Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with R2"
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→WiFi and Ap mode on R2) |
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→AP mode) |
||
| Line 144: | Line 144: | ||
* create your hostapd.conf: "vim /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf " | * create your hostapd.conf: "vim /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf " | ||
| − | + | interface=ap0 | |
| + | bridge=br0 | ||
| + | ssid=test_r2 | ||
| + | driver=nl80211 | ||
| + | country_code=US | ||
| + | hw_mode=b | ||
| + | channel=1 | ||
| + | max_num_sta=5 | ||
| + | wpa=2 | ||
| + | auth_algs=1 | ||
| + | rsn_pairwise=CCMP | ||
| + | wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK | ||
| + | wpa_passphrase=ledetest | ||
| + | logger_stdout=-1 | ||
| + | logger_stdout_level=2 | ||
* According to your network interface(can search internet) to config ap0: | * According to your network interface(can search internet) to config ap0: | ||
| − | |||
my network interface which can search internet is wan, and ip is 192.168.30.102, so I config ap0 as follows: | my network interface which can search internet is wan, and ip is 192.168.30.102, so I config ap0 as follows: | ||
| Line 153: | Line 166: | ||
* Run hostapd : “hostapd -d /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf” | * Run hostapd : “hostapd -d /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf” | ||
| − | |||
* Config dhcp file : “vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf” | * Config dhcp file : “vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf” | ||
| Line 165: | Line 177: | ||
* Config dhcp of ap0, then the devices which connect ap0 could get IP: "dhcpd ap0 -pf /var/run/dhcpd.pid " | * Config dhcp of ap0, then the devices which connect ap0 could get IP: "dhcpd ap0 -pf /var/run/dhcpd.pid " | ||
| − | |||
* And a bridge | * And a bridge | ||
| − | |||
* brctl addbr br0 | * brctl addbr br0 | ||
| − | |||
* brctl addif br0 ap0 | * brctl addif br0 ap0 | ||
| − | |||
* brctl addif br wan | * brctl addif br wan | ||
| − | |||
* Config br0 : “ifconfig br0 192.168.30.180 netmask 255.255.255.0” | * Config br0 : “ifconfig br0 192.168.30.180 netmask 255.255.255.0” | ||
| − | |||
* Add br0 gw as : “route add -net default netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.30.1 dev br0” | * Add br0 gw as : “route add -net default netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.30.1 dev br0” | ||
Revision as of 23:09, 6 May 2018
Contents
Introduction
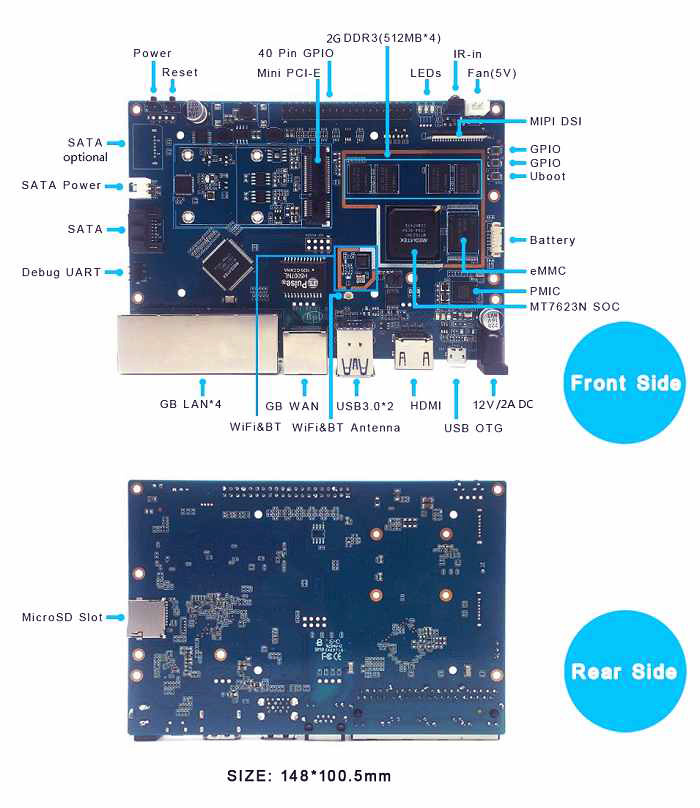
The Banana Pi R2 is a router based development board, which can run on a variety of open source operating systems including OpenWrt, Android, and Bananian. It has 4 Gigabit LAN ports, 1 Gigabit WAN, and 300Mbs wireless N capabilities.
Key Features
- MediaTek MT7623N, Quad-core ARM Cortex-A7
- Mali 450 MP4 GPU
- 2G DDR3 SDRAM
- Mini PCIE interface
- SATA interface
- 4x Gigabit LAN 1x Gigabit WAN
Hardware
Development
Let's get start to develop on BPI-R2, see amazing things happen.
Basic Development
Prepare to develop
1.Prepare 16G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, Ubuntu System
2.Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on R2
Load your first image on R2
1.You could download latest image from our forum * Here is the example image link: http://forum.banana-pi.org/t/bpi-r2-new-image-release-ubuntu-16-04-v1-3-2018-3-30/5293
2.Install bpi-tools on your Ubuntu * apt-get install pv * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash
3.After you download the image, insert your TF card into your Ubuntu * Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card.
4.After step 3, then you can insert your TF card into R2, and press power button for around 10s to setup R2.
Build your own image on R2
Ubuntu
1. Clone Bsp project from Github * Execute "git clone [email protected]:BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-R2-bsp.git"
2. Execute "./build.sh", to build your own uboot and kernel.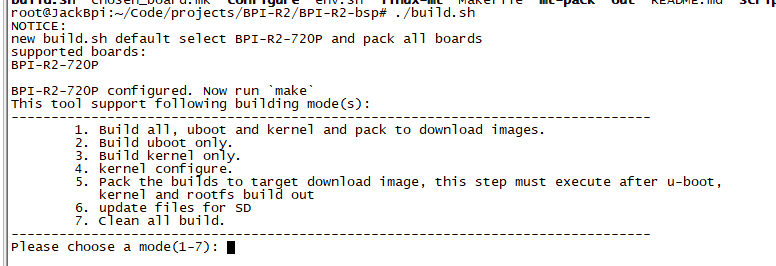
3. After finish built, Execute "cd SD", plug your Ubuntu TFcard in PC.
4. Execute "bpi-update -c bpi-r2.conf -d /dev/sdX", to update the compiled kernel to your TFcard.
5. If you want to install Ubuntu on EMMC, follow these steps: * Program ubuntu image to SD card * Install this SD to R2 board and boot from SD * Enter the Uboot prompt, and run command emmc pconf 48 to change Partition config of EMMC * And then run command reset, let it boot to OS * Enter the system with username pi or root * Run command echo 0 > /sys/block/mmcblk1boot0/force_ro to enable /dev/mmcblk1boot0 write mode` * To write preloader to EMMC by running command: "bpi-bootsel BPI-R2-EMMC-boot0-DDR1600-0k-0905.img.gz /dev/mmcblk1boot0" where BPI-R2-EMMC-boot0-DDR1600-0k-0905.img.gz is the preloader for emmc, please download it from link:https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-files/blob/master/SD/100MB/BPI-R2-EMMC-boot0-DDR1600-0k-0905.img.gz
* To copy ubuntu image to EMMC: unzip -p <XXX.img.zip> | pv | dd of=<device> bs=10M status=noxfer or bpi-copy <XXX.img.zip> <device> where the XXX.img.zip is ubuntu image we can get it from http://www.banana-pi.org/r2-download.html 40, and where should be /dev/mmcblk1. * power off * remove SD & power on
OpenWrt
1. Clone OpenWrt project from Github. * Execute "git clone https://github.com/garywangcn/bpi-r2_lede.git"
2. You need to have installed gcc, binutils, bzip2, flex, python, perl, make, find, grep, diff, unzip, gawk, getopt, subversion, libz-dev and libc headers.
3. Run "./scripts/feeds update -a" to get all the latest package definitions defined in feeds.conf / feeds.conf.default respectively and "./scripts/feeds install -a" to install symlinks of all of them into package/feeds/.
4. Use "make menuconfig" to configure your image. * Choose "Target System" to config as "MediaTek Ralink ARM" * Choose "Boot Loaders" to config as "u-boot-bpi_r2"
5. Execute "make -j1 V=s" to build your own OpenWrt image.
6. After built, we have two ways to install image.
(1) Plug your TFcard in Ubuntu PC, and enter to "build_dir/target-arm_cortex-a7+neon-vfpv4_musl_eabi/linux-mediatek_32/",
you will find two images:
* mtk-bpi-r2-EMMC.img
* mtk-bpi-r2-SD.img
(2) Write image to TF card, execute "bpi-copy if=mtk-bpi-r2-SD.img of=/dev/sdX"
(3) If you want to install image to EMMC, We need another system which is running on SD card to program EMMC image to EMMC, please follow below steps to do:
* Copy EMMC image to a running system which is from SD card
* Program EMMC image to User Data Area of EMMC: dd if=mtk-bpi-r2-EMMC.img of=/dev/mmcblk0 (assume /dev/mmcblk0 is for EMMC)
* Unlock EMMC boot0 block: echo 0 > /sys/block/mmcblk0boot0/force_ro
* Program preloader to EMMC boot0 block: dd if=mtk-bpi-r2-EMMC.img of=/dev/mmcblk0boot0 bs=1M count=1
* Change the Partition configurion of EMMC is 48h: reboot the system which is running SD, and enter the U-boot command line, run command emmc pconf 48 (for this steps, we can change partition configuration in userspace by using mmc-utils,see more information in BPI-R2 OpenWrt(LEDE) Souce code : 2018-04-11)
* Power off, remove SD card, and then power on R2 board
7. This step is for upgrade, if you don't want to install image after you built, you could use runtime upgrade. * Copy "bin/targets/mediatek/32/lede-mediatek-32-bananapi,bpi-r2-sysupgrade.tar" to R2 board which is running OpenWrt system(no matter where(SD or EMMC) it boots from), and then run command "sysupgrade lede-mediatek-32-bananapi,bpi-r2-sysupgrade.tar" to update both kernel and rootfs.
Advanced Development
GPIO
GPIO Control
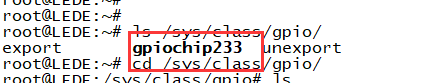
- echo xxx > /sys/class/gpio/export
- echo in/out > /sys/class/gpio/gpioxxx/direction
- echo 0/1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpioxxx/value
Check the base gpio, you could see mine is 233
For example: if you want to change gpio 22 as out highlevel, you need input commands like this:
- echo 255(22+233) > /sys/class/gpio/export
- echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio255/direction
- echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio255/value
PWM Control
- echo 4 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export
- echo 200000 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm4/period
- echo 100000 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm4/duty_cycle
- echo 1 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwm4/enable
Develop 4G module with R2
Gets more info from here:
WiFi and Ap mode on R2
WiFi Client
- wmt_loader (ignore errors)
- stp_uart_launcher -p /etc/firmware &
- ip link set wlan0 up
- iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID
- vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
- network={ ssid=“ssid” psk=“password” priority=1}
- wpa_supplicant -i wlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
- dhclient wlan0
AP mode
- wmt_loader (ignore errors)
- stp_uart_launcher -p /etc/firmware &
- echo A >/dev/wmtWifi
- create your hostapd.conf: "vim /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf "
interface=ap0 bridge=br0 ssid=test_r2 driver=nl80211 country_code=US hw_mode=b channel=1 max_num_sta=5 wpa=2 auth_algs=1 rsn_pairwise=CCMP wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK wpa_passphrase=ledetest logger_stdout=-1 logger_stdout_level=2
- According to your network interface(can search internet) to config ap0:
my network interface which can search internet is wan, and ip is 192.168.30.102, so I config ap0 as follows:
“ifconfig ap0 192.168.30.188 netmask 255.255.255.0”
- Run hostapd : “hostapd -d /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf”
- Config dhcp file : “vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf”
subnet 192.168.30.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.30.2 192.168.30.250;
option domain-name-servers 8.8.8.8;
option routers 192.168.30.1; }
- Config dhcp of ap0, then the devices which connect ap0 could get IP: "dhcpd ap0 -pf /var/run/dhcpd.pid "
- And a bridge
- brctl addbr br0
- brctl addif br0 ap0
- brctl addif br wan
- Config br0 : “ifconfig br0 192.168.30.180 netmask 255.255.255.0”
- Add br0 gw as : “route add -net default netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.30.1 dev br0”