Difference between revisions of "BPI-Bit"
(→bpi:bit VS micro:bit) |
(→bpi:bit VS micro:bit) |
||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
|CPU||Dual-core 32bit Xtensa LX6, up to 240MHz||32bit ARM Cortex M0, up to 16MHz | |CPU||Dual-core 32bit Xtensa LX6, up to 240MHz||32bit ARM Cortex M0, up to 16MHz | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |RAM||520KB|| | + | |RAM||520KB||16KB |
|- | |- | ||
|ROM||448KB||Unkown | |ROM||448KB||Unkown | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |Flash||4MB|| | + | |Flash||4MB||256KB |
|- | |- | ||
|Bluetooth||BT4.2 BR/EDR and BLE|| BLE only | |Bluetooth||BT4.2 BR/EDR and BLE|| BLE only | ||
Revision as of 05:58, 27 May 2018
Contents
Introduction
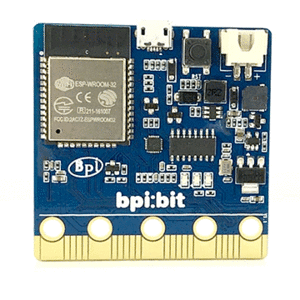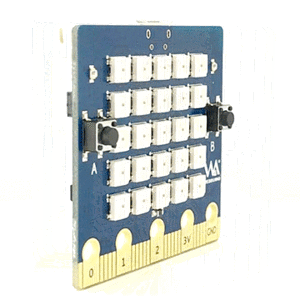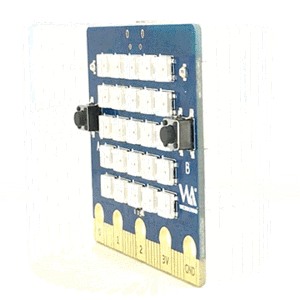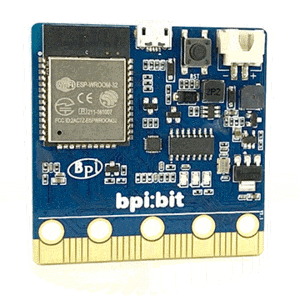
The BPI bit (also referred to as BPI-bit, stylised as bpi:bit) is an ESP32 with 32-bit Xtensa LX6 dual-core processor based embedded system. It supports Webduino, Arduino, MicroPython as well as Scratch X programming environments.
bpi:bit board is 5 cm x 5 cm in size, weighs 10 ~ 12 grams, it houses a 20-Pin edge connector, built-in lighting matrix with 25 programmable full-color LEDs , two photosensitive light sensors, two programmable buttons, an NTC resistor, a buzzer and a nine shaft sensor (triaxial acceleration Three-axis gyroscope and three-axis magnetic compass), the I/O space configuration is as follows:
- Full color LED matrix: GPIO4
- Photosensitive sensor: GPIO36 (Analog A0, upper left), GPIO39 (Analog A3, upper right)
- Button switch : GPIO35 (A), GPIO27 (B)
- Temperature sensor: GPIO34 (Analog A6)
- Buzzer: GPIO25
- MPU-9250 9-axis sensor: GPIO0, GPIO21, GPIO22, GPIO33
Hardware
Description
The board is 5 cm × 5 cm and has an ESP32 module with 32bit Xtensa LX6 dual-core processor, with a capacity of up to 600DMIPS, with a built-in 448KB ROM and 520 KB SRAM.accelerometer and magnetometer sensors,2.4G WiFI,Bluetooth and USB connectivity, a display consisting of 25 LEDs, two programmable buttons, and can be powered by either USB or an external battery pack.The device inputs and outputs are through five ring connectors that are part of the 23-pin edge connector.
BPI:bit provides a wide range of onboard resources, supports photosensitive sensor, digital triaxial sensor, digital compass, temperature sensor interface.Webduino:bit have 25 intelligent control LED light source that the control circuit and RGB chip are integrated in a package of 5050 components.Cascading port transmission signal by single line.Each pixel of the three primary color can achieve 256 brightness display, completed 16777216 color full color display, and scan frequency not less than 400Hz/s.
BPI:bit use MPU9250 onboard, MPU-9250 is a multi-chip module (MCM) consisting of two dies integrated into a single QFN package. One die houses the 3-Axis gyroscope and the 3-Axis accelerometer. The other die houses the AK8963 3-Axis magnetometer from Asahi Kasei Microdevices Corporation. Hence, the MPU-9250 is a 9-axis MotionTracking device that combines a 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, 3-axis magnetometer and a Digital Motion Processor™ (DMP) all in a small 3x3x1mm package available as a pin-compatible upgrade from the MPU-6515. With its dedicated I2C sensor bus, the MPU-9250directly provides complete 9-axis MotionFusion™ output. The MPU-9250 MotionTracking device, with its 9-axis integration, on-chip MotionFusion™, and runtime calibration firmware, enables manufacturers to eliminate the costly and complex selection, qualification, and system level integration of discrete devices, guaranteeing optimal motion performance for consumers. MPU-9250 is also designed to interface with multiple non-inertial digital sensors, such as pressure sensors, on its auxiliary I²C port.
Interface
Edge interface
File:BPI bit edge pin define.png
PIN definition
The edge interface is much compatible with those of micro:bit. so you may able to use micro:bit accessories on bpi:bit
| HardWare PIN define of BPI:bit | |||||
| Pin Name | Analog Function1 | Analog Function2 | Function1 | Function2 | Power |
| P3 | ADC2_CH4 | GPIO13 | |||
| P0 | ADC2_CH8 | DAC_1 | GPIO25 | ||
| P4 | ADC2_CH3 | GPIO16 | |||
| P5 | ADC1_CH7 | GPIO35 | |||
| P6 | ADC2_CH5 | GPIO12 | |||
| P7 | ADC2_CH6 | GPIO14 | |||
| P1 | ADC1_CH4 | GPIO32 | |||
| P8 | GPIO16 | ||||
| P9 | GPIO17 | ||||
| P10 | ADC2_CH9 | DAC_2 | GPIO26 | ||
| P11 | ADC2_CH7 | GPIO27 | |||
| P12 | ADC2_CH2 | GPIO02 | |||
| P2 | ADC1_CH5 | GPIO33 | |||
| P13 | GPIO18 | SPI_SS | |||
| P14 | GPIO19 | SPI_SCK | |||
| P15 | GPIO23 | SPI_MISO | |||
| P16 | GPIO05 | SPI_MOSI | |||
| 3V3 | POWER:3V3 | ||||
| 3V3 | POWER:3V3 | ||||
| 3V3 | POWER:3V3 | ||||
| P19 | GPIO22 | I2C_SCL | |||
| P20 | GPIO21 | I2C_SDA | |||
| GND | GROUND | ||||
| GND | GROUND | ||||
| GND | GROUND | ||||
5*5 LED list
BPI:bit have 25 LEDs on board, it can be controlled with a single GPIO.
| 25 5*5 LED list of BPI:bit | ||||
| 20 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 0 |
| 21 | 16 | 11 | 6 | 1 |
| 22 | 17 | 12 | 7 | 2 |
| 23 | 18 | 13 | 8 | 3 |
| 24 | 19 | 14 | 9 | 4 |
MPU9250 9-axis sensor
The 9-axis sensor, MPU9250, is placed on the BPI:bit board. and MPU9250 uses I2C 0x69 address.
The 9-axis is the combination of 3 separate triple axis sensors. For more detailed information of this chip, click here[1] to view the datasheet.
bpi:bit VS micro:bit
| bpi:bit VS micro:bit | |||||||
| Module | bpi:bit | micro:bit | |||||
| CPU | Dual-core 32bit Xtensa LX6, up to 240MHz | 32bit ARM Cortex M0, up to 16MHz | |||||
| RAM | 520KB | 16KB | |||||
| ROM | 448KB | Unkown | |||||
| Flash | 4MB | 256KB | |||||
| Bluetooth | BT4.2 BR/EDR and BLE | BLE only | |||||
| WIFI | 802.11 b/g/n/e/i | N/A | |||||
| Buzzer | 1x Buzzer | N/A | |||||
| 5*5 LEDS | 25 intelligent-control full-color (16777216 color) LEDs, Cascading all LEDs by a single line. | 25 red LEDs | |||||
| photosensitive sensor | 2 light sensors | Basic light detection function on LEDs | |||||
| temperature sensor | Stand along temperature sensor | On CPU chip temperature sensor | |||||
| other senesor | MPU-9250 9-axis MotionTracking : 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, 3-axis magnetometer | 3-axis Accelerometer; 3-axis magnetometer | |||||
| IO interface | edge interface (compatible with most micro:bit I/O features) | edge interface | |||||
| Button | 2 programmable buttons | 2 programmable buttons | |||||
| micro USB | 1x micro USB(UART) | 1 x micro USB(Mass Storage Device) | |||||
| Software | Webduino, Arduino, MicroPython, Scratch X | Microsoft MakeCode, MicroPython, Scratch X | |||||
| Size | 5*5 cm | 5*4 cm | |||||
BPI-bit software
BPI:bit for webduino
About webduino
Webduino = WebComponents + Arduino
Webduino working principle:
- 1 use WebComponents integration Breakout.
- 2 use WebSocket(Firmata) to interacting with the server.
- 3 Server use TCP/IP(Firmata) to control webduino terminal.
Webduino project VS Arduino and micro:bit project
| Webduino project VS Arduino and micro:bit project | |||
| item compared | Webduino | Arduino | Micro:bit |
| development language | HTML/JavaScript | C/C++ | Python/JavaScript |
| development environment | WEB browser | Arduino IDE | JavaScript Blocks |
| Simulator | Webduino Simulator | Third-party support | Microsoft MakeCode |
| graphical programming | Wbduino blockly | Third-party Scratch | Blockly |
| Cloud Server | webduino cloud | N/A | N/A |
| attended mode | WiFi | USB | USB |
| Update the program | web online update | USB burn | USB disk |
BPI:bit Webduino Blockly and simulator support
- Webduino Blockly and simulator
- Quick start Webduino Blockly and simulator
BPI:bit Webduino Cloud support
Webduino cloud platform provides your complete Internet of things services. You can update and operate various iot devices through platform management.
BPI:bit Webduino Firmware Burning
BPI:bit can be perfectly adapted to Webduino. Of course, before using it, we need to burn the Webduino firmware first.
Note: BPI:bit have burn webduino Firmware defaults. Only when you clear the factory Settings and use arduino open source, will you need to burn webduinofirmware again.
Firmware download address:Webduino for bpi:bit Firmware
Burning method:
There are two kinds of burning methods to choose from, we can use ESP Flash Download Tool to burn, we can also use the built-in Python script inside the PlatformIO to achieve burn.
One, ESP Flash Download Tool Tool download address:ESP Flash Download Tool
After downloading, unzip the archive and you will see an ESPFlashDownloadTool_v3.6.2.exe inside the folder. Open this shortcut and open an interface selection mode.
Select ESP32 DownloadTool:
Under `Download Path Config`, we need to select the four bin files that need to be burned and fill in the corresponding burn locations.
- File and burn position corresponding to:
| File and burn position corresponding | |||
| set | file name | Position | |
| 1 | bootloader_dio_40m.bin | 0x1000 | |
| 2 | partitions.bin | 0x8000 | |
| 3 | boot_app0.bin | 0xe000 | |
| 4 | bit_default.bin | 0x10000 | |
- SpiFlashConfig:
| SpiFlashConfig | |||
| 1 | SPI SPEED | 40MHz | |
| 2 | SPI MODE | DIO | |
| 3 | FLASH SIZE | 32Mbit | |
| 4 | COM | COMx(Fill in the port number assigned by the computer) | |
| 5 | BAUD | 1152000 | |
Normally, you do not need to burn two boot boot files. You can directly burn the firmware (bit_default.bin) and partitions (partitions.bin). If the bootloader is damaged, you can choose to burn along with bootloader_dio_40m.bin and boot_app0.bin. But be sure to pay attention to the settings below
`SpiFlashConfig` Please configure according to the software screenshot, and then select the port in the COM. Porter 115200 does not need to be changed. Select “START” to start recording.
During the burning process:
Finished:
After the burn is completed, you must reset or re-energize, and then you find the LED red light flashing, indicating that the burn is successful.
Burn time is about 20s
then you can use webduino all function on BPI:bit. Please see the webduino teaching documents
Second: PlatformIO comes with a script
This method needs to install PlatformIO in advance. Of course, if you are not using PlatformIO for development, you are advised to use the first method. This method is to disassemble the PlatformIO burning procedure.
First of all, you need to find the installation location of PlatformIO on your computer. For example, my installation location is as follows
Of course, your installation location is not necessarily the same as mine, you need to find it yourself.
Then, we can find a script file .platformio\packages\tool-esptoolpy\esptool.py according to the following path. This file is the script we need to burn. Then, we open the terminal of PlatformIO, or open the computer. Command line tool, enter the following code
Python ~\.platformio\packages\tool-esptoolpy\esptool.py --port COM19 --baud 115200 write_flash -fm dio -fs 4MB 0x010000 ~\BIT\bit_default.bin
The ~ in the above code needs to be replaced with your actual path, and then fill in the corresponding burning position in order, select the corresponding file path, and then execute this code. This method may be very specific for certain situations. Help, usually used at the time, it is recommended to use the first method of burning.
Normally, you do not need to burn two boot boot files. You can directly burn the firmware (bit_default.bin) and partitions (partitions.bin). If the bootloader is damaged, you can choose to burn along with bootloader_dio_40m.bin and boot_app0.bin. But be sure to pay attention to the settings below
BPI: bit Online tutorials
BPI:bit for arduino
Arduino IDE
microPyhton
Scratch
How to test 9 axis sensor-MPU9250
- code update to github : https://github.com/yelvlab/BPI-BIT/tree/master/Code/MPU9250
The following is the result of the return of the serial port
Resources
Source code
- BPI:bit for webduino source code on github: https://github.com/webduinoio
- BPI:bit for arduino Source code on Github: https://github.com/yelvlab/BPI-BIT
documents
- BPI:bit schematic diagram : https://github.com/yelvlab/BPI-BIT/blob/master/doc/BPI-WEBDUINO-BIT-V1_2-20180417.pdf
- BPI:bit user manual : https://github.com/yelvlab/BPI-BIT/blob/master/doc/BPI-bit_user_manual.pdf
- BPI:bit dxf file : http://forum.banana-pi.org/uploads/default/original/2X/0/0b86ccaeb565cdeef093164fd1ff837727ca2887.rar
- ESP32 datasheet: https://github.com/yelvlab/BPI-BIT/blob/master/doc/ESP32-datesheet_english.pdf
- MPU9250 datasheet:http://www.invensense.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/PS-MPU-9250A-01-v1.1.pdf
- More others : https://github.com/yelvlab/BPI-BIT/tree/master/doc
- Taiwan server : http://webuino.io
- Overworld server: http://webduino.io
- china mainland : http://www.webduino.com.cn
- Easy to buy BPI:bit sample form aliexpress
- Facebook group