Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with R64"
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→BPI-R2 SATA interface) |
(→Prepare to develop) |
||
| (90 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[zh:快速上手 香蕉派 BPI-R64]] | [[zh:快速上手 香蕉派 BPI-R64]] | ||
| − | = | + | =Introduction= |
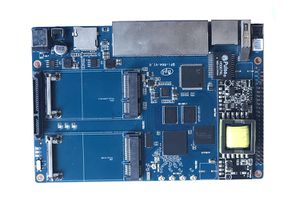
| − | + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-R64_1.jpg|thumb|Overview:[[Banana Pi BPI-R64]]]] | |
| + | [[File:BPI-R64_case_1.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-R64]] Metal Jacket]] | ||
| + | [[File:BPI-R64_PoE.JPG|thumb|BPI-R64 with BPI-7402 POE function support]] | ||
| + | [[File:BPI-7402_IEEE_802.3at_PoE_module_1.jpg|thumb|[[BPI-7402 IEEE 802.3at PoE module]]]] | ||
| + | [[File:5G_gateway_2.jpg|thumb|BPI:4.0 [[Successful case]] 5G Converged communication gateway]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_pi_BPI-R1_1.JPG|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-R1]] Allwinner A20]] | ||
| + | [[File:BPI-R2_3.JPG|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-R2]] with MTK MT7623N chip design]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-R2_Pro_1_750.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-R2 Pro]] Rockchip RK3568 design]] | ||
| + | [[File:O2A0500.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-W2]] with Realtek RTD1296 chip design]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-R3_Router_2.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-R3]] with MediaTek MT7986(Filogic 830)]] | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_Pi_BPI-M2S_1.jpg|thumb|[[Banana Pi BPI-M2S]] Amlogic A311D chip]] | ||
The Banana Pi R64 is a router based development board, which can run on a variety of open source operating systems including OpenWrt,Linux. It has 4 Gigabit LAN ports, 1 Gigabit WAN, and AC wifi AP function. use 64 bit chip design. | The Banana Pi R64 is a router based development board, which can run on a variety of open source operating systems including OpenWrt,Linux. It has 4 Gigabit LAN ports, 1 Gigabit WAN, and AC wifi AP function. use 64 bit chip design. | ||
| − | |||
Read more: [[Banana Pi BPI-R64]] | Read more: [[Banana Pi BPI-R64]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 30: | ||
* POE function support | * POE function support | ||
| − | = | + | =Development= |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Basic Development== | ==Basic Development== | ||
===Prepare to develop=== | ===Prepare to develop=== | ||
| − | * Prepare | + | * Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, Ubuntu System |
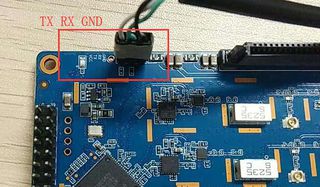
| − | * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on | + | * Using your USB-Serial('''3.3V,Baud: 115200''') Connect debug console on R64 |
| − | + | * Default IP address for LAN port: '''192.168.1.1''' | |
| − | + | * User name/password: '''pi/bananapi''' ,'''root/bananapi'''. | |
| + | Or the user is '''root without a password'''. | ||
| + | * WIFI: '''Operwrt''' | ||
| − | + | [[Image:R64_debug_console.jpg|320px]] | |
| − | === | + | ===How to burn image to SD card=== |
1.You could download latest image from our forum | 1.You could download latest image from our forum | ||
| − | * Here is the example image link: | + | * Here is the example image link: |
| − | 2.Install bpi-tools on your Ubuntu | + | 2.Install bpi-tools on your Ubuntu. If you can't access this URL or any other problems, please go to [https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools bpi-tools repo] and install this tools manually. |
* apt-get install pv | * apt-get install pv | ||
* curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash | * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash | ||
| Line 44: | Line 53: | ||
* Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card | * Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card | ||
| − | 4.After step 3, then you can insert your TF card into | + | 4.After step 3, then you can insert your TF card into R64, and press power button to setup R64 |
| − | ==== | + | ====How to burn image to onboard eMMC==== |
| − | + | Before burning image to eMMC, please prepare a SD card with flashed bootable image and a USB disk. Let's take OpenWrt image (mtk-bpi-r64-preloader-emmc.bin,2020-04-09-OpenWRT-mtk-bpi-r64-EMMC.img) for example, the steps are below: | |
| − | + | Note: You can download the .bin file from github: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-R64-openwrt/tree/master/staging_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a53_musl/image | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 1. Insert the flashed SD card and power on to start the board.(the image on the SD card can be OpenWrt or other linux OS like ubuntu...) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | 2. Copy eMMC bootable OpenWrt image(mtk-bpi-r64-preloader-emmc.bin,2020-04-09-OpenWRT-mtk-bpi-r64-EMMC.img) to USB disk, if the image is compressed please uncompress it before copying to USB disk. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | 3. Plug in USB disk to the board, and mount the USB to /mnt or other directory as follows: (you can skip mounting if it is mounted automatically) | |
| − | + | * mount -t vfat /dev/sda1 /mnt | |
| − | + | * change your directory to the mounting point, here is : cd /mnt | |
| − | + | 4. Execute following command to enable and copy image to eMMC: | |
| − | + | * echo 0 > /sys/block/mmcblk0boot0/force_ro | |
| − | + | * dd if=2020-04-09-OpenWRT-mtk-bpi-r64-EMMC.img of=/dev/mmcblk0 | |
| − | + | * dd if=mtk-bpi-r64-preloader-emmc.bin of=/dev/mmcblk0boot0 | |
| − | + | * mmc bootpart enable 1 1 /dev/mmcblk0 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | 5. Shutdown, remove SD card and USB disk, and restart the board from eMMC. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Network-Configuration=== | === Network-Configuration=== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 80: | ||
==Advanced Development== | ==Advanced Development== | ||
===GPIO=== | ===GPIO=== | ||
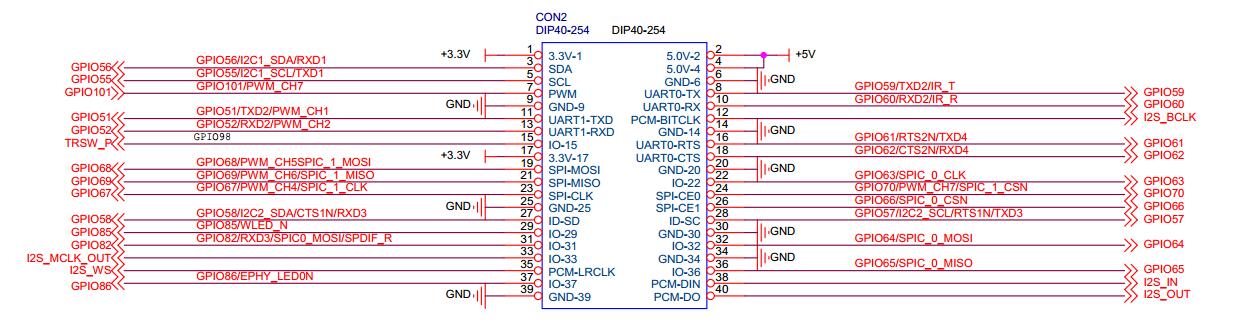
| + | ====40 Pins Definition==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:R64_gpio_40.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
====GPIO Control==== | ====GPIO Control==== | ||
* echo xxx > /sys/class/gpio/export | * echo xxx > /sys/class/gpio/export | ||
| Line 113: | Line 89: | ||
* echo 0/1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpioxxx/value | * echo 0/1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpioxxx/value | ||
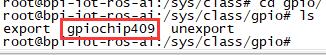
| − | Check the base gpio, you could see mine is | + | Check the base gpio, you could see mine is 409 |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:R64_gpio_base.jpg]] |
For example: if you want to change gpio 22 as out highlevel, you need input commands like this: | For example: if you want to change gpio 22 as out highlevel, you need input commands like this: | ||
| − | * echo | + | * echo 431(22+409) > /sys/class/gpio/export |
| − | * echo out > /sys/class/gpio/ | + | * echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio431/direction |
| − | * echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/ | + | * echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio431/value |
====PWM Control==== | ====PWM Control==== | ||
| Line 129: | Line 105: | ||
* echo 1 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwmx/enable | * echo 1 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwmx/enable | ||
| − | + | ====SPI touch panel==== | |
| + | SPI Panel module: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.4" Touch Screen TFT LCD with SPI Interface, 240x320 (ILI9341 + ADS7843/XPT2046/HR2046) | ||
| + | |||
| + | SPI Panel <–> BPIR64 | ||
| + | |||
| + | T_DO, T_DIN, T_CLK <–> SPIC_0: MOSI / MISO / CLK | ||
| + | T_CS <–> SPI-CE0 | ||
| + | T_IRQ <–> IO-37 | ||
| + | SDO, SCK, SDI <–> SPIC_1: MOSI / MISO / CLK | ||
| + | LED <–> PIN-31 | ||
| + | DC <–> PIN-11 | ||
| + | RESET <–> PIN-13 | ||
| + | CS <–> SPI-CE1 | ||
| + | GND <–> GND-9 | ||
| + | VCC <–> 3.3V-1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | DTS Modification: | ||
| + | |||
| + | / { | ||
| + | backlight: backlight { | ||
| + | compatible = "gpio-backlight"; | ||
| + | gpios = <&pio 82 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; //PIN31 IO-31 : GPIO82 | ||
| + | default-on; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| − | === | + | &pio { |
| − | + | spic0_pins: spic0-pins { | |
| + | mux { | ||
| + | function = "spi"; | ||
| + | groups = "spic0_0"; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | |||
| + | spic1_pins: spic1-pins { | ||
| + | mux { | ||
| + | function = "spi"; | ||
| + | groups = "spic1_0"; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | &spi0 { | |
| + | pinctrl-names = "default"; | ||
| + | pinctrl-0 = <&spic0_pins>; | ||
| + | status = "okay"; | ||
| + | touch@0 { | ||
| + | reg = <0>; //CE0 | ||
| + | compatible = "ti,ads7843"; | ||
| + | interrupt-parent = <&pio>; | ||
| + | interrupts = <86 0>; //PIN37: IO-37 == GPIO86 | ||
| + | pendown-gpio = <&pio 86 0>; | ||
| + | spi-max-frequency = <1000000>; | ||
| + | vcc-supply = <®_3p3v>; | ||
| + | wakeup-source; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| − | + | &spi1 { | |
| − | = | + | pinctrl-names = "default"; |
| − | + | pinctrl-0 = <&spic1_pins>; | |
| − | + | status = "okay"; | |
| − | + | display@0{ | |
| − | + | compatible = "ilitek,ili9341"; | |
| − | + | reg = <0>; //CE0 | |
| − | + | spi-max-frequency = <32000000>; | |
| − | + | dc-gpios = <&pio 51 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; //PIN11 UART1-TXD : GPIO51 | |
| − | + | reset-gpios = <&pio 52 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; //PIN13 UART1-RXD : GPIO52 | |
| − | + | backlight = <&backlight>; | |
| − | + | }; | |
| − | + | }; | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Kernel config: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | +CONFIG_FB_TFT_ILI9341 | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_FB_TFT | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_FB | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_LCD_SUPPORT | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_CLASS_DEVICE | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_GPIO | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_INPUT | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_INPUT_TOUCHSCREEN | |
| − | + | +CONFIG_TOUCHSCREEN_ADS7846 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Application: | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Package ||+ Description || Source | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | fbv || framebuffer image viewer || https://github.com/godspeed1989/fbv | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | input-event-daemon || input-event-daemon with touchTEST event || https://github.com/SAM33/input-event-daemon | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | input-event-daemon config that show image by touch area: | |
| − | + | (I don't know why are the coordinates so strange, but the result of my actual touch and | |
| + | print out that it is like this) | ||
| − | + | [Global] | |
| − | + | listen = /dev/input/event0 | |
| − | + | listen = /dev/input/event1 | |
| − | + | [TouchTEST] | |
| + | 340,400,3440,1860 = cat /dev/zero > /dev/fb0; fbv -f /root/bpi_608x429.jpg -s 1 | ||
| + | 340,2260,3440,1860 = cat /dev/zero > /dev/fb0; fbv -f /root/openwrt_449x449.png -s 1 | ||
| − | + | Banana Pi BPI-R64 SPI touch panel test: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ikag-D_TI0g&feature=youtu.be | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Sata=== |
| − | + | * '''If you want to use Sata interface on R64, you need to give GPIO90 low level''' | |
| − | + | ** echo 499 > /sys/class/gpio/export | |
| − | * | + | ** echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/direction |
| − | + | ** echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/value | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Test a TOSHIBA HDD DISK, the Read/Write performance are below: | |
| − | * | ||
| − | + | ::Read from disk: 50MB/s command: dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ::Write to disk: 38MB/s command: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1M count=1024 | |
| − | + | [[Image:R64_hdd_sata_test.jpg]] | |
| − | |||
| − | === | + | *Test a SAMSUNG SSD DISK, the Read/Write performance are below: |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | ::Read from disk: 360MB/s command: dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024 |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | ::Write to disk: 200MB/s command: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1M count=1024 |
| − | * | + | [[Image:R64_ssd_sata_test.jpg]] |
| + | |||
| + | ===PCIe=== | ||
| + | * '''If you want to use PCIe interface on R64, you need to give GPIO90 high level''' | ||
| + | ** echo 499 > /sys/class/gpio/export | ||
| + | ** echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/direction | ||
| + | ** echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/value | ||
| + | |||
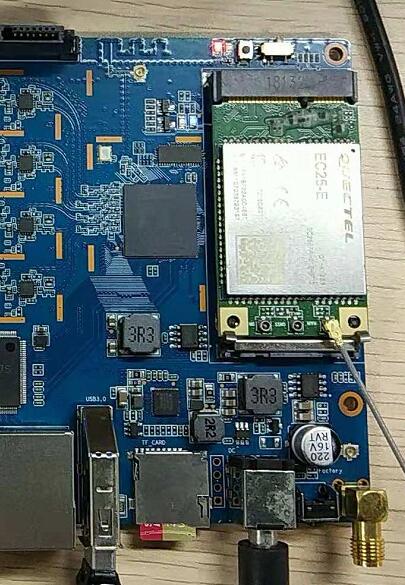
| + | * PCIe supports EC-25 4G module. | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_pcie_test_1.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:R64_pcie_test_2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===GMAC=== | ||
| + | Use iperf3 to test gmac | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. On PC Terminal: | ||
| + | * Execute "iperf3 -s" | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. On R64 console: | ||
| + | * TCP test: "iperf3 -c serverIP" | ||
| + | * UDP test: "iperf3 -u -c serverIP" | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_Gmac_test.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
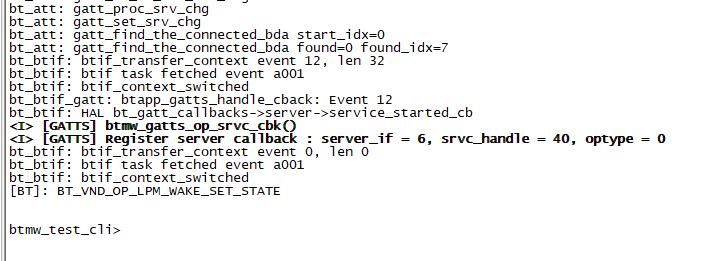
| + | ===BT & BLE on R64=== | ||
| + | '''R64 BT Architectural''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:R64_BT_Arch.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * BLE on R64 | ||
| + | * Input Command "btmw-test", you will enter to "btmw_test_cli" command line | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:R64_BT_cli.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Here are some example commands: | ||
| + | ** MW_GAP name 7622_BT /*rename bt device*/ | ||
| + | ** MW_GAP info /*check local BT device info*/ | ||
| + | ** MW_GATTC scan /* start ble scan*/ | ||
| + | ** MW_GATTC stop_scan /* stop ble scan*/ | ||
| + | |||
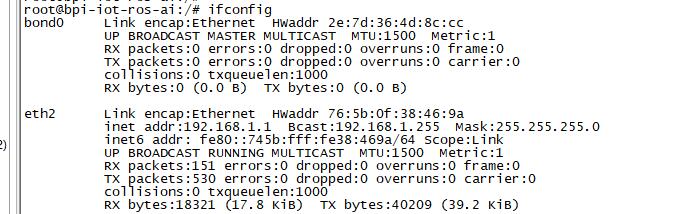
| + | ===R64 LAN Function=== | ||
| + | * LAN eth interface is eth2, use "ifconfig eth2 up" to enable it. | ||
| + | * Config the ip, "ifconfig eth2 192.168.1.1". | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_Lan_test_1.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
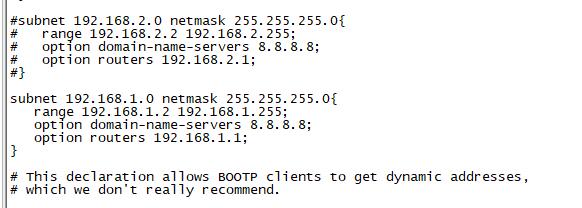
| + | * Config your dhcp server, "vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf", add these configurations. | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_Lan_test_2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
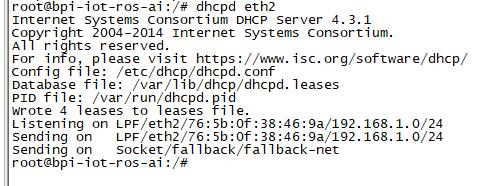
| + | * Start dhcp server, "dhcpd eth2". | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_Lan_test_3.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * then config iptables and set package forward. | ||
| + | ** Add "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" to "/etc/sysctl.conf" | ||
| + | ** "/sbin/sysctl -p" to make forward work | ||
| + | ** "iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.1/24 -o eth3 -j MASQUERADE" | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ap mode on R64=== | ||
| + | * Find "mt_wifi.ko" and insmod it. | ||
| + | ** insmod ./lib/modules/4.4.92-BPI-R64-Kernel/extra/mt_wifi.ko | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Then you will see ra0 and rai0. | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_wifi_test_1.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * ra0 is MT7622 2.4G wifi | ||
| + | * rai0 is MT7615 5G wifi | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====2.4G WiFi==== | ||
| + | * Use "ifconfig ra0 up" to enable it. | ||
| + | * Config the ip, "ifconfig ra0 192.168.1.1". | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Config your dhcp server, "vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf", add these configurations. | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_Lan_test_2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Start dhcp server, "dhcpd ra0". | ||
| + | |||
| + | * then config iptables and set package forward. | ||
| + | ** Add "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" to "/etc/sysctl.conf" | ||
| + | ** "/sbin/sysctl -p" to make forward work | ||
| + | ** "iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.1/24 -o eth3 -j MASQUERADE" | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====5G WiFi==== | ||
| + | * Use "ifconfig rai0 up" to enable it. | ||
| + | * Config the ip, "ifconfig rai0 192.168.1.1". | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Config your dhcp server, "vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf", add these configurations. | ||
| + | [[Image:R64_Lan_test_2.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Start dhcp server, "dhcpd rai0". | ||
| + | |||
| + | * then config iptables and set package forward. | ||
| + | ** Add "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" to "/etc/sysctl.conf" | ||
| + | ** "/sbin/sysctl -p" to make forward work | ||
| + | ** "iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.1/24 -o eth3 -j MASQUERADE" | ||
==FAQ== | ==FAQ== | ||
| − | * | + | *MT7622 Reference Manual for Develope Board(BPi) |
| − | :: | + | ::Google Drive:https://drive.google.com/open?id=1UhaIM9ork1O9cNO-t6ENMVVamB75AThV |
| + | ::BaiDu Drive:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1KduFT2MUvMs2FhOF4A8kQQ | ||
='''Reference Link'''= | ='''Reference Link'''= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
http://forum.banana-pi.org/ | http://forum.banana-pi.org/ | ||
Latest revision as of 23:21, 3 January 2024
Contents
Introduction

Overview:Banana Pi BPI-R64

Banana Pi BPI-R64 Metal Jacket

BPI:4.0 Successful case 5G Converged communication gateway

Banana Pi BPI-R1 Allwinner A20

Banana Pi BPI-R2 with MTK MT7623N chip design

Banana Pi BPI-R2 Pro Rockchip RK3568 design

Banana Pi BPI-W2 with Realtek RTD1296 chip design

Banana Pi BPI-R3 with MediaTek MT7986(Filogic 830)

Banana Pi BPI-M2S Amlogic A311D chip
The Banana Pi R64 is a router based development board, which can run on a variety of open source operating systems including OpenWrt,Linux. It has 4 Gigabit LAN ports, 1 Gigabit WAN, and AC wifi AP function. use 64 bit chip design.
Read more: Banana Pi BPI-R64
Key Features
- MediaTek MT7622,1.35GHZ 64 bit dual-core ARM Cortex-A53
- 1G DDR3 SDRAM
- Mini PCIE interface support 4G module
- Built-in 4x4n 802.11n/Bluetooth 5.0 system-on-chip
- MTK7615 4x4ac wifi on board
- Support 1 SATA interface
- MicroSD slot supports up to 256GB expansion
- 8G eMMC flash (option 16/32/64G)
- 5 port 10/100/1000 Mb Ethernet port
- 1 Port USB 3.0
- Slow I/O:ADC, Audio Amplifier, GPIO, I2C, I2S, IR, PMIC I/F, PWM, RTC, SPI, UART
- POE function support
Development
Basic Development
Prepare to develop
* Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, Ubuntu System * Using your USB-Serial(3.3V,Baud: 115200) Connect debug console on R64 * Default IP address for LAN port: 192.168.1.1 * User name/password: pi/bananapi ,root/bananapi. Or the user is root without a password. * WIFI: Operwrt
How to burn image to SD card
1.You could download latest image from our forum * Here is the example image link: 2.Install bpi-tools on your Ubuntu. If you can't access this URL or any other problems, please go to bpi-tools repo and install this tools manually. * apt-get install pv * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash 3.After you download the image, insert your TF card into your Ubuntu * Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card 4.After step 3, then you can insert your TF card into R64, and press power button to setup R64
How to burn image to onboard eMMC
Before burning image to eMMC, please prepare a SD card with flashed bootable image and a USB disk. Let's take OpenWrt image (mtk-bpi-r64-preloader-emmc.bin,2020-04-09-OpenWRT-mtk-bpi-r64-EMMC.img) for example, the steps are below: Note: You can download the .bin file from github: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-R64-openwrt/tree/master/staging_dir/target-aarch64_cortex-a53_musl/image
1. Insert the flashed SD card and power on to start the board.(the image on the SD card can be OpenWrt or other linux OS like ubuntu...)
2. Copy eMMC bootable OpenWrt image(mtk-bpi-r64-preloader-emmc.bin,2020-04-09-OpenWRT-mtk-bpi-r64-EMMC.img) to USB disk, if the image is compressed please uncompress it before copying to USB disk.
3. Plug in USB disk to the board, and mount the USB to /mnt or other directory as follows: (you can skip mounting if it is mounted automatically)
* mount -t vfat /dev/sda1 /mnt
* change your directory to the mounting point, here is : cd /mnt
4. Execute following command to enable and copy image to eMMC:
* echo 0 > /sys/block/mmcblk0boot0/force_ro
* dd if=2020-04-09-OpenWRT-mtk-bpi-r64-EMMC.img of=/dev/mmcblk0
* dd if=mtk-bpi-r64-preloader-emmc.bin of=/dev/mmcblk0boot0
* mmc bootpart enable 1 1 /dev/mmcblk0
5. Shutdown, remove SD card and USB disk, and restart the board from eMMC.
Network-Configuration
- Network-Configuration : http://www.fw-web.de/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=en:bpi-r2:network:start
Advanced Development
GPIO
40 Pins Definition
GPIO Control
- echo xxx > /sys/class/gpio/export
- echo in/out > /sys/class/gpio/gpioxxx/direction
- echo 0/1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpioxxx/value
Check the base gpio, you could see mine is 409
For example: if you want to change gpio 22 as out highlevel, you need input commands like this:
- echo 431(22+409) > /sys/class/gpio/export
- echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio431/direction
- echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio431/value
PWM Control
- echo x >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/export
- echo 200000 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwmx/period
- echo 100000 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwmx/duty_cycle
- echo 1 >/sys/class/pwm/pwmchip0/pwmx/enable
SPI touch panel
SPI Panel module:
2.4" Touch Screen TFT LCD with SPI Interface, 240x320 (ILI9341 + ADS7843/XPT2046/HR2046)
SPI Panel <–> BPIR64
T_DO, T_DIN, T_CLK <–> SPIC_0: MOSI / MISO / CLK T_CS <–> SPI-CE0 T_IRQ <–> IO-37 SDO, SCK, SDI <–> SPIC_1: MOSI / MISO / CLK LED <–> PIN-31 DC <–> PIN-11 RESET <–> PIN-13 CS <–> SPI-CE1 GND <–> GND-9 VCC <–> 3.3V-1
DTS Modification:
/ {
backlight: backlight {
compatible = "gpio-backlight";
gpios = <&pio 82 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; //PIN31 IO-31 : GPIO82
default-on;
};
};
&pio {
spic0_pins: spic0-pins {
mux {
function = "spi";
groups = "spic0_0";
};
};
spic1_pins: spic1-pins {
mux {
function = "spi";
groups = "spic1_0";
};
};
}
&spi0 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&spic0_pins>;
status = "okay";
touch@0 {
reg = <0>; //CE0
compatible = "ti,ads7843";
interrupt-parent = <&pio>;
interrupts = <86 0>; //PIN37: IO-37 == GPIO86
pendown-gpio = <&pio 86 0>;
spi-max-frequency = <1000000>;
vcc-supply = <®_3p3v>;
wakeup-source;
};
};
&spi1 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&spic1_pins>;
status = "okay";
display@0{
compatible = "ilitek,ili9341";
reg = <0>; //CE0
spi-max-frequency = <32000000>;
dc-gpios = <&pio 51 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; //PIN11 UART1-TXD : GPIO51
reset-gpios = <&pio 52 GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH>; //PIN13 UART1-RXD : GPIO52
backlight = <&backlight>;
};
};
Kernel config:
+CONFIG_FB_TFT_ILI9341 +CONFIG_FB_TFT +CONFIG_FB +CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_LCD_SUPPORT +CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_CLASS_DEVICE +CONFIG_BACKLIGHT_GPIO +CONFIG_INPUT +CONFIG_INPUT_TOUCHSCREEN +CONFIG_TOUCHSCREEN_ADS7846
Application:
| Package | + Description | Source |
| fbv | framebuffer image viewer | https://github.com/godspeed1989/fbv |
| input-event-daemon | input-event-daemon with touchTEST event | https://github.com/SAM33/input-event-daemon |
input-event-daemon config that show image by touch area: (I don't know why are the coordinates so strange, but the result of my actual touch and print out that it is like this)
[Global] listen = /dev/input/event0 listen = /dev/input/event1 [TouchTEST] 340,400,3440,1860 = cat /dev/zero > /dev/fb0; fbv -f /root/bpi_608x429.jpg -s 1 340,2260,3440,1860 = cat /dev/zero > /dev/fb0; fbv -f /root/openwrt_449x449.png -s 1
Banana Pi BPI-R64 SPI touch panel test: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ikag-D_TI0g&feature=youtu.be
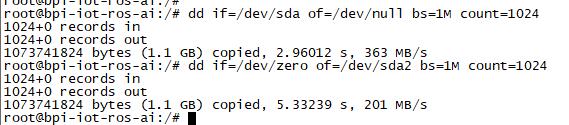
Sata
- If you want to use Sata interface on R64, you need to give GPIO90 low level
- echo 499 > /sys/class/gpio/export
- echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/direction
- echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/value
- Test a TOSHIBA HDD DISK, the Read/Write performance are below:
- Read from disk: 50MB/s command: dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024
- Write to disk: 38MB/s command: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1M count=1024
- Test a SAMSUNG SSD DISK, the Read/Write performance are below:
- Read from disk: 360MB/s command: dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1024
- Write to disk: 200MB/s command: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1M count=1024
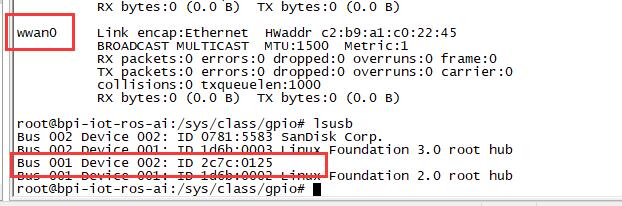
PCIe
- If you want to use PCIe interface on R64, you need to give GPIO90 high level
- echo 499 > /sys/class/gpio/export
- echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/direction
- echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio499/value
- PCIe supports EC-25 4G module.
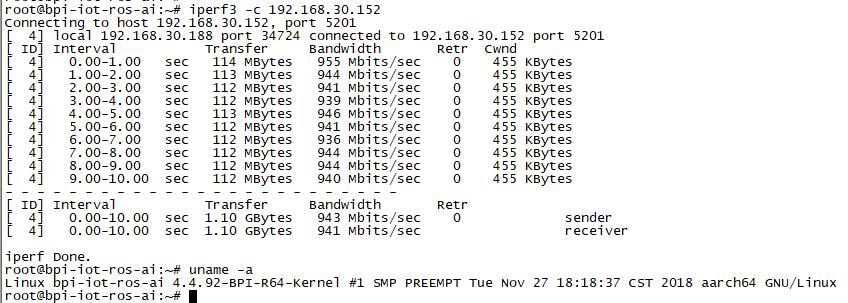
GMAC
Use iperf3 to test gmac
1. On PC Terminal:
- Execute "iperf3 -s"
2. On R64 console:
- TCP test: "iperf3 -c serverIP"
- UDP test: "iperf3 -u -c serverIP"
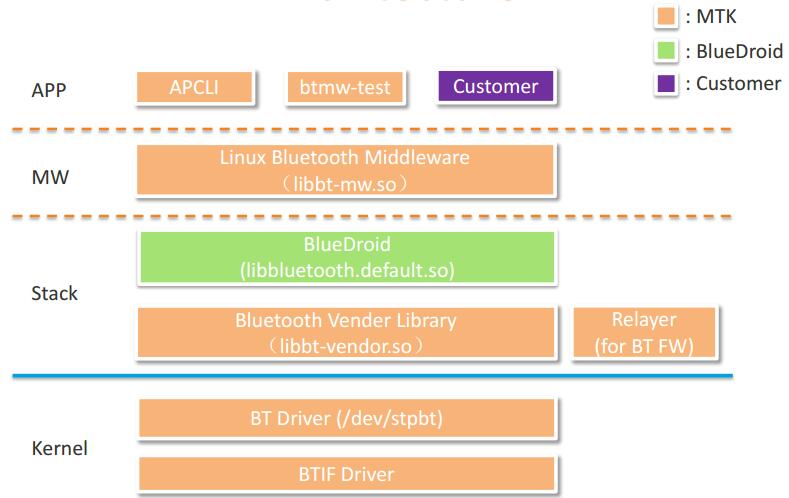
BT & BLE on R64
R64 BT Architectural
- BLE on R64
- Input Command "btmw-test", you will enter to "btmw_test_cli" command line
- Here are some example commands:
- MW_GAP name 7622_BT /*rename bt device*/
- MW_GAP info /*check local BT device info*/
- MW_GATTC scan /* start ble scan*/
- MW_GATTC stop_scan /* stop ble scan*/
R64 LAN Function
- LAN eth interface is eth2, use "ifconfig eth2 up" to enable it.
- Config the ip, "ifconfig eth2 192.168.1.1".
- Config your dhcp server, "vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf", add these configurations.
- Start dhcp server, "dhcpd eth2".
- then config iptables and set package forward.
- Add "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" to "/etc/sysctl.conf"
- "/sbin/sysctl -p" to make forward work
- "iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.1/24 -o eth3 -j MASQUERADE"
Ap mode on R64
- Find "mt_wifi.ko" and insmod it.
- insmod ./lib/modules/4.4.92-BPI-R64-Kernel/extra/mt_wifi.ko
- Then you will see ra0 and rai0.
- ra0 is MT7622 2.4G wifi
- rai0 is MT7615 5G wifi
2.4G WiFi
- Use "ifconfig ra0 up" to enable it.
- Config the ip, "ifconfig ra0 192.168.1.1".
- Config your dhcp server, "vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf", add these configurations.
- Start dhcp server, "dhcpd ra0".
- then config iptables and set package forward.
- Add "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" to "/etc/sysctl.conf"
- "/sbin/sysctl -p" to make forward work
- "iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.1/24 -o eth3 -j MASQUERADE"
5G WiFi
- Use "ifconfig rai0 up" to enable it.
- Config the ip, "ifconfig rai0 192.168.1.1".
- Config your dhcp server, "vim /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf", add these configurations.
- Start dhcp server, "dhcpd rai0".
- then config iptables and set package forward.
- Add "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" to "/etc/sysctl.conf"
- "/sbin/sysctl -p" to make forward work
- "iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.1.1/24 -o eth3 -j MASQUERADE"
FAQ
- MT7622 Reference Manual for Develope Board(BPi)