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD1p ||13 ||14 ||BT-LED | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD1n ||5 ||16 ||BT-LED | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD2p ||17 ||18 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD2n ||19 ||20 ||SM_GPIO6/UART_WAKE#Puboot | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD3p ||21 ||22 ||GPIO43/UART3_RXD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI0_RD3n ||23 ||24 ||NOTCH | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NOTCH ||25 ||26 ||NOTCH | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NOTCH ||27 ||28 ||NOTCH | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NOTCH ||29 ||30 ||NOTCH | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |NOTCH ||31 ||32 ||GPIO42/UART3_TXD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||33 ||34 ||GPIO41/UART3_CTSn | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_TX0p ||35 ||36 ||GPIO40/UART3_RTSn | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_TX0n ||37 ||38 ||NI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||39 ||40 ||MIPI_CSI0_RCKp | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_RX0p ||41 ||42 ||MIPI_CSI0_RCKn | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_RX0n ||43 ||44 ||NI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||45 ||46 ||NI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_CLKp ||47 ||48 ||NI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_CLKn ||49 ||50 ||CLK32_OUT | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||51 ||52 ||PCIE_PERSTn | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIE_CLKREQ ||53 ||54 ||GPIO10/DISABLE_BT | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIE_PEWAKE ||55 ||56 ||GPIO09/DISABLE_WiFi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||57 ||58 ||GPIO46/TW0_SDA(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_TX1p ||59 ||60 ||GPIO47/TW0_SCL(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_TX1n ||61 ||62 ||NI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||63 ||64 ||MIPI_CSI1_RD0p | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_RX1p ||65 ||66 ||MIPI_CSI1_RD0n | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |PCIe_RX1n ||67 ||68 ||MIPI_CSI1_RD1p | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||69 ||70 ||MIPI_CSI1_RD1n | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI1_RCKp ||71 ||72 ||VCC-NGFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |MIPI_CSI1_RCKn ||73 ||74 ||VCC-NGFF | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |GND ||75 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ===MIPI DSI(CN12)=== | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" colspan="4"| ''' BPI-M6 MIPI DSI(CN12)''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P1 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D0n | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P2 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D0p | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P3 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D1n | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P4 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D1p | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P5 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_CLKn | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P6 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_CLKp | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P7 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D2n | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P8 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D2p | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P9 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D3n | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P10 ||MIPI_DSI_TX1_D3p | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P11 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P12 ||LCD_ADC | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P13 ||GPIO2/LCD1_PWR_EN(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P14 ||GPIO3/LCD1_RST(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P15 ||GPIO39/LCD1_BL_PWM(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P16 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P17 ||GPIO0/TP_INT(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P18 ||GPIO1/TP_RST(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P19 ||GPIO47/TW0_SCL(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P20 ||GPIO46/TW0_SDA(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P21 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P22 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P23 ||PWR_5V | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CN12-P24 ||PWR_5V | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | ===Debug UART(CON2)=== | |
| − | : | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="background: PaleTurquoise; color: black" colspan="4"| '''BPI-M6 Debug UART(CON2)''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CON2-P1 ||GND | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CON2-P2 ||UART0-RX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |CON2-P3 ||UART0-TX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | = | + | =Software= |
| + | ==Source code on github== | ||
| − | + | Armbian Source code: | |
| − | : | + | *https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/armbian-build/commit/9163a04ca984461bec2516e9be0acd8a990863b9 |
| − | + | *https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/armbian-build/tree/v23.12.18 | |
| − | + | Linux Source code: | |
| − | + | *https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/pi-linux/tree/pi-5.4-vs680-hdmi-rx | |
| + | *https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/pi-u-boot/tree/v2019.10-vs680-hdmi-rx | ||
| − | : | + | ==Documents== |
| − | : | + | *Senary VS680(Synaptics SN3680) datasheet: |
| + | *The VS680 NPU is ranked first on AI benchmark website: https://ai-benchmark.com/ranking_IoT.html | ||
| − | :: | + | *BPI-M6 AI function test: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIO0K_V12D4 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :: | + | *BPI-M6 VS680 SOC System Tool Manual V1.3.2.1 |
| + | :Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1tX7UVSJQOcNhMlazQRQkpw?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888) | ||
| + | :Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gQalGLqNN24TeTBmJGzS0e3HeXxRD1fP/view?usp=sharing | ||
| − | == | + | *BPI-M6 schematic diagram |
| + | :Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/18VTAdGtQFb2nu1bku8mHBw?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888) | ||
| + | :Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1z-o5dZWcYrmTqNH3Wz9ttWUzptveCS6s/view?usp=sharing | ||
| − | + | *BPI-M6 DXF File: | |
| + | :Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Ngc11CcnufAdDcdwMd2mmQ?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888) | ||
| + | :Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HJmpC5L3YqrJt4IsN0SMD5HoowqfGCyU/view?usp=sharing | ||
| − | : | + | *Vergleich Banana Pi Bpi M6 Vs Raspberry Pi 5:https://cool-web.de/raspberry/vergleich-banana-pi-bpi-m6-vs-raspberry-pi-5.htm |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | : | + | *Banana Pi Bpi M6 Raspberry Pi 5 Alternative Ersteinrichtung Firmware Image Hochladen:https://cool-web.de/raspberry/banana-pi-bpi-m6-raspberry-pi-5-alternative-ersteinrichtung-firmware-image-hochladen.htm |
| − | == | + | =Image Release= |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Android== | |
| + | *2023-08-30 release aosp_dolphin_tablet-syna-image-lpddr4x | ||
| + | :Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1unEibD-NI8-Ti5le2E6d7g?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888) | ||
| + | :Google Drive:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1egPBOusdlNGJDdp5muAjiv2MvMya0F-H/view?usp=sharing | ||
| − | : | + | ==Linux== |
| + | ===Armbian=== | ||
| + | *2024.05.22-Armbian-bpi-senarytech_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6 | ||
| + | :Default account/password: pi/bananapi. | ||
| + | :'''Automatically set up at first boot, avoiding the trouble of using serial line configuration before fbconsole supports it.''' | ||
| + | :Google drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/14RinIcN2t8aalVt6tww4t-goOQTJf1M0/view?usp=drivesdk | ||
| + | :Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1WrHOiA_2XPjv2Uvhv2G9oQ?pwd=8888 | ||
| − | + | *2024.05.0-Armbian-bpi_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6 : Resolve sound playback issues | |
| − | + | :Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1iUooyTawTBGKnVOzZl9lSve5WLLtEarl?usp=sharing | |
| − | + | :Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UfH-2M5rImuz3ZaF2gzuDg?pwd=8888 (PIN code:8888) | |
| − | : | ||
| − | |||
| − | : | ||
| − | = | + | *Banana Pi BPI-M6 Synaptics VS680 SBC new image : fixed voice issue when play video |
| − | : | + | :Image name : 2024-04-16-Armbian-unofficial_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6_bookworm_legacy_5.4.195_cinnamon_desktop.img.xz |
| + | :Google link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1E2jS7RtWMP0ihqXgv1oo9rUxAWCC69n_/view?usp=drivesdk | ||
| + | :Baidu link : https://pan.baidu.com/s/1E_zNbfCIZtoft0nC8JJ99w?pwd=8888 | ||
| − | + | *2024-04-07-Armbian-unofficial_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6 | |
| − | = | + | :Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cEHX-n3EYtMWn1fkQd3ECA?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888) |
| − | : | + | :Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Rr874RdjsEZcdgKmVN83G08vBgGMX6f-?usp=sharing |
| − | |||
| − | : | + | *2024-03-20 armbian-unoffcial_24.2.0 image for BPI-M6,support NPU yolov6 AI recognition |
| − | + | :Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1t9aDdKxTeUnawz_vBIni0g?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888) | |
| + | :Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1CZbac_R6VgfLBoJbIzbyCzwYCmQ_j8oQ?usp=sharing | ||
| − | : | + | *2024-02-29 armbian-unoffcial_24.2.0 image for BPI-M6 |
| − | : | + | :Baidu cloud:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pZFEna3CwR-v8lS-7Z88vA?pwd=8888 (PIN code:8888) |
| − | + | :Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1uh01OPtJ05Q_TAb-5HEcSMSiLTuSivKc?usp=sharing | |
| − | === | + | ===Ubuntu=== |
| − | + | *2024-01-25-ubuntu-20.04-mate-desktop-vpu-npu-bpi-m6-aarch64-sd.img | |
| − | + | :Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1IUDdKI0lT53-jFqUgqrdGA?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888) | |
| − | : | + | :Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1mw0Fiwa0fmXyTs6c6DI9Z4bcQZEy83p2/view?usp=sharing |
| − | : | ||
| − | : | ||
| − | : | ||
| − | = | + | =Easy to buy sample= |
| − | + | *SINOVOIP Aliexpress Shop: https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256805894958914.html | |
| − | + | *BIPAI Aliexpress Shop: https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256805895088983.html | |
| − | + | *Taobao Shop:https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a213gs.success.result.1.27e34831MXYuie&id=740957817652&qq-pf-to=pcqq.group | |
| − | + | *OEM&ODM, please contact: judyhuang@banana-pi.com | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 21:53, 30 May 2024
Introduction







Banana Pi BPI-M6 is the next generation single board computer from Banana Pi in 2022,It is powered by Synaptics VS680 quad-core Cortex-A73 (2.1GHz) and One Cortex-M3 processor,Imagination GE9920 GPU.and NPU Up to 6 .75Tops. Onboard 4GB LPDDR4 memory and 16GB EMMC storage, and supports 4 USB 3.0 interface, a gigabit network port.onboard 1 HDMI-rx port and 1 Hdmi-tx port.
About VideoSmart VS680
VideoSmart™ VS680 solution, an industry-first edge computing SoC that combines a CPU, NPU, and GPU. This new multimodal platform with integrated neural network accelerator is purpose built with perceptive intelligence for applications including smart displays, smart cameras, set-top-boxes and media streamers.The Synaptics VideoSmart VS680 is a multimedia powerhouse that combines a Qdeo 4K-video engine, an audio processor capable of far-field keyword detection and voice recognition, and a proprietary SyNap deep-learning accelerator (DLA). it also integrates a higher-performance Imagination PowerVR Series9 GPU. Another new feature is an ISP with HDR capabilities that can handle two 4K cameras. Previous VideoSmart products target the streaming-video set-top-box (STB) market, but the VS680 aims for a broader range of smart-home devices. It s well suited to the Facebook Portal and other smart displays, which enable video calling. The audio processor can drive a smart speaker or sound bar, but when coupled with the DLA, it handles on-device voice-UI functions in addition to providing the front end to a cloud-based digital assistant. The DLA works with the dual ISP to run neural networks on video streams from front and rear cameras, enabling face ID, object recognition, and security monitoring, among other tasks. The Qdeo engine can drive two displays, allowing the device to power a 1080p touchscreen panel in an STB while simultaneously streaming to a 4K TV.
VS680 chip official Developer Center: https://developer.senarytech.com/index.html
Key Features
- Synaptics VideoSmart VS680 quad-core Cortex-A73 (2.1GHz) and One Cortex-M3 processor
- Imagination GE9920 GPU
- NPU for AI up to 6 .75Tops
- 4GB LPDDR4
- 16GB eMMC flash
- M.2 Key E(PCIe + MIPI CSI)
- 4 USB 3.0
- 1 GbE ethernet
- 1 HDMIin and 1 HDMIout
Getting Start
Hardware
Hardware interface
Hardware spec
| HardWare Specification of Banana pi BPI-M6 | |||
| CPU | Synaptics VS680 quad-core Cortex-A73 (2.1GHz) and One Cortex-M3 processor | ||
| GPU | Imagination GE9920 GPU | ||
| NPU for AI | Up to 6 .75Tops | ||
| Memory | 4 GB LPDDR4 | ||
| Storage | MicroSD slot with support for up to 256GB expansion and 16G eMMC flash with support for up to 64GB | ||
| Network | 10/100/1000 Mbit/s Ethernet ,Optional WiFi USB dongle | ||
| Video | 1 x HDMI 2.1 (up to 4K@60Hz with HDR, CEC, EDID) out, and 1 HDMI in Port | ||
| Audio Output(s) | 1 x HDMI digital output | ||
| Display | MIPI DSI interface | ||
| M.2 interface | M.2 Key E(PCIe + MIPI CSI) | ||
| USB ports | USB 3.0 PORT (x4) | ||
| GPIO | 40 Pin Header : GPIO (x28) and Power (+5V, +3.3V and GND). GPIO pins can be used for UART, I2C, SPI or PWM | ||
| Switches | SPI boot and U-boot | ||
| LED | Power Status and Activity status | ||
| Power Source | 5 volt @3A TYPE C | ||
| Size & Weight | 92x60mm, 48g | ||
| OS | Android and Linux | ||
GPIO PIN define
40PIN Header(CON3)
| BPI-M6 40PIN Header(CON3) | |||
| BPI-M6-CON3 | PIN | PIN | BPI-M6-CON3 |
| PWR_3V3_CTL | 1 | 2 | PWR_5V |
| GPIO46/TW0_SDA | 3 | 4 | PWR_5V |
| GPIO47/TW0_SCL | 5 | 6 | GND |
| GPIO53/PWM1 | 7 | 8 | SM_GPIO15/UART2_TXD |
| GND | 9 | 10 | SM_GPIO14/UART2_RXD |
| GPIO36/PWM3 | 11 | 12 | GPIO20/I2S1_BCLK |
| GPIO37/PWM2 | 13 | 14 | GND |
| EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_4 | 15 | 16 | EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_0 |
| PWR_3V3_CTL | 17 | 18 | EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_1 |
| SM_GPIO13/SPI2_SDO/URT2_RTS/SM_STRAP1 | 19 | 20 | GND |
| SM_GPIO12/SPI2_SDI/URT2_CTS | 21 | 22 | GPIO4/SPDIF |
| SM_GPIO11/SPI2_SCK | 23 | 24 | SM_GPIO17/SPI2_SS0/SM_STRAP2 |
| GND | 25 | 26 | SM_GPIO16/SPI2_SS1/SM_STRAP3 |
| GPIO15/I2S1_DO3 | 27 | 28 | GPIO16/I2S1_DO2 |
| EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_7 | 29 | 30 | GND |
| EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_6 | 31 | 32 | EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_3 |
| EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_5 | 33 | 34 | GND |
| GPIO21/I2S1_LRCK | 35 | 36 | EXPANDER_TW3_GPIO1_2 |
| GPIO18/I2S1_MCLK | 37 | 38 | GPIO17/I2S1_DO1 |
| GND | 39 | 40 | GPIO19/I2S1_DO0 |
M.2 E-KEY(CN10)
| BPI-M6 M.2 E-KEY(CN10) | |||
| PIN | PIN | ||
| GND | 1 | 2 | VCC-NGFF |
| NGFF_KEYE_DP | 3 | 4 | VCC-NGFF |
| NGFF_KEYE_DM | 5 | 6 | WiFi-LED |
| GND | 7 | 8 | SM_GPIO10/TW3_SDA |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD0p | 9 | 10 | SM_GPIO9/TW3_SCL |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD0n | 11 | 12 | NI |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD1p | 13 | 14 | BT-LED |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD1n | 5 | 16 | BT-LED |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD2p | 17 | 18 | GND |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD2n | 19 | 20 | SM_GPIO6/UART_WAKE#Puboot |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD3p | 21 | 22 | GPIO43/UART3_RXD |
| MIPI_CSI0_RD3n | 23 | 24 | NOTCH |
| NOTCH | 25 | 26 | NOTCH |
| NOTCH | 27 | 28 | NOTCH |
| NOTCH | 29 | 30 | NOTCH |
| NOTCH | 31 | 32 | GPIO42/UART3_TXD |
| GND | 33 | 34 | GPIO41/UART3_CTSn |
| PCIe_TX0p | 35 | 36 | GPIO40/UART3_RTSn |
| PCIe_TX0n | 37 | 38 | NI |
| GND | 39 | 40 | MIPI_CSI0_RCKp |
| PCIe_RX0p | 41 | 42 | MIPI_CSI0_RCKn |
| PCIe_RX0n | 43 | 44 | NI |
| GND | 45 | 46 | NI |
| PCIe_CLKp | 47 | 48 | NI |
| PCIe_CLKn | 49 | 50 | CLK32_OUT |
| GND | 51 | 52 | PCIE_PERSTn |
| PCIE_CLKREQ | 53 | 54 | GPIO10/DISABLE_BT |
| PCIE_PEWAKE | 55 | 56 | GPIO09/DISABLE_WiFi |
| GND | 57 | 58 | GPIO46/TW0_SDA(VDDIO_1.8V) |
| PCIe_TX1p | 59 | 60 | GPIO47/TW0_SCL(VDDIO_1.8V) |
| PCIe_TX1n | 61 | 62 | NI |
| GND | 63 | 64 | MIPI_CSI1_RD0p |
| PCIe_RX1p | 65 | 66 | MIPI_CSI1_RD0n |
| PCIe_RX1n | 67 | 68 | MIPI_CSI1_RD1p |
| GND | 69 | 70 | MIPI_CSI1_RD1n |
| MIPI_CSI1_RCKp | 71 | 72 | VCC-NGFF |
| MIPI_CSI1_RCKn | 73 | 74 | VCC-NGFF |
| GND | 75 | ||
MIPI DSI(CN12)
| BPI-M6 MIPI DSI(CN12) | |||
| CN12-P1 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D0n | ||
| CN12-P2 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D0p | ||
| CN12-P3 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D1n | ||
| CN12-P4 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D1p | ||
| CN12-P5 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_CLKn | ||
| CN12-P6 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_CLKp | ||
| CN12-P7 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D2n | ||
| CN12-P8 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D2p | ||
| CN12-P9 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D3n | ||
| CN12-P10 | MIPI_DSI_TX1_D3p | ||
| CN12-P11 | GND | ||
| CN12-P12 | LCD_ADC | ||
| CN12-P13 | GPIO2/LCD1_PWR_EN(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| CN12-P14 | GPIO3/LCD1_RST(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| CN12-P15 | GPIO39/LCD1_BL_PWM(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| CN12-P16 | GND | ||
| CN12-P17 | GPIO0/TP_INT(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| CN12-P18 | GPIO1/TP_RST(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| CN12-P19 | GPIO47/TW0_SCL(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| CN12-P20 | GPIO46/TW0_SDA(VDDIO_1.8V) | ||
| CN12-P21 | GND | ||
| CN12-P22 | GND | ||
| CN12-P23 | PWR_5V | ||
| CN12-P24 | PWR_5V | ||
Debug UART(CON2)
| BPI-M6 Debug UART(CON2) | |||
| CON2-P1 | GND | ||
| CON2-P2 | UART0-RX | ||
| CON2-P3 | UART0-TX | ||
Software
Source code on github
Armbian Source code:
- https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/armbian-build/commit/9163a04ca984461bec2516e9be0acd8a990863b9
- https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/armbian-build/tree/v23.12.18
Linux Source code:
- https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/pi-linux/tree/pi-5.4-vs680-hdmi-rx
- https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/pi-u-boot/tree/v2019.10-vs680-hdmi-rx
Documents
- Senary VS680(Synaptics SN3680) datasheet:
- The VS680 NPU is ranked first on AI benchmark website: https://ai-benchmark.com/ranking_IoT.html
- BPI-M6 AI function test: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIO0K_V12D4
- BPI-M6 VS680 SOC System Tool Manual V1.3.2.1
- Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1tX7UVSJQOcNhMlazQRQkpw?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888)
- Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gQalGLqNN24TeTBmJGzS0e3HeXxRD1fP/view?usp=sharing
- BPI-M6 schematic diagram
- Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/18VTAdGtQFb2nu1bku8mHBw?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888)
- Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1z-o5dZWcYrmTqNH3Wz9ttWUzptveCS6s/view?usp=sharing
- BPI-M6 DXF File:
- Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Ngc11CcnufAdDcdwMd2mmQ?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888)
- Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HJmpC5L3YqrJt4IsN0SMD5HoowqfGCyU/view?usp=sharing
- Vergleich Banana Pi Bpi M6 Vs Raspberry Pi 5:https://cool-web.de/raspberry/vergleich-banana-pi-bpi-m6-vs-raspberry-pi-5.htm
- Banana Pi Bpi M6 Raspberry Pi 5 Alternative Ersteinrichtung Firmware Image Hochladen:https://cool-web.de/raspberry/banana-pi-bpi-m6-raspberry-pi-5-alternative-ersteinrichtung-firmware-image-hochladen.htm
Image Release
Android
- 2023-08-30 release aosp_dolphin_tablet-syna-image-lpddr4x
- Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1unEibD-NI8-Ti5le2E6d7g?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888)
- Google Drive:https://drive.google.com/file/d/1egPBOusdlNGJDdp5muAjiv2MvMya0F-H/view?usp=sharing
Linux
Armbian
- 2024.05.22-Armbian-bpi-senarytech_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6
- Default account/password: pi/bananapi.
- Automatically set up at first boot, avoiding the trouble of using serial line configuration before fbconsole supports it.
- Google drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/14RinIcN2t8aalVt6tww4t-goOQTJf1M0/view?usp=drivesdk
- Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1WrHOiA_2XPjv2Uvhv2G9oQ?pwd=8888
- 2024.05.0-Armbian-bpi_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6 : Resolve sound playback issues
- Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1iUooyTawTBGKnVOzZl9lSve5WLLtEarl?usp=sharing
- Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UfH-2M5rImuz3ZaF2gzuDg?pwd=8888 (PIN code:8888)
- Banana Pi BPI-M6 Synaptics VS680 SBC new image : fixed voice issue when play video
- Image name : 2024-04-16-Armbian-unofficial_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6_bookworm_legacy_5.4.195_cinnamon_desktop.img.xz
- Google link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1E2jS7RtWMP0ihqXgv1oo9rUxAWCC69n_/view?usp=drivesdk
- Baidu link : https://pan.baidu.com/s/1E_zNbfCIZtoft0nC8JJ99w?pwd=8888
- 2024-04-07-Armbian-unofficial_24.2.0-trunk_Bananapim6
- Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cEHX-n3EYtMWn1fkQd3ECA?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888)
- Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Rr874RdjsEZcdgKmVN83G08vBgGMX6f-?usp=sharing
- 2024-03-20 armbian-unoffcial_24.2.0 image for BPI-M6,support NPU yolov6 AI recognition
- Baidu cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1t9aDdKxTeUnawz_vBIni0g?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888)
- Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1CZbac_R6VgfLBoJbIzbyCzwYCmQ_j8oQ?usp=sharing
- 2024-02-29 armbian-unoffcial_24.2.0 image for BPI-M6
- Baidu cloud:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pZFEna3CwR-v8lS-7Z88vA?pwd=8888 (PIN code:8888)
- Google drive: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1uh01OPtJ05Q_TAb-5HEcSMSiLTuSivKc?usp=sharing
Ubuntu
- 2024-01-25-ubuntu-20.04-mate-desktop-vpu-npu-bpi-m6-aarch64-sd.img
- Baidu Cloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1IUDdKI0lT53-jFqUgqrdGA?pwd=8888 (pincode:8888)
- Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1mw0Fiwa0fmXyTs6c6DI9Z4bcQZEy83p2/view?usp=sharing
Easy to buy sample
- SINOVOIP Aliexpress Shop: https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256805894958914.html
- BIPAI Aliexpress Shop: https://www.aliexpress.us/item/3256805895088983.html
- Taobao Shop:https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a213gs.success.result.1.27e34831MXYuie&id=740957817652&qq-pf-to=pcqq.group
- OEM&ODM, please contact: [email protected]