Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with R2"
(→Ubuntu) |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
===Build your own image on R2=== | ===Build your own image on R2=== | ||
====Ubuntu==== | ====Ubuntu==== | ||
| + | 1. Clone Bsp project from Github, | ||
| + | git clone | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Execute "./build.sh", to build your own uboot and kernel. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. After finish built, you will find xxSD.img and xxEMMC.img in SD directory. | ||
====OpenWrt==== | ====OpenWrt==== | ||
Revision as of 00:44, 6 May 2018
Contents
Introduction
The Banana Pi R2 is a router based development board, which can run on a variety of open source operating systems including OpenWrt, Android, and Bananian. It has 4 Gigabit LAN ports, 1 Gigabit WAN, and 300Mbs wireless N capabilities.
Key Features
- MediaTek MT7623N, Quad-core ARM Cortex-A7
- Mali 450 MP4 GPU
- 2G DDR3 SDRAM
- Mini PCIE interface
- SATA interface
- 4x Gigabit LAN 1x Gigabit WAN
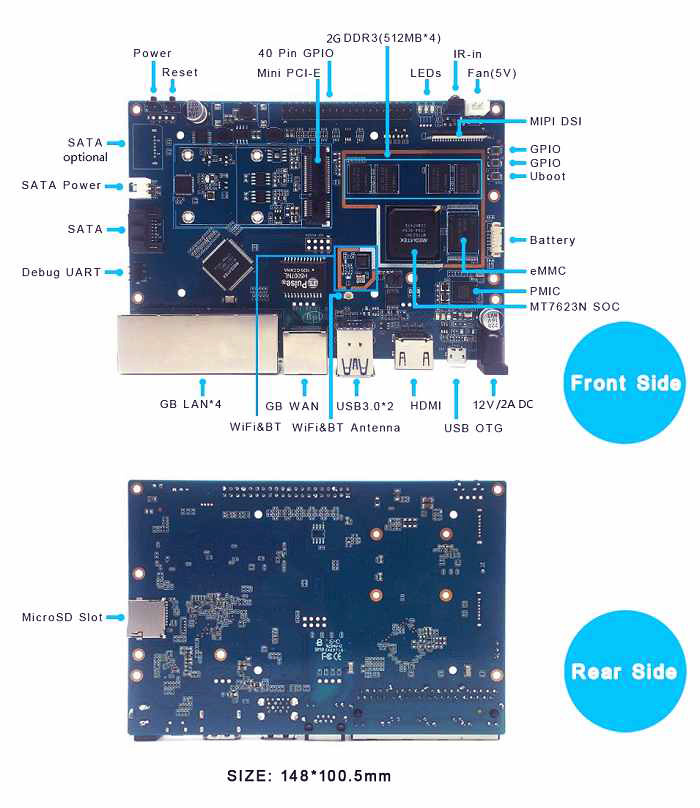
Hardware
Development
Let's get start to develop on BPI-R2, see amazing things happen.
Basic Development
Prepare to develop
1.Prepare 16G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, Ubuntu System
2.Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on R2
Load your first image on R2
1.You could download latest image from our forum * Here is the example image link: http://forum.banana-pi.org/t/bpi-r2-new-image-release-ubuntu-16-04-v1-3-2018-3-30/5293
2.Install bpi-tools on your Ubuntu * apt-get install pv * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash
3.After you download the image, insert your TF card into your Ubuntu * Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card.
4.After step 3, then you can insert your TF card into R2, and press power button for around 10s to setup R2.
Build your own image on R2
Ubuntu
1. Clone Bsp project from Github, git clone
2. Execute "./build.sh", to build your own uboot and kernel.
3. After finish built, you will find xxSD.img and xxEMMC.img in SD directory.