Difference between revisions of "BPI-FSM1819D Servo motor controller"
(Created page with "zh:BPI-FSM1819D 伺服电机驱动控制器 =Product overview= thumb|[[BPI-FSM1819D 伺服电机驱动控制器 采用峰岹科技方案]] ...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 20:05, 12 July 2023
Contents
- 1 Product overview
- 2 Application direction
- 3 Hardware
- 4 Hardware Specifications
- 4.1 Common servo controller electrical specifications made of modules
- 4.2 Servo module control specifications
- 4.3 Servo module communication specifications
- 4.4 Servo module I/O specifications
- 4.5 Servo module supports motor feedback specifications
- 4.6 Motor signal feedback wire pin definition
- 4.7 Servo module I/O port pin definition
- 4.8 Servo module protection function and use environment requirements
- 5 development
Product overview


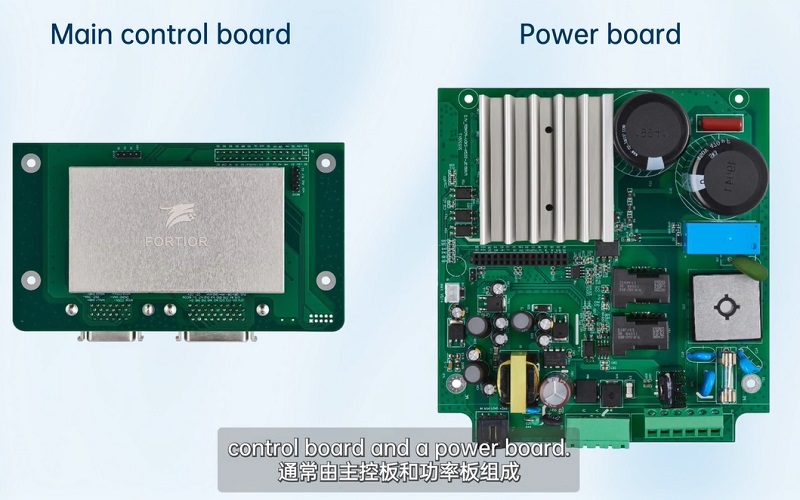
BPI-FSM8191D servo motor controller is an industrial-grade servo motor control product created by Bananapai open source community and Fortior technology. It is a servo module used to drive rotary servo motor, linear servo motor and torque motor. In practical applications, it is composed of main control board and power board, providing motor control core algorithm and various communication functions. BPI-FSM8191D servo module main control board, configured with two application ports and a power board interface, the servo module pin contains a number of signal interfaces, which can meet the debugging of most servo functions. In different application scenarios, the servo power board can be customized to provide power input and output, power supply and energy consumption requirements. The power board has a rich debugging interface, which fully meets the needs of developers for different power and power supplies.
Application direction
- New energy industry: die cutting machine, laminating machine, cutting and laminating machine, pole ear welding, coating machine, shell machine, top welding, helium detector, liquid injection machine, forming cabinet, replenishing machine, sealing welding machine, parting cabinet, Pack line, etc.
- Semiconductor industry: cleaning equipment, lithography machine, etching machine, repair testing equipment, scribing machine, wafer probe testing equipment, sorting machine, chip placement machine, bonding machine and other equipment
- New display industry: solid crystal machine, rerepair machine, dispensing machine, laminating equipment, bonding equipment, backlight assembly equipment, defoaming equipment, cutting equipment, AOI equipment and other basic complete set of process equipment.
- Optical industry: welding machine, focusing machine, pendulum machine, assembly machine, imaging detection, etc.
Hardware
Hardware Specifications
Common servo controller electrical specifications made of modules
| Servo controller electrical specifications | |||
| Number | spec | ||
| Power circuit input power supply(L1,L2,L3) | Rated Voltage(VAC line-line)±10% | 240 | |
| frequency(Hz) | 50 | ||
| 240VAC | Single phase/three phase | ||
| Control circuit input power supply(L1C,L2C) | 240±10VAC | Single phase | |
| Logic input fuse (delay) | 240VAC(A) | 0.5 | |
| STO(Safe torque cut-off) | STP DC(VDC) | 24±10% | |
| STO Fuse (delay) | 240VAC(A) | 1.5 | |
| Motor outputs(U,V,W) | Continuous output power supply(Arms) | 4.5 | |
| Continuous output power supply (Apeak) | 6.63 | ||
| Peak output current in 2 seconds(Arms) | 14 | ||
| Peak output current in 2 seconds(Apeak) | 20 | ||
| PWM frequency(kHz) | 16 | ||
| Soft boot | maximum surge current(A) | 7 | |
| Maximum charging time(ms) | 250 | ||
| tripping voltage | under voltage tripping(rated)(VDC) | 50 | |
| overvoltage tripping(VDC) | 420 | ||
| over-temperature | Power board overtemperature Indicates the fault temperature(Stable temperature)(℃) | 100±5% | |
| regenerative brake | Internal busbar capacitance(uF) | ||
| VLOW(Regenerative circuit off)(VDC) | 380 (can set) | ||
| VMAX(Regenerative circuit on)(VDC) | 400 (can set) | ||
Servo module control specifications
| Interface options: Analog voltage/pulse instruction /RS232 control specification | |||
| Item | spec | explain | |
| motor | Ac and DC | Rotary servo motor, linear servo motor | |
| Auto Config | Automatic configuration of motor phase and phase line Settings | ||
| running mode | Selectable mode | Torque control, speed control, position control | |
| torque control | Input instruction/output instruction | Speed command/PCOC | |
| performance | refresh rate62.5us (16kHz) | ||
| Step response time | |||
| control method | DQ, PI | ||
| reference command | simulate±10VDC,serial RS232 | ||
| auto adjust | Manually adjust the current loop parameters | ||
| speed control | Input instruction/output instruction | Speed command / PCOC | |
| performance | refresh rate: 125 μs (8 kHz) | ||
| Optional speed control method | PI | ||
| filter | First-order low-pass filter, two-cascaded first-order low-pass filter | ||
| reference command | simulation±10 VDC, serial RS232 or USB | ||
| position control | Input instruction/output instruction | Position command/speed command | |
| performance | refresh rate:250us(4kHz) | ||
| control method | PID and acceleration feedforward | ||
| reference command | Pulse & direction with electronic drive,serial ,serial RS232 | ||
| status display | modality | Fase 7 LED (Red),Display drive status (alarm, running, enable, etc.) | |
| electronic gear | method | User defined gear ratio | |
| GUI | UI | base on Windows serial port software | |
| function | Set connection, drive information, power information, motor, feedback, I/O selection/configuration, motion Settings/adjustments, fault history/status display, etc. | ||
| Rotate toward unit | position | pulse(Counts) | |
| speed | per minute (rpm) | ||
| Acceleration/deceleration | rps/s | ||
| line unit | position | pulse(Counts)、mm | |
| speed | mm/s | ||
| Acceleration/deceleration | mm/s2 | ||
Servo module communication specifications
| Communication specification | |||
| number | spec | ||
| RS232 | base on modbus RTU | ||
| Baud rate: 19200 bit/s | |||
| Maximum conductor length: 10 m | |||
| High-Speed Serial (Specially used to observe waveforms) | Based on custom protocols | ||
| Baud rate: 115200 - 750000 bit/s | |||
| Maximum conductor length:2 m | |||
Servo module I/O specifications
| Servo module I/O specifications | |||
| Item | standard | explain | |
| analog input | voltage range | simulate ±10 VDC Finite difference | |
| zero attenuation | 100 Hz | ||
| bandwidth (-3 dB) | 500 Hz | ||
| Pulse & Direction | signal | RS 422 line receiver | |
| Maximum input frequency | 1.6 MHz (will be increased to 5MHz in the future) | ||
| Digital input (8 channels) | signal | Configurable, light isolated, drain input. | |
| (General IO configurable related pin function) | voltage | 24 V | |
| Maximum input current | 10 mA | ||
| Transfer delay time | 1 ms | ||
| Digital output (6 channels) | signal | Configurable, light isolated, drain input. | |
| (General IO configurable related pin function) | voltage | 24 V | |
| Maximum input current | 40 mA | ||
| Transfer delay time | 1 ms | ||
| Main I/O function signal | function | explain | |
| input signal(Ports can be configured) | forward limit | Positive limit switch | |
| Negative limit | Negative limit switch | ||
| Return Origin | Origin switch | ||
| Motor enable | External enable signal | ||
| ALM-RST | External clear alarm signal | ||
| speed limitation | Torque control with speed limit input | ||
| Output signal (port configurable) | Servo positioning complete | Servo execution positioning complete signal | |
| SERVO stoped | Servo execution stop signal | ||
| SERVO ALARM | Servo error alarm signal | ||
| Servo brake | Servo brake control signal | ||
| Servo phase seeking complete | Servo phase seeking complete signal | ||
| Servo return to zero complete | Servo return to zero complete signal | ||
Servo module supports motor feedback specifications
| Supported motor feedback specifications | |||
| motor feedback | specifications | explain | |
| summary | Driver output voltage | 5 VDC | |
| Maximum output current of the driver | 250 mA | ||
| Maximum cable length | AWG 28 – 3 m; AWG 24 – 10 m | ||
| incremental encoder | signal | With (or without) a zero/hall signal AB quadrature signal encoder differential output | |
| AB Orthogonal maximum input frequency | 1.6 MHz (Orthogonality conditions) (It will be increased to 5MHz in the future) | ||
| Minimum zero pulse width | 1 µs | ||
| Hall sensor | signal | single-ended | |
| Sinusoidal encoder (will be added in next version) | signal | Sine-cosine difference, with or without Hall | |
| signal level | 1 Vpp @ 2.5 V | ||
| Maximum input frequency | 270 kHz | ||
| input impedance | 120 Ω | ||
| interpolation | Max to 16384 (14 bit) | ||
| Effective interpolation | Max to 4096 (12 bit) | ||
Motor signal feedback wire pin definition
The motor feedback interface is wired according to the type of feedback device used in practical applications. See the pin outlet table below for details.
The motor temperature sensor uses 12/25 pins and has been pulled up to 5V through the module interior.
| Motor signal feedback wire pin definition | |||||
| Pin define | Module pin | function | Pin define | Module pin | function |
| 1 | 97 | incremental encoder A+ | 14 | 98 | incremental encoder A- |
| SSI encoder data+ | |||||
| 2 | 96 | incremental encoder B+ | 15 | 95 | incremental encoder B- |
| SSI encoder clock+ | SSI encoder clock- | ||||
| 3 | 93 | incremental encoder Z+ | 16 | 94 | incremental encoder Z- |
| 4 | 116 | Hall U+ | 17 | 115 | Hall V+ |
| 5 | 114 | Hall W+ | 18 | / | / |
| 6 | / | / | 19 | / | / |
| 7 | / | / | 20 | / | / |
| 8 | / | / | 21 | / | / |
| 9 | 111 | Sine encoder sine+ | 22 | 110 | Sine encoder sine- |
| 10 | 109 | Sine encoder cosine+ | 23 | 108 | Sine encoder cosine- |
| 11 | 3、4 | 5V power | 24 | Common ground with module | ground(5V loop) |
| 12 | 91 | Motor temperature sensor | 25 | 90 | Motor temperature sensor |
| 13 | 3、4 | 5V power | 26 | / | shield |
Servo module I/O port pin definition
The digital/analog inputs and outputs are wired according to the requirements of your application. To keep the digital I/O isolated, the ground of your 24V loop is connected to pins 1 and 19, which drive the digital input pins and require you to provide a 24V signal.
| Servo module I/O port pin definition | |||||||
| Pin define | Module pin | function | explain | Pin define | Module pin | function | explain |
| 1 | 64 | Digital input to the public ground | user provides a 24V input signa ground | 19 | 72 | Digital output to the public ground | provides 24V pull-up ground |
| 2 | 107 | Equivalent encoder output Z+ | Equivalent encoder output signal Z forward direction | 20 | 84 | RS485 ommunication input - | RS485 ommunication input -(Or B terminal) |
| 3 | / | / | 21 | 83 | 485 input + | RS485 communication input +(Or A terminal) | |
| 4 | 106 | Equivalent encoder output Z- | Equivalent encoder output signal Z negative | 22 | 73 | Digital input 8 | Optically isolated programmable digital input 8 |
| 5 | 104 | Equivalent encoder output B+ | Equivalent encoder output signal B forward direction | 23 | 74 | Digital input 7 | Optically isolated programmable digital input 7 |
| 6 | / | / | 24 | 75 | Digital input 6 | Optically isolated programmable digital input 6 | |
| 7 | 105 | Equivalent encoder output B- | Equivalent encoder output signal B negative | 25 | Common ground with module | DGND | DGND |
| 8 | 112 | Analog input AN+ | Diff forward direction of analog instruction input | 26 | 76 | Digital input 5 | Optically isolated programmable digital input 5 |
| 9 | 103 | Equivalent encoder output A- | Equivalent encoder output signal A negative | 27 | 77 | Digital input 4 | Optically isolated programmable digital input 4 |
| 10 | Common ground with module | DGND | DGND | 28 | 78 | Digital input 3 | Optically isolated programmable digital input 3 |
| 11 | 102 | Equivalent encoder output A+ | Equivalent encoder output signal A forward direction | 29 | Common ground with module | DGND | DGND |
| 12 | 113 | Analog input AN- | Differential analog instruction input in negative direction | 30 | 68 | Digital output 3 | Optically isolated programmable digital output, can be read with OUT3 |
| 13 | Common ground with module | DGND | DGND | 31 | 65 | Digital output 6 | Optically isolated programmable digital output, can be read with OUT6 |
| 14 | 87 | direction input - | Direction Indicates the negative direction of the input | 32 | 69 | Digital output 2 | Optically isolated programmable digital output, can be read with OUT2 |
| 15 | 79 | Digital input 2 | Optically isolated programmable digital input,Read with IN2 | 33 | 80 | Digital input 1 | Optically isolated programmable digital input,Read with IN1 |
| 16 | 86 | direction input + | Direction Indicates the positive direction of the input | 34 | 70 | Digital output 1 | Optically isolated programmable digital output, can be read with OUT1 |
| 17 | 89 | impulse input + | The pulse input is positive | 35 | 66 | Digital output 5 | Optically isolated programmable digital output, can be read with OUT5 |
| 18 | 88 | impulse input - | The negative direction of the pulse input | 36 | 67 | Digital output 4 | Optically isolated programmable digital output, can be read with OUT4 |
Servo module protection function and use environment requirements
| Servo module protection function and use environment requirements | |||
| item | spec | ||
| Protection function | Overcurrent, undervoltage and overvoltage, overtemperature, missing feedback, STO signal not connected, position following error, speed over, parameter error, etc. | ||
| Anti-flying car protection function | When the motor is seeking phase, the external pulse input signal function (pulse & direction) and the receiving motion command function (RS232) are shielded to prevent motor accidents. | ||
development
BPI-FSM8191D servo motor controller installation
General installation instructions
Follow the steps below to install and configure the driver module.
- 1.According to the required operating power, select the appropriate power base plate.
- 2.Complete all electrical links:
- a)Install the servo module onto the module switching base plate
- b)Connect the switching base plate to the power plate
- c)motor
- d)motor feedback
- e)Safe torque switching (STO), or shorting with a jumper
- f)IO control signal
- g)AC input power supply
- 3.Connect the drive to the PC using a USB/232 cable.
- 4.Power drives and PC。
- 5.Connect to a fieldbus device (optional).
- 6.Open FortiorTechServoStudio.exe(no need installation ).
- 7.use FortiorTechServoStudio Configure and debug drives.
FortiorTechServoStudio testing software
FortiorTechServoStudio
- FortiorTechServoStudio is a graphical user interface (GUI) that comes with the servo module to install, configure, and debug the drive. FortiorTechServoStudio can be used to debug drive parameters online and perform specific drive operations.
- FortiorTechServoStudio support two methods for initial system configuration:
- Using [General - Backup and Recovery], click "Default Parameters" to complete the initial parameter configuration, then configure the motor parameters in [Motor], and configure the encoder resolution in [Feedback].
- With [General - Backup and Recovery], the motor "Import Parameters" import previously configured motor parameter data.
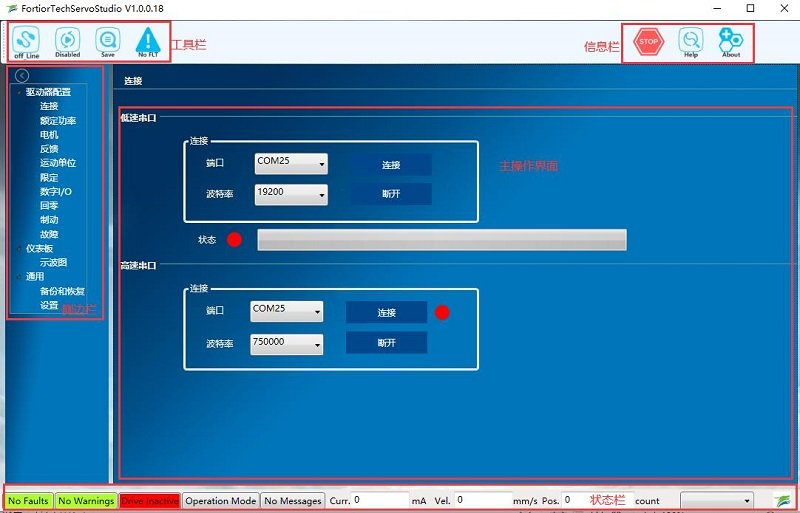
FortiorTechServoStudio main interface consists of 5 functional areas:
- 1.Toolbar, containing common quick function buttons。
- Offline|Online – Toggle FortiorTechServoStudio online/offline and display the connection status. See section [Drive Online and Offline] 。
- Enable|Disable – Enable/disable the drive and display the enable status of the drive
- Save – Saves the parameters in the current drive RAM to the drive memory. It is recommended to use the Save button after configuring parameters to save parameter values in memory.
- No FLT — Clear drive faults. This bit turns red when the drive fails, and the motor can clear the fault.
- 2.information bar:
- Stop —Stop the motor and disable the drive.
- Help —FortiorTechServoStudio software online help. This feature is not enabled in this version of the software.
- About —Information about the software version. In this version, the function is not available.
- 3.sidebar:
- include FortiorTechServoStudio A navigation menu of the interface.
- The sidebar can be hidden or displayed with this arrow button.
- 4.Main operating interface: Displays interactive interfaces for viewing, setting, and testing parameters and configuring drives. These interfaces are described in detail in other sections of this manual
- Fault display: If there is no fault, the background of the status bar is green. If there is a fault, it is red. Click this area to open the [Fault] screen.
- Warning: If there is no warning, the background of the status bar is green; If there is a warning, it is red.
- Drive status: When the drive is enabled, the background of the status bar is green and Drive Active is displayed. When the drive is not enabled, it is red and ".
- 5.Status bar: Displays the drive status.
- Fault display: If there is no fault, the background of the status bar is green. If there is a fault, it is red. Click this area to open the [Fault] screen.
- Warning: If there is no warning, the background of the status bar is green; If there is a warning, it is red (currently, no distinction is made between warning and fault).
- Drive status: When the drive is enabled, the background of the status bar is green and Drive Active is displayed. If the Drive is not enabled, it is red and Drive Inactive is displayed.
- Run mode: The background of this segment is gray. Displays the current running mode.
- Curr:Displays the current running current
- Vel:Displays the current motor speed.
- Pos:Displays the current position of the motor.
- Online/Offline:Connection status between the upper computer and the drive
Upper computer
referenced document
- BPI-FSM1819D hardware introduction and quick start video:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1oT411x77T/?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=9cec068046db4b144de233a027e084ce