Difference between revisions of "BPI-Nano robot board"
(→Sample code) |
(→Sample code) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
==Sample code== | ==Sample code== | ||
| − | //This motor shield use Pin 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 to control the motor | + | //This motor shield use Pin 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 to control the motor |
| − | // Just plug the nano into the shield | + | // Just plug the nano into the shield |
| − | // Simply connect your motors to M1 ,M2 | + | // Simply connect your motors to M1 ,M2 |
| − | // Upload the code to BPI-NANO/arduino | + | // Upload the code to BPI-NANO/arduino |
| − | // Through serial monitor, type 'a','s', 'w','d','x' to control the motor | + | // Through serial monitor, type 'a','s', 'w','d','x' to control the motor |
| − | // http://www.banana-pi.org/ | + | // http://www.banana-pi.org/ |
| − | // http://www.banana-pi.org/ | + | // http://www.banana-pi.org/ |
| − | // Last modified on 20/09/2019 | + | // Last modified on 20/09/2019 |
| − | int EN1 = 5; //Motor 1 Enable | + | int EN1 = 5; //Motor 1 Enable |
| − | int EN2 = 3; //Motor 2 Enable | + | int EN2 = 3; //Motor 2 Enable |
| − | int IN1 = 7; | + | int IN1 = 7; |
| − | int IN2 = 8; //Motor 1 | + | int IN2 = 8; //Motor 1 |
| − | int IN3 = 2; | + | int IN3 = 2; |
| − | int IN4 = 4; //Motor 2 | + | int IN4 = 4; //Motor 2 |
| − | void Motor1(int ENA, boolean reverse) | + | void Motor1(int ENA, boolean reverse) |
{ | { | ||
digitalWrite(ENA,HIGH); | digitalWrite(ENA,HIGH); | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | void Motor2(int ENB, boolean reverse) | + | void Motor2(int ENB, boolean reverse) |
{ | { | ||
digitalWrite(ENB,HIGH); | digitalWrite(ENB,HIGH); | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | void setup() | + | void setup() |
| − | { | + | { |
int i; | int i; | ||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
Serial.begin(9600); | Serial.begin(9600); | ||
| − | } | + | } |
| − | void loop() | + | void loop() |
| − | { | + | { |
int x,delay_en; | int x,delay_en; | ||
char val; | char val; | ||
| Line 138: | Line 138: | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | } | |
| − | } | + | } |
Revision as of 23:46, 28 September 2019
Contents
Overview
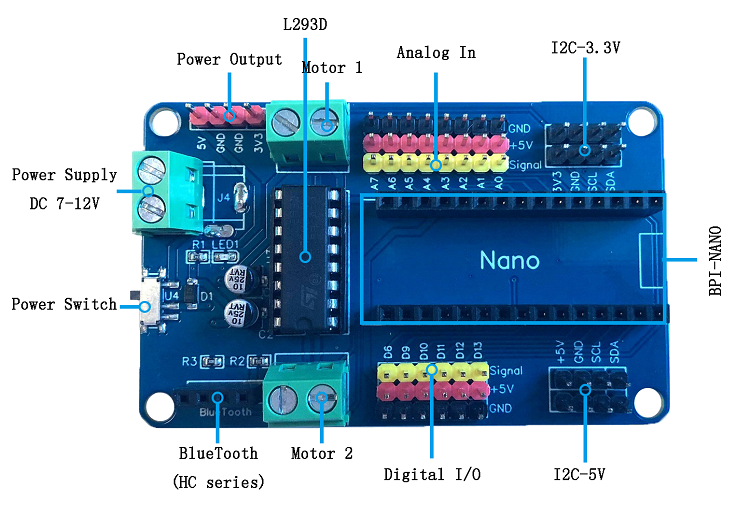
This robot board is design for Arduino Nano and Nano compatible boards. It is designed by Harsh Dethe and made by BPI factory.
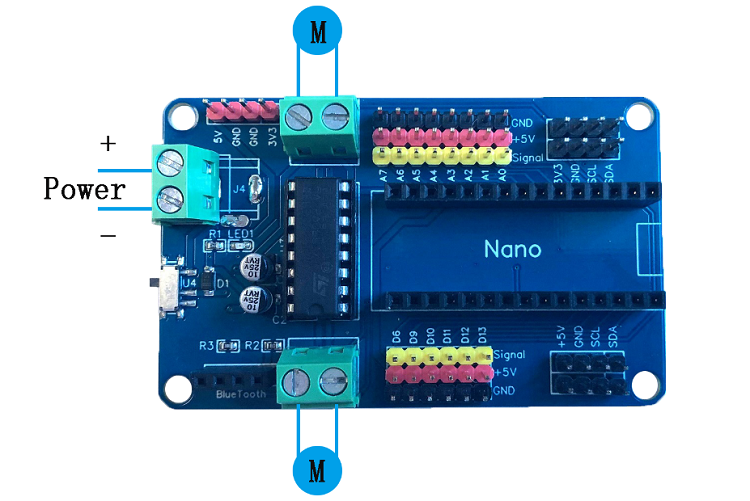
BPI-Nano robot boards motor drive expansion plate available in the bpi-nano controller supports dual-circuit motor control, with single maximum current up to 1A.
Arduino standard pin design interface, also can be used with Arduino Nano.It can be applied to the development of small mobile robot.
Hardware
Technical specifications
- Driver chip: L293B
- Logical working voltage: 5V DC
- Motor drive voltage: 7-12v DC
- Maximum driving current: 1A (per circuit)
- Pin for motor drive: pin4/5/6/7 (Arduino controller)
- Size: 56x57mm
Hardware interface
PIN define
| BPI-Nano aruino Nano robort GPIO pin define | |||
| Pin | Function | ||
| Digital 2、4 | Motor2 Steering control, 2 high level, 4 low level positive turn;Whereas inversion | ||
| Digital 3 | Motor 2 Enable interface, high level enable | ||
| Digital 5 | Motor 1 Enable interface, high level enable | ||
| Digital 7、8 | Motor 1 Steering control, 7 high level, 8 low level positive turn;Whereas inversion | ||
Software
Sample code
//This motor shield use Pin 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 to control the motor // Just plug the nano into the shield // Simply connect your motors to M1 ,M2 // Upload the code to BPI-NANO/arduino // Through serial monitor, type 'a','s', 'w','d','x' to control the motor // http://www.banana-pi.org/ // http://www.banana-pi.org/ // Last modified on 20/09/2019 int EN1 = 5; //Motor 1 Enable int EN2 = 3; //Motor 2 Enable int IN1 = 7; int IN2 = 8; //Motor 1 int IN3 = 2; int IN4 = 4; //Motor 2
void Motor1(int ENA, boolean reverse)
{
digitalWrite(ENA,HIGH);
if(reverse)
{
digitalWrite(IN1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2,LOW);
}
else
{
digitalWrite(IN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(IN1,HIGH);
}
}
void Motor2(int ENB, boolean reverse)
{
digitalWrite(ENB,HIGH);
if(reverse)
{
digitalWrite(IN3,HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN4,LOW);
}
else
{
digitalWrite(IN3,LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4,HIGH);
}
}
void setup()
{
int i;
for(i=2;i<=8;i++) //For BPI-NANO Motor Shield pinMode(i, OUTPUT); //set pin 2,3,4,5,6,78 to output mode
Serial.begin(9600); }
void loop()
{
int x,delay_en;
char val;
while(1)
{
val = Serial.read();
if(val!=-1)
{
switch(val)
{
case 'w'://Move ahead
Motor1(100,true);
Motor2(100,true);
break;
case 's'://move back
Motor1(100,false);
Motor2(100,false);
break;
case 'a'://turn left
Motor1(100,true);
Motor2(100,false);
break;
case 'd'://turn right
Motor1(100,false);
Motor2(100,true);
break;
case 'x'://stop
digitalWrite(ENA,LOW);
digitalWrite(ENB,LOW);
break;
}
}
}
}