Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with M64"
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→WringPi) |
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→WiFi Client) |
||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
* iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | * iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | ||
* vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | * vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | ||
| − | + | network={ | |
| − | * wpa_supplicant - | + | ssid="ssid" |
| + | psk="password" | ||
| + | priority=1 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | * wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | ||
* dhclient wlan0 | * dhclient wlan0 | ||
Revision as of 23:38, 19 November 2018
Contents
[hide]- 1 Introduction
- 2 Development
Introduction
BPI-M64
Banana Pi BPI-M64 is a 64-bit quad-core mini single board computer. It features 2GB of RAM and 8GB eMMC. It also has onboard WiFi and BT. On the ports side, the BPI-M64 has 2 USB A 2.0 ports, 1 USB OTG port, 1 HDMI port, 1 audio jack, and lastly a DC power port. The processor is pin-to-pin comptialbe with R18, so it comes with two versions:M64 and M64-R18
- Read more about : Banana Pi BPI-M64
A64 Key Features
- 1.2 Ghz Quad-Core ARM Cortex A53 64-Bit Processor-A64
- 2GB DDR3 SDRAM
- 8G EMMC
- 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet
- WiFi (AP6212) & Bluetooth
R18 Key Features
- 1.2 Ghz Quad-Core ARM Cortex A53 64-Bit Processor-R18
- 2GB DDR3 SDRAM
- 8G EMMC
- 10/100/1000Mbps Ethernet
- WiFi (AP6212) & Bluetooth
Development
Basic Development
Prepare to develop
* Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Ubuntu System * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on M64
Load your first image on M64
1.You could download latest image from our forum 2.Install bpi-tools on your system * apt-get install pv * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash 3.After you download the image, insert your TF card into your Ubuntu * Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card. 4.After step 3, then you can insert your TF card into M64, and press power button setup M64
Load your first image on M64 EMMC
* Run your M64 with TF card * Copy "xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip / xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img" to your USB disk * Plug your USB disk in M2U * After M64 recognise USB disk, execute "bpi-copy xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip / xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img" to install image on EMMC * Then power off M64, take TF card out, power on M64
Advanced Development
Update your image
* execute “bpi-tools”, to update your bpi tools; * execute “bpi-update -c bpi-m64.conf”, to download new driver to update your image * execute “file *.tgz”, to check download files’ type is compressed data * execute “bpi-bootsel”, you will see the bootloader path, “/usr/lib/u-boot/bananapi/bpi-m64/u-boot-with-dtb-bpi-m64-720P-8k.img.gz” * execute “bpi-bootsel /usr/lib/u-boot/bananapi/bpi-m64/u-boot-with-dtb-bpi-m64-720P-8k.img.gz”, to update your bootloader * reboot
How to build uboot & kernel
Install tools
- apt-get udpate
- apt-get install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf u-boot-tools
- apt-get install pv
- curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash
Touch screen
LCD 7"
- Execute "bpi-bootsel", you'll see a list of boot files
- Find "BPI_A64_LCD7.img.gz"
- Then execute "bpi-bootsel /usr/lib/u-boot/bananapi/bpi-m64/u-boot-with-dtb-bpi-m64-lcd7-8k.img.gz"
GMAC
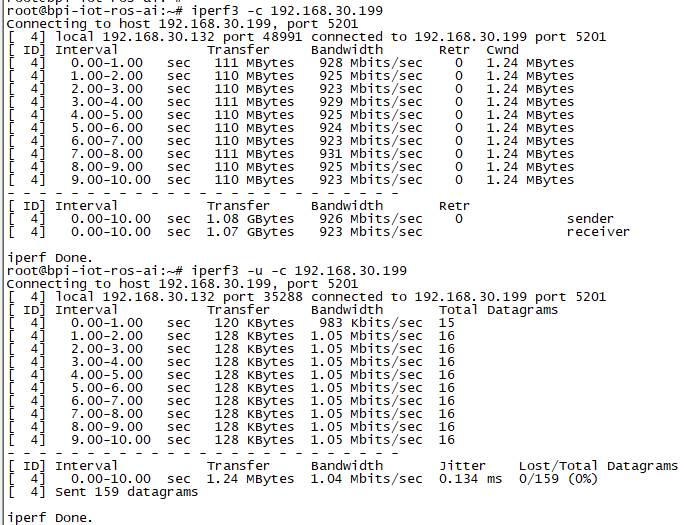
Use iperf3 to test gmac
1. On PC Terminal:
- Execute "iperf3 -s"
2. On M2U console:
- TCP test: "iperf3 -c serverIP"
- UDP test: "iperf3 -u -c serverIP"
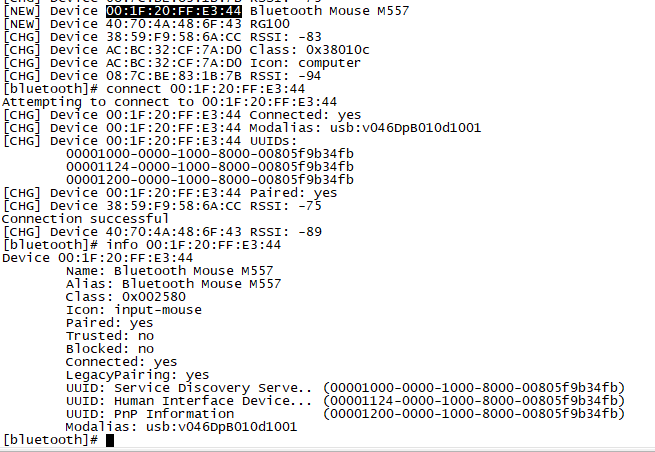
Bluetooth
- Use bluetoothctl tool to operate BT
- Execute "bluetoothctl"
- If you don't know how to use bluetoothctl, type "help", you will see more commands
- Execute these commands:
WiFi on A64
WiFi Client
You have two ways to setup WiFi Client
1. Use commands to setup WiFi client
- ip link set wlan0 up
- iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID
- vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
network={
ssid="ssid"
psk="password"
priority=1
}
- wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
- dhclient wlan0
2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client
Clear boot
- git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-files/tree/master/SD/100MB
- bpi-bootsel BPI-cleanboot-8k.img.gz /dev/sdX
Camara function
We use HDF5640 camara.
Guvcview
- Use your UI interface to operate camara
- Applications -> Sound & Video -> guvcview
Shell
- We also have built-in command in "/usr/local/bin" to test camara
- "./test_ov5640_image_mode.sh" to test picture taking function
- "./cameratest.sh" to test video recording function
IR function
- Execute "getevent"
- Use your IR device to send information to A64
RPi.GPIO
Install RPi.GPIO
- Execute "git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/RPi.GPIO"
- after clone the repo, cd RPi.GPIO
- Execute "sudo apt-get update"
- Execute "sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev"
- Execute "sudo python setup.py install" or "sudo python3 setup.py install" to install the module
Using RPi.GPIO
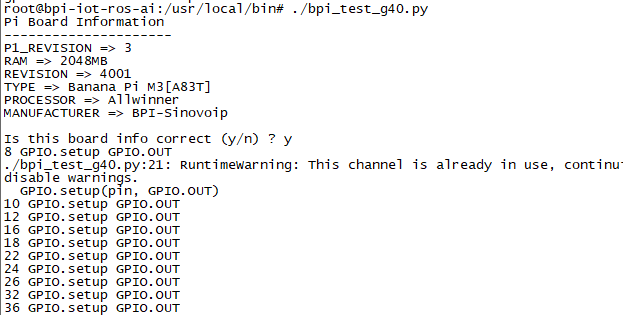
- cd /usr/local/bin
- Execute "./bpi_test_g40.py" to test RPi.GPIO
WringPi
- GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git
- We also have built-in test command in "/usr/local/bin"
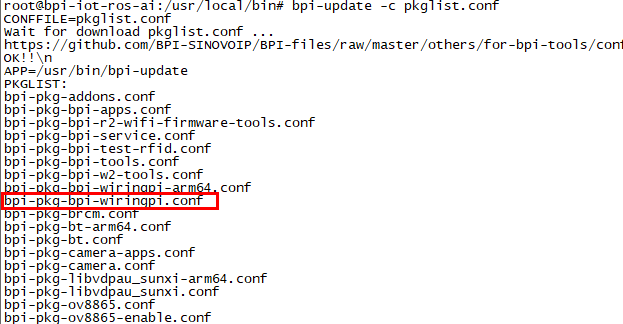
How to Update WiringPi
- Execute "bpi-update -c pkglist.conf"
- Execute "bpi-update -c bpi-pkg-bpi-wiringpi.conf"
RGB 1602 LCD
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602.sh"
0.96 Inch OLED Display
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_52pi.sh"
8x8 RGB LED Martix
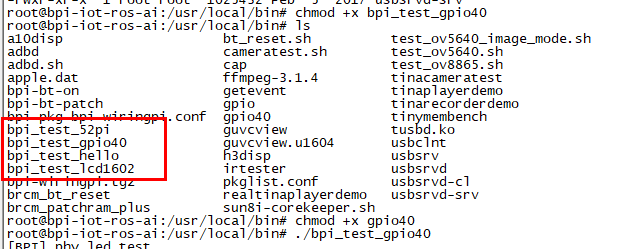
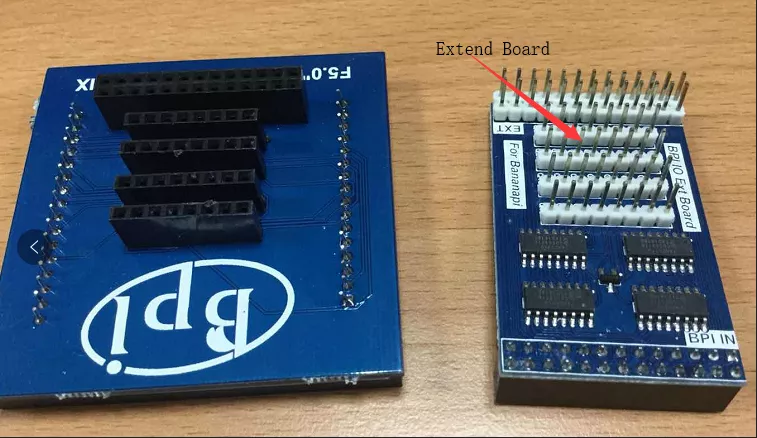
- Firstly you need a GPIO Extend Board for 8x8 LED Martix
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40.sh"
File System
- read only system change to read & write mode: "mount -o remount,rw /"