快速上手 M1P
介绍
BPI-M1P
Banana Pi M1+ 提供板载 WiFi g/b/n支持, 开发板支持所有项目甚至更多的板载WiFi, 其可以运行Android, Lubuntu, Ubuntu, Debian, and Raspbian等系统. Banana Pi M1+ 是 M1 的升级版, 新增 WiFi 后, 用户可以更加方便的开发自己的应用或者路由项目.
- 关于更多 : Banana Pi BPI-M1+
关键特性
- Dual-core 1.0GHz CPU
- 1 GB DDR3 memeory
- Mali-400 MP2 with Open GL ES 2.0/1.1
- WiFi onbaord
开发
基础开发
开发前准备
* 准备一张容量不低于8Gb的TF卡, USB-Serial 串口线, 一台运行Ubuntu系统的PC机 * 使用你的串口线去连接M1P的调试串口
烧录第一个Linux镜像到 M1P
1.你可以从下面链接下载最近的镜像 * http://forum.banana-pi.org/t/bananapi-m1-m1p-r1-new-image-android-and-ubuntu-sever-release-2018-07-28/6357 2.在你的Ubuntu系统电脑上安装bpi-tools, 执行以下命令即可安装: * apt-get install pv * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash 3.下载完镜像后, 插入TF卡到你的Ubuntu电脑中 * 运行命令 "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" 烧录镜像到你的TF卡中. 4.烧录完成后, 把TF卡插到M1P中, 按住M1P的电源键启动M1.
进阶开发
SATA 接口
1. 挂载 SATA 到 M1P
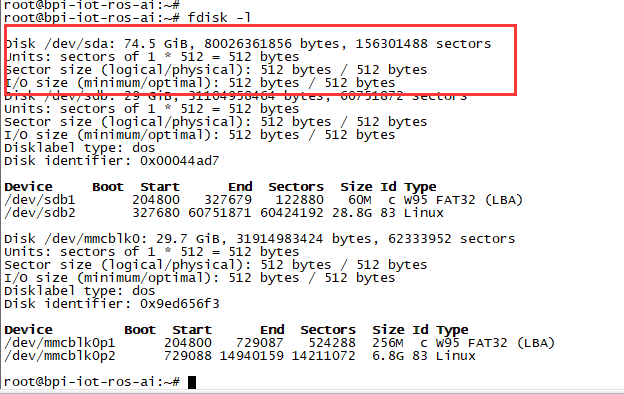
- 将硬盘接到SATA接口后, 执行命令"fdisk -l"
- 然后执行命令 "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
2. 如果你在挂载SATA的过程中遇到一些错误, 你可以尝试以下步骤来修复:
- "fdisk /dev/sdx" 来创建一个新的分区, 设置分区号和大小, 创建分区之后, 输入 "wq" 来保存退出.
- "mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdx" 来格式化 SATA
- "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
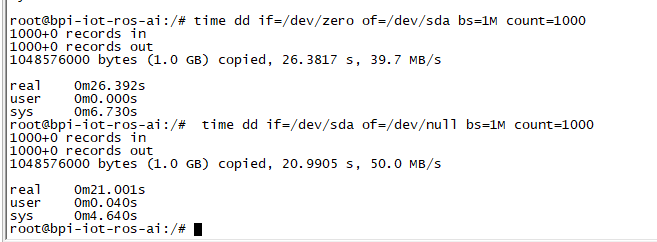
3. 挂载SATA成功后, 可以执行以下命令来测试SATA接口的性能:
- "time dd if=/dev/xxx of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1000" to test read speed
- "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed
触摸屏
GMAC
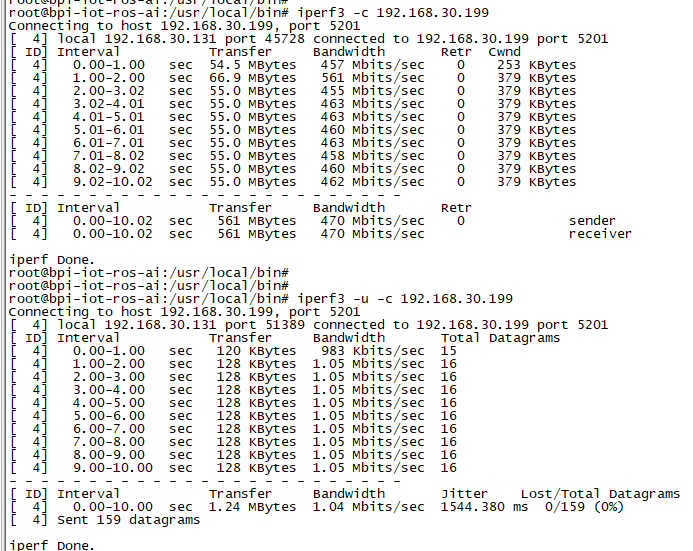
使用 iperf3 来测试 gmac
1. 在 PC 终端启动Server:
- 执行命令 "iperf3 -s"
2. 在开发板端启动Client:
- 测试 TCP: "iperf3 -c serverIP"
- 测试 UDP: "iperf3 -u -c serverIP"
WiFi on M1P
WiFi Client
这里提供两种方法来开启WiFi
1. 使用命令行来开启WiFi ip link set wlan0 up iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf network={ ssid="ssid" psk="password" priority=1 } wpa_supplicant -B -dd -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf dhclient wlan0 2. 使用图形界面来开启WiFi
2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client
清除 boot
1. 执行以下命令来清除boot git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-files/tree/master/SD/100MB bpi-bootsel BPI-cleanboot-8k.img.gz /dev/sdX
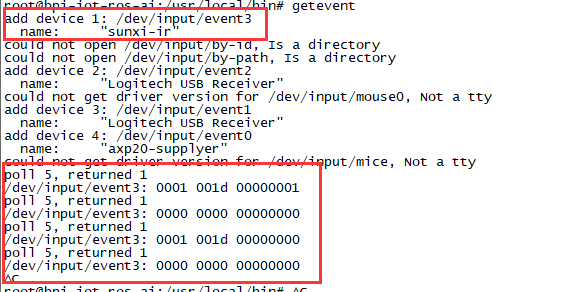
红外功能
- 执行命令 "getevent"
- 使用红外控制器发送数据到 M1P
RPi.GPIO
安装 RPi.GPIO
执行命令 "git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/RPi.GPIO" 克隆代码后, 进入到 "cd RPi,GPIO" 执行命令 "sudo apt-get update" 执行命令 "sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev" 执行命令 "sudo python setup.py install" or "sudo python3 setup.py install" to install the module
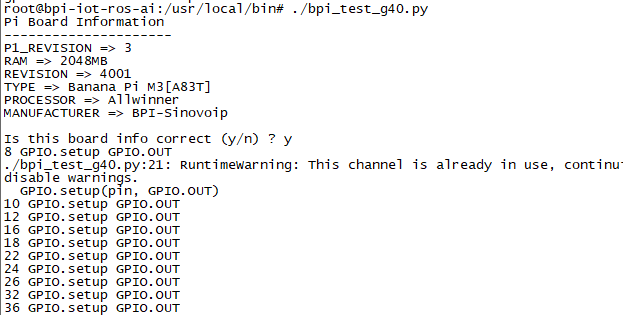
使用 RPi.GPIO
- cd /usr/local/bin
- 执行命令 "./bpi_test_g40.py" 可以测试Rpi.GPIO
WringPi
- GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git
- 我们提供了集成的命令在 "/usr/local/bin" 中
RGB 1602 LCD
- 执行命令 "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602.sh"
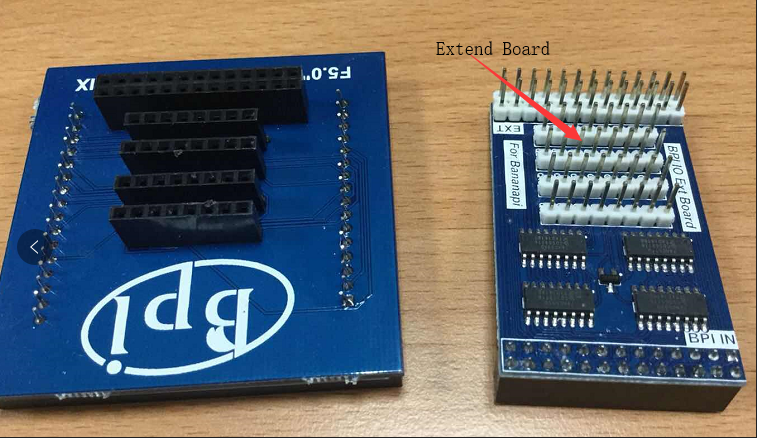
8x8 RGB LED Martix
- 首先你需要一个8x8 LED Martix 的 GPIO 扩展板
- 执行命令 "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40.sh"
文件系统
- 只读文件系统改为可读可写: "mount -o remount,rw /"
安装 QT
- sudo apt-get install build-essential
- sudo apt-get install libgl1-mesa-dev
- sudo apt-get install libglu1-mesa-dev
- sudo apt-get install freeglut3-dev
- sudo apt-get install cmake
- sudo apt-get install qt5-default qtcreator
A20 CAN Bus
In order to port can4linux to the BananaPi, the CAN module description is needed from the A20 hardware manual. can4linux is a character-driver-based Linux driver used already on desktop PCs and embedded platforms like Freescale FlexCAN (the i.MX series of micro controllers) or Xiliny Zynq.
There is a more detailed document about CAN on the A20 at: https://dl.linux-sunxi.org/A20/CAN%20Bus1.pdf
This is a tutorial for using CAN BUS on bananapi with bananian 15-01
Thank selqcir share this example:
- Download and install "bananian-1501.img" into 8 GB SDCard.
- Expand the root file system using "bananian-config"
- Install missing package:
apt-get install git apt-get update apt-get upgrade reboot
- Get last bananian available, and continu to install missing package:
git clone https://github.com/Bananian/linux-bananapi apt-get install build-essential u-boot-tools uboot-mkimage apt-get install libusb-1.0-0 libusb-1.0-0-dev git wget fakeroot kernel-package zlib1g-dev libncurses5-dev apt-get install subversion
- Build kernel:
cd linux-bananapi make menuconfig
- Exit without saving when menu appears
zcat /proc/config.gz > /root/linux-bananapi/.config make uImage modules make INSTALL_MOD_PATH=output modules_install
- At this step, kernel should be compiled and "Module.symvers" should be available
- Then rename modules and firmware provide by Bananian, and replace by the new one.
mv /lib/modules /lib/modules.old mv /lib/firmware /lib/firmware.old mv /root/linux-bananapi/output/lib/modules /lib/modules mv /root/linux-bananapi/output/lib/firmware /lib/firmware
- Same for uImage:
mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /mnt cd /mnt mv uImage uImage.old mv /root/linux-bananapi/arch/arm/boot/uImage /mnt reboot
- Create link for further build:
cd /lib/modules/3.4.104/ ln -s /root/linux-bananapi build cd ~
- Get Can4Linux and build it:
svn checkout https://svn.code.sf.net/p/can4linux/code/trunk can4linux-code cd /root/can4linux-code/can4linux/ make TARGET=BANANAPI
- Install module for each startup of the board:
insmod can4linux.ko cp can4linux.ko /lib/modules/3.4.104/kernel/net/can/ depmod -A -v modprobe -v can4linux echo "" >> /etc/modules ; echo "can4linux" >> /etc/modules reboot
- Build CAN example
apt-get install swig apt-get install python-dev cd can4linux-code/can4linux-examples/
- Update CAN speed and device in file "pyCan-example.py"
# setting the device number device = 0 defaultBaudrate = '250'
- Connect CAN transceiver and CAN bus, and check with for example:
python pyCan-example.py
That's all
With this method, kernel version is "Linux bananapi 3.4.104" instead of "Linux bananapi 3.4.104+", because i was unable to find same sources than Bananian 15-01 , but CAN bus work !