Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with M1P"
(→A20 CAN Bus) |
(→Load your first image on M1+) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[zh:快速上手 香蕉派 BPI-M1+]] | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
==BPI-M1P== | ==BPI-M1P== | ||
| + | [[File:Banana_pi_BPI-M1+_1.jpg|thumb|Overview [[Banana Pi BPI-M1+ ]]]] | ||
[[File:M1P_ubuntu.png|thumb|Overview: BPI-M1P ubuntu linux]] | [[File:M1P_ubuntu.png|thumb|Overview: BPI-M1P ubuntu linux]] | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
=Development= | =Development= | ||
Let's get start to develop on BPI-M1P, see amazing things happen. | Let's get start to develop on BPI-M1P, see amazing things happen. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Linux== |
===Prepare to develop=== | ===Prepare to develop=== | ||
| − | * Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with | + | * Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with windows System |
* Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on M1P | * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on M1P | ||
| + | ===Load the linux image on M1+=== | ||
| + | 1.Download the latest image from the forum. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.Put the TF card into a card reader and plug it to your PC USB interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3.Download the flashing tools "BalenaEtcher" and start it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4.Click "Flash from file" to select your image file.(.img or .zip) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5.Click "Select target" to choose your USB device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6.Start to flash and wait for a moment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Etcher.jpg | 600px]] | ||
| − | ===Load your first image on | + | ==Android== |
| − | 1.You could download latest image from our forum | + | ===Load your first image on M1+=== |
| + | 1.You could download latest image from our forum. | ||
| + | Ex: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.Put your TF card into a TF-USB adapter, and then plug adapter in your Windows PC usb interface. | ||
| − | + | 3.Prepare your image, and download image burning tools PhoenixCard.exe. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | 4.Use "PhoenixCard.exe" to burn android image to TF card. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:M3_Android_Burning.png | 600px]] | |
| + | |||
| + | * Download PhoenixCard: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-fjvPqtG_zewVzqnXf1AHw?pwd=eid9 | ||
==Advanced Development== | ==Advanced Development== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 69: | ||
* "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed | * "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed | ||
[[Image:Sata_test.png]] | [[Image:Sata_test.png]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Touch screen=== | ===Touch screen=== | ||
| Line 89: | Line 91: | ||
* iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | * iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | ||
* vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | * vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | ||
| − | + | network={ | |
| − | * wpa_supplicant - | + | ssid="ssid" |
| + | psk="password" | ||
| + | priority=1 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | * wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | ||
* dhclient wlan0 | * dhclient wlan0 | ||
| Line 99: | Line 105: | ||
* bpi-bootsel BPI-cleanboot-8k.img.gz /dev/sdX | * bpi-bootsel BPI-cleanboot-8k.img.gz /dev/sdX | ||
| − | === | + | ===IR function=== |
| − | + | * Execute "getevent" | |
| + | * Use your IR device to send information to M1P | ||
| + | [[Image:M1P_IR.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===RPi.GPIO=== | ||
| + | ====Install RPi.GPIO==== | ||
| + | * Execute "git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/RPi.GPIO" | ||
| + | * after clone the repo, cd RPi,GPIO | ||
| + | * Execute "sudo apt-get update" | ||
| + | * Execute "sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev" | ||
| + | * Execute "sudo python setup.py install" or "sudo python3 setup.py install" to install the module | ||
| − | + | ====Using RPi.GPIO==== | |
| − | + | * cd /usr/local/bin | |
| − | ==== | + | * Execute "./bpi_test_g40.py" to test RPi.GPIO |
| − | * | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | + | [[Image: RPi_GPIO.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===WringPi=== |
| − | * Execute " | + | * GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git |
| − | * | + | * We also have built-in test command in "/usr/local/bin" |
| − | [[Image: | + | |
| + | ====RGB 1602 LCD==== | ||
| + | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602.sh" | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====8x8 RGB LED Martix==== | ||
| + | * Firstly you need a GPIO Extend Board for 8x8 LED Martix | ||
| + | [[Image: WringPi_LED_Martix_Extend_Board.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40.sh" | ||
===File System=== | ===File System=== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:13, 19 March 2023
Introduction
BPI-M1P

The Banana Pi M1+ features onboard WiFi g/b/n. The board supports all classic projects and even more because of the onboard WIFi chip. Like its sibling, it can run operating systems including Android, Lubuntu, Ubuntu, Debian, and Raspbian. The Banana Pi M1+ is our upgraded M1 board. We feel like the onboard WiFi adds a lot more features to the board and makes it more convient for users to set up their linx desktop or router projects.
- Read more about : Banana Pi BPI-M1+
Key Features
- Dual-core 1.0GHz CPU
- 1 GB DDR3 memeory
- Mali-400 MP2 with Open GL ES 2.0/1.1
- WiFi onbaord
Development
Let's get start to develop on BPI-M1P, see amazing things happen.
Linux
Prepare to develop
* Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with windows System * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on M1P
Load the linux image on M1+
1.Download the latest image from the forum. 2.Put the TF card into a card reader and plug it to your PC USB interface. 3.Download the flashing tools "BalenaEtcher" and start it. 4.Click "Flash from file" to select your image file.(.img or .zip) 5.Click "Select target" to choose your USB device. 6.Start to flash and wait for a moment.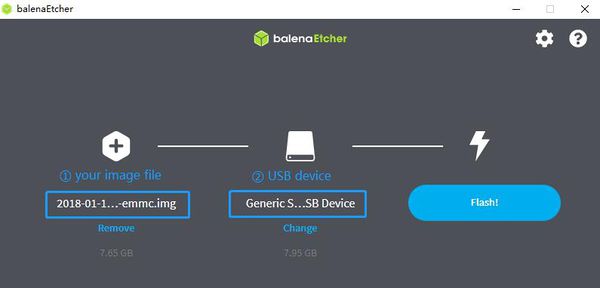
Android
Load your first image on M1+
1.You could download latest image from our forum. Ex: 2.Put your TF card into a TF-USB adapter, and then plug adapter in your Windows PC usb interface. 3.Prepare your image, and download image burning tools PhoenixCard.exe. 4.Use "PhoenixCard.exe" to burn android image to TF card.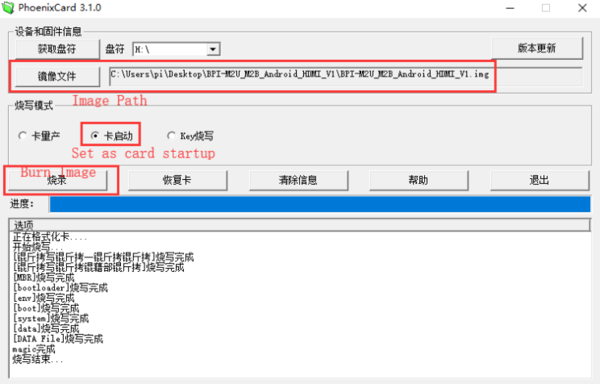
* Download PhoenixCard: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-fjvPqtG_zewVzqnXf1AHw?pwd=eid9
Advanced Development
SATA
1. Mount SATA on M1P
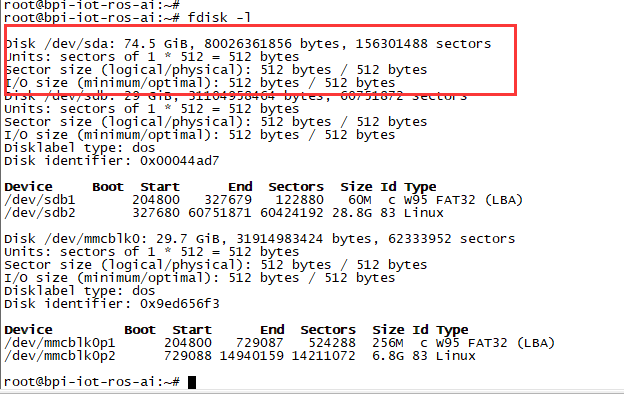
- After insert sata interface, execute "fdisk -l"
- Then "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
2. If you meet some errors when you mount SATA, try these following commands:
- "fdisk /dev/sdx" to create new partition , set your partition numbers and size, after created partitions, input "wq" to save and quit.
- "mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdx" to format the SATA
- "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
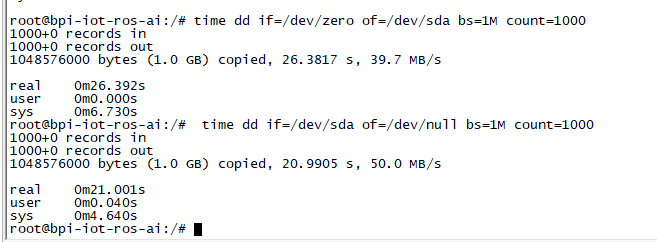
3. After you success to insert SATA, we could input following commands to test SATA interface:
- "time dd if=/dev/xxx of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1000" to test read speed
- "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed
Touch screen
GMAC
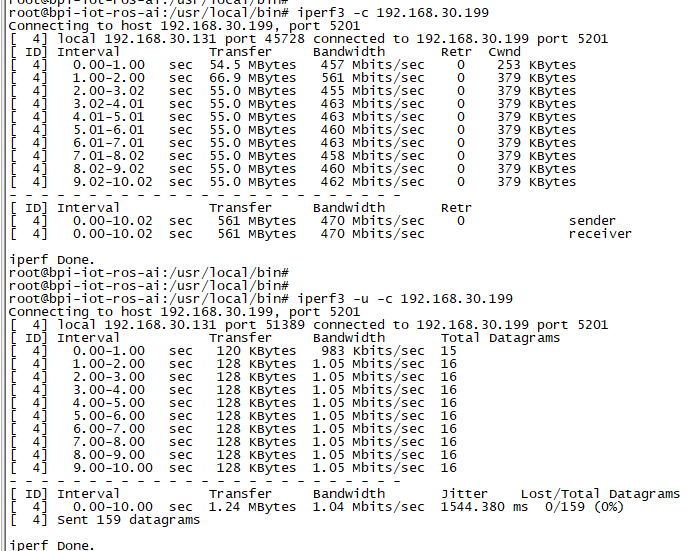
Use iperf3 to test gmac
1. On PC Terminal:
- Execute "iperf3 -s"
2. On M1P console:
- TCP test: "iperf3 -c serverIP"
- UDP test: "iperf3 -u -c serverIP"
WiFi on M1P
WiFi Client
You have two ways to setup WiFi Client
1. Use commands to setup WiFi client
- ip link set wlan0 up
- iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID
- vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
network={
ssid="ssid"
psk="password"
priority=1
}
- wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
- dhclient wlan0
2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client
Clear boot
- git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-files/tree/master/SD/100MB
- bpi-bootsel BPI-cleanboot-8k.img.gz /dev/sdX
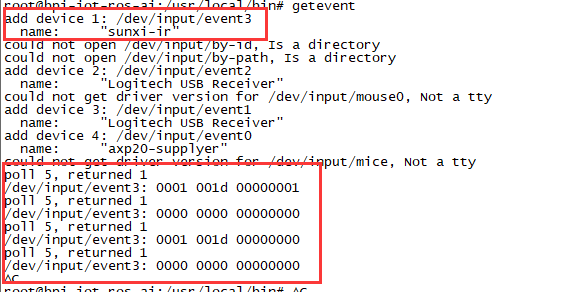
IR function
- Execute "getevent"
- Use your IR device to send information to M1P
RPi.GPIO
Install RPi.GPIO
- Execute "git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/RPi.GPIO"
- after clone the repo, cd RPi,GPIO
- Execute "sudo apt-get update"
- Execute "sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev"
- Execute "sudo python setup.py install" or "sudo python3 setup.py install" to install the module
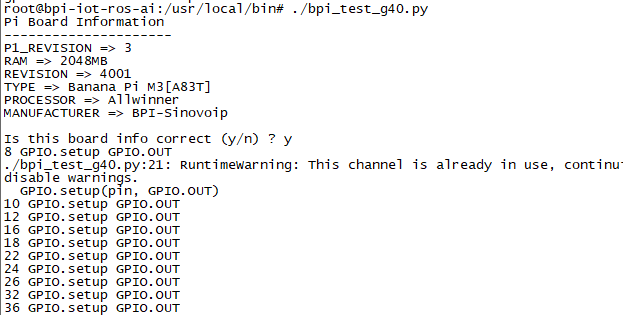
Using RPi.GPIO
- cd /usr/local/bin
- Execute "./bpi_test_g40.py" to test RPi.GPIO
WringPi
- GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git
- We also have built-in test command in "/usr/local/bin"
RGB 1602 LCD
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602.sh"
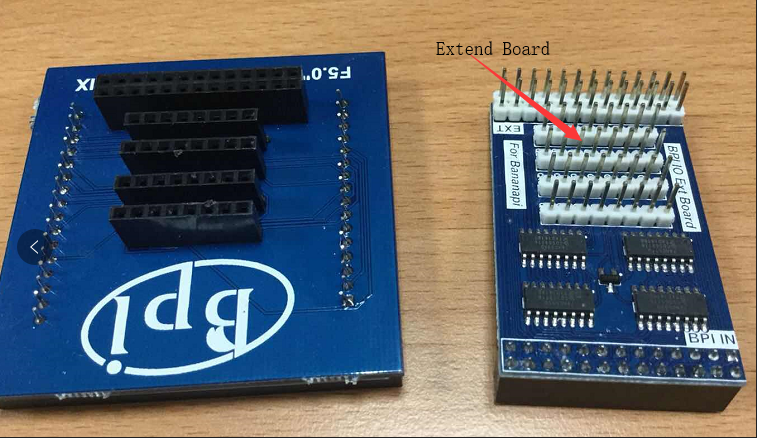
8x8 RGB LED Martix
- Firstly you need a GPIO Extend Board for 8x8 LED Martix
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40.sh"
File System
- read only system change to read & write mode: "mount -o remount,rw /"
Install QT
- sudo apt-get install build-essential
- sudo apt-get install libgl1-mesa-dev
- sudo apt-get install libglu1-mesa-dev
- sudo apt-get install freeglut3-dev
- sudo apt-get install cmake
- sudo apt-get install qt5-default qtcreator
A20 CAN Bus
In order to port can4linux to the BananaPi, the CAN module description is needed from the A20 hardware manual. can4linux is a character-driver-based Linux driver used already on desktop PCs and embedded platforms like Freescale FlexCAN (the i.MX series of micro controllers) or Xiliny Zynq.
There is a more detailed document about CAN on the A20 at: https://dl.linux-sunxi.org/A20/CAN%20Bus1.pdf
This is a tutorial for using CAN BUS on bananapi with bananian 15-01
Thank selqcir share this example:
- Download and install "bananian-1501.img" into 8 GB SDCard.
- Expand the root file system using "bananian-config"
- Install missing package:
apt-get install git apt-get update apt-get upgrade reboot
- Get last bananian available, and continu to install missing package:
git clone https://github.com/Bananian/linux-bananapi apt-get install build-essential u-boot-tools uboot-mkimage apt-get install libusb-1.0-0 libusb-1.0-0-dev git wget fakeroot kernel-package zlib1g-dev libncurses5-dev apt-get install subversion
- Build kernel:
cd linux-bananapi make menuconfig
- Exit without saving when menu appears
zcat /proc/config.gz > /root/linux-bananapi/.config make uImage modules make INSTALL_MOD_PATH=output modules_install
- At this step, kernel should be compiled and "Module.symvers" should be available
- Then rename modules and firmware provide by Bananian, and replace by the new one.
mv /lib/modules /lib/modules.old mv /lib/firmware /lib/firmware.old mv /root/linux-bananapi/output/lib/modules /lib/modules mv /root/linux-bananapi/output/lib/firmware /lib/firmware
- Same for uImage:
mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /mnt cd /mnt mv uImage uImage.old mv /root/linux-bananapi/arch/arm/boot/uImage /mnt reboot
- Create link for further build:
cd /lib/modules/3.4.104/ ln -s /root/linux-bananapi build cd ~
- Get Can4Linux and build it:
svn checkout https://svn.code.sf.net/p/can4linux/code/trunk can4linux-code cd /root/can4linux-code/can4linux/ make TARGET=BANANAPI
- Install module for each startup of the board:
insmod can4linux.ko cp can4linux.ko /lib/modules/3.4.104/kernel/net/can/ depmod -A -v modprobe -v can4linux echo "" >> /etc/modules ; echo "can4linux" >> /etc/modules reboot
- Build CAN example
apt-get install swig apt-get install python-dev cd can4linux-code/can4linux-examples/
- Update CAN speed and device in file "pyCan-example.py"
# setting the device number device = 0 defaultBaudrate = '250'
- Connect CAN transceiver and CAN bus, and check with for example:
python pyCan-example.py
That's all
With this method, kernel version is "Linux bananapi 3.4.104" instead of "Linux bananapi 3.4.104+", because i was unable to find same sources than Bananian 15-01 , but CAN bus work !