Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with M2 Ultra & Berry"
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→Introduction) |
(→Reference Link) |
||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[zh:快速上手 香蕉派 BPI-M2 Ultra / BPI-M2 Berry]] | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
==BPI-M2U== | ==BPI-M2U== | ||
| − | [[File:M2p_respbian. | + | [[File:Banana_pi_BPI-M2_Ultra_4.JPG|thumb|Overview [[Banana Pi BPI-M2U ]]]] |
| + | [[File:Banana_pi_BPI-M2_Berry_5.JPG|thumb|Overview [[Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry]]]] | ||
| + | [[File:M2p_respbian.png|thumb|Overview: BPI-M2U respbian linux]] | ||
| − | Banana Pi BPI-M2 Ultra is a quad-core mini single board computer built with Allwinner R40 SoC. It features 2GB of RAM and 8GB eMMC. It also has onboard WiFi and BT. On the ports side, the BPI-M2 Ultra has 2 USB A 2.0 ports, 1 USB OTG port, 1 HDMI port, 1 audio jack, a DC power port, and last but not least, a SATA port.. | + | Banana Pi BPI-M2 Ultra is a quad-core mini single board computer built with Allwinner R40 SoC. It features 2GB of RAM and 8GB eMMC. It also has onboard WiFi and BT. On the ports side, the BPI-M2 Ultra has 2 USB A 2.0 ports, 1 USB OTG port, 1 HDMI port, 1 audio jack, a DC power port, and last but not least, a SATA port.. |
*Read more about : [[Banana Pi BPI-M2U]] | *Read more about : [[Banana Pi BPI-M2U]] | ||
| − | |||
===Key Features=== | ===Key Features=== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
==BPI-M2 Berry== | ==BPI-M2 Berry== | ||
| − | Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry is a quad-core mini single board computer built with Allwinner V40 SoC. It features 1GB of RAM . It also has onboard WiFi and BT. On the ports side, the BPI-M2 Ultra has 4 USB A 2.0 ports, 1 USB OTG port, 1 HDMI port, 1 audio jack, a DC power port, and last but not least, a SATA port.. | + | Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry is a quad-core mini single board computer built with Allwinner V40 SoC. It features 1GB of RAM . It also has onboard WiFi and BT. On the ports side, the BPI-M2 Ultra has 4 USB A 2.0 ports, 1 USB OTG port, 1 HDMI port, 1 audio jack, a DC power port, and last but not least, a SATA port.. |
*Read more about : [[Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry]] | *Read more about : [[Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry]] | ||
| Line 29: | Line 31: | ||
Let's get start to develop on BPI-M2U, see amazing things happen. | Let's get start to develop on BPI-M2U, see amazing things happen. | ||
==Basic Development== | ==Basic Development== | ||
| − | === | + | ===Linux=== |
| − | + | * Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Windows System | |
| + | * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on M2P | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1.You could download the latest image from our wiki. | ||
| + | * BPI-M2U: https://wiki.banana-pi.org/Banana_Pi_BPI-M2U#Image_Release | ||
| + | * BPI-M2 Berry: https://wiki.banana-pi.org/Banana_Pi_BPI-M2_Berry#Image_Release | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.Put the TF card into a TF-USB adapter and plug it to your PC USB interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3.Download the flashing tools "BalenaEtcher" and start it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4.Click "Flash from file" to select your image file.(.img or .zip) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5.Click "Select target" to choose your USB device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6.Start to flash and wait for burning completely. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Etcher.jpg | 600px]] | ||
| − | 2. | + | ===Android=== |
| + | 1.You could download latest image from our forum. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.Put your TF card into a TF-USB adapter, and then plug adapter in your Windows PC usb interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3.Prepare your image, and download image burning tools PhoenixCard.exe. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4.Use "PhoenixCard.exe" to burn android image to TF card. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:M3_Android_Burning.png | 600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Download PhoenixCard: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-fjvPqtG_zewVzqnXf1AHw?pwd=eid9 | ||
| − | ===Load your first image on M2U=== | + | ===Load your first image on M2U EMMC=== |
| − | 1. | + | 1.Bootup your M2U with Micro SD card |
| − | + | 2.Copy "xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip / xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img" to your USB disk | |
| + | 3.Plug your USB disk in M2U | ||
| + | 4.Mount the USB disk and flash the image file to eMMC | ||
| − | + | * bpi-tools | |
| − | + | curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools|sudo -E bash | |
| − | + | mount /dev/sda1 /mnt | |
| − | + | cd /mnt | |
| + | bpi-copy xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip /dev/mmcblk0 | ||
| − | + | * dd command | |
| − | + | mount /dev/sda1 /mnt | |
| + | cd /mnt | ||
| + | unzip -p xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip |pv| dd of=/dev/mmcblk0 bs=10M status=noxfer | ||
| − | + | 5.Then power off M2U, take TF card out, power on M2U | |
==Advanced Development== | ==Advanced Development== | ||
| + | ===How to build uboot & kernel=== | ||
| + | ====Install tools==== | ||
| + | * apt-get udpate | ||
| + | * apt-get install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf u-boot-tools | ||
| + | * apt-get install pv | ||
| + | * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash | ||
| + | ====Clone code==== | ||
| + | * git clone: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-M2U-bsp.git | ||
| + | * ./build.sh | ||
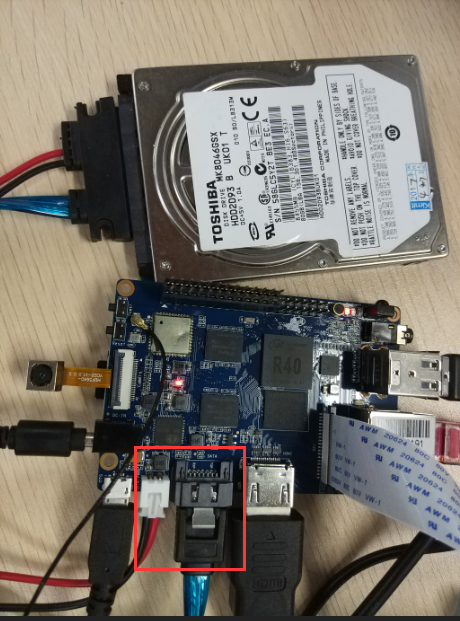
===SATA=== | ===SATA=== | ||
1. Mount SATA on M2U | 1. Mount SATA on M2U | ||
| Line 61: | Line 105: | ||
2. If you meet some errors when you mount SATA, try these following commands: | 2. If you meet some errors when you mount SATA, try these following commands: | ||
| − | * "fdisk /dev/sdx" to create new partition , after created input "wq" to save and quit. | + | * "fdisk /dev/sdx" to create new partition , set your partition numbers and size, after created partitions, input "wq" to save and quit. |
* "mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdx" to format the SATA | * "mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdx" to format the SATA | ||
* "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx" | * "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx" | ||
| Line 72: | Line 116: | ||
===OTG=== | ===OTG=== | ||
1. On M2U console: | 1. On M2U console: | ||
| − | * Execute " | + | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/adbd.sh", then execute "ps -ax | grep adbd" to see if adbd is set up |
[[Image:M2P_ADBD.png]] | [[Image:M2P_ADBD.png]] | ||
| Line 116: | Line 160: | ||
* iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | * iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | ||
* vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | * vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | ||
| − | + | network={ | |
| − | * wpa_supplicant - | + | ssid="ssid" |
| + | psk="password" | ||
| + | priority=1 | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | * wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf | ||
* dhclient wlan0 | * dhclient wlan0 | ||
| Line 133: | Line 181: | ||
* Use your UI interface to operate camara | * Use your UI interface to operate camara | ||
* Applications -> Sound & Video -> guvcview | * Applications -> Sound & Video -> guvcview | ||
| − | + | ====Shell==== | |
* We also have built-in command in "/usr/local/bin" to test camara | * We also have built-in command in "/usr/local/bin" to test camara | ||
* "./test_ov5640_image_mode.sh" to test picture taking function | * "./test_ov5640_image_mode.sh" to test picture taking function | ||
| Line 141: | Line 189: | ||
* Execute "getevent" | * Execute "getevent" | ||
* Use your IR device to send information to M2U | * Use your IR device to send information to M2U | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===RPi.GPIO=== | ||
| + | ====Install RPi.GPIO==== | ||
| + | * Execute "git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/RPi.GPIO" | ||
| + | * after clone the repo, cd RPi,GPIO | ||
| + | * Execute "sudo apt-get update" | ||
| + | * Execute "sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev" | ||
| + | * Execute "sudo python setup.py install" or "sudo python3 setup.py install" to install the module | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Using RPi.GPIO==== | ||
| + | * cd /usr/local/bin | ||
| + | * Execute "./bpi_test_g40.py" to test RPi.GPIO | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image: RPi_GPIO.png]] | ||
===WringPi=== | ===WringPi=== | ||
* GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git | * GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git | ||
| − | * We also have built-in test command in /usr/local/bin | + | * We also have built-in test command in "/usr/local/bin" |
====RGB 1602 LCD==== | ====RGB 1602 LCD==== | ||
| − | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602" | + | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602.sh" |
====0.96 Inch OLED Display==== | ====0.96 Inch OLED Display==== | ||
| − | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_52pi" | + | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_52pi.sh" |
====8x8 RGB LED Martix==== | ====8x8 RGB LED Martix==== | ||
| Line 156: | Line 218: | ||
[[Image: WringPi_LED_Martix_Extend_Board.png]] | [[Image: WringPi_LED_Martix_Extend_Board.png]] | ||
| − | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40" | + | * Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40.sh" |
| + | |||
| + | ===File System=== | ||
| + | * read only system change to read & write mode: "mount -o remount,rw /" | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Install Qt5.7 & Qtcreator=== | ||
| + | 1.Prepare a 32Gb TF card | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.Use GParted to resize root point '/' as 32Gb | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3.apt-get install libxcb* | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4.download qt5.7 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5.make & make install | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6.apt-get install qtcreator | ||
| + | |||
| + | 7.Config qtcreator | ||
==FAQ== | ==FAQ== | ||
=Reference Link= | =Reference Link= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
http://forum.banana-pi.org/ | http://forum.banana-pi.org/ | ||
Latest revision as of 00:30, 28 August 2023
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Development
- 2.1 Basic Development
- 2.2 Advanced Development
- 2.3 FAQ
- 3 Reference Link
Introduction
BPI-M2U

Overview Banana Pi BPI-M2U

Overview Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry
Banana Pi BPI-M2 Ultra is a quad-core mini single board computer built with Allwinner R40 SoC. It features 2GB of RAM and 8GB eMMC. It also has onboard WiFi and BT. On the ports side, the BPI-M2 Ultra has 2 USB A 2.0 ports, 1 USB OTG port, 1 HDMI port, 1 audio jack, a DC power port, and last but not least, a SATA port..
- Read more about : Banana Pi BPI-M2U
Key Features
- Quad Core ARM Cortex A7 CPU R40
- 2GB DDR3 SDRAM
- 8 GB eMMC storage
- WiFi (AP6212) & Bluetooth onboard
- SATA Interface
BPI-M2 Berry
Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry is a quad-core mini single board computer built with Allwinner V40 SoC. It features 1GB of RAM . It also has onboard WiFi and BT. On the ports side, the BPI-M2 Ultra has 4 USB A 2.0 ports, 1 USB OTG port, 1 HDMI port, 1 audio jack, a DC power port, and last but not least, a SATA port..
- Read more about : Banana Pi BPI-M2 Berry
Key Features
- Quad Core ARM Cortex A7 CPU V40.
- 1GB DDR3 SDRAM.
- WiFi (AP6212) & Bluetooth onboard.
- SATA Interface
Development
Let's get start to develop on BPI-M2U, see amazing things happen.
Basic Development
Linux
* Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Windows System * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on M2P 1.You could download the latest image from our wiki. * BPI-M2U: https://wiki.banana-pi.org/Banana_Pi_BPI-M2U#Image_Release * BPI-M2 Berry: https://wiki.banana-pi.org/Banana_Pi_BPI-M2_Berry#Image_Release 2.Put the TF card into a TF-USB adapter and plug it to your PC USB interface. 3.Download the flashing tools "BalenaEtcher" and start it. 4.Click "Flash from file" to select your image file.(.img or .zip) 5.Click "Select target" to choose your USB device. 6.Start to flash and wait for burning completely.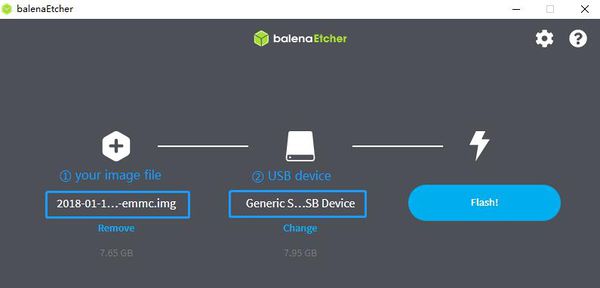
Android
1.You could download latest image from our forum. 2.Put your TF card into a TF-USB adapter, and then plug adapter in your Windows PC usb interface. 3.Prepare your image, and download image burning tools PhoenixCard.exe. 4.Use "PhoenixCard.exe" to burn android image to TF card.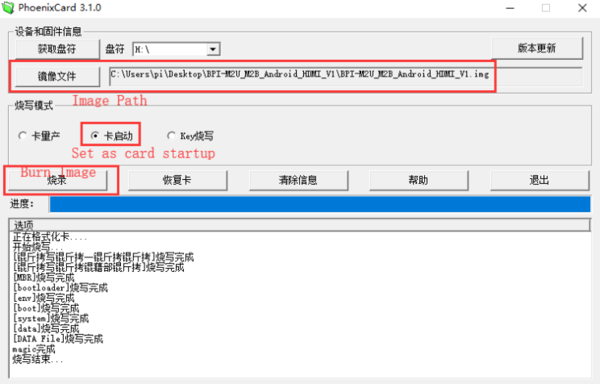
* Download PhoenixCard: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-fjvPqtG_zewVzqnXf1AHw?pwd=eid9
Load your first image on M2U EMMC
1.Bootup your M2U with Micro SD card 2.Copy "xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip / xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img" to your USB disk 3.Plug your USB disk in M2U 4.Mount the USB disk and flash the image file to eMMC
* bpi-tools curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools%7Csudo -E bash mount /dev/sda1 /mnt cd /mnt bpi-copy xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip /dev/mmcblk0
* dd command mount /dev/sda1 /mnt cd /mnt unzip -p xxx-sd-emmc-xxx.img.zip |pv| dd of=/dev/mmcblk0 bs=10M status=noxfer
5.Then power off M2U, take TF card out, power on M2U
Advanced Development
How to build uboot & kernel
Install tools
- apt-get udpate
- apt-get install gcc-arm-linux-gnueabihf u-boot-tools
- apt-get install pv
- curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash
Clone code
- git clone: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-M2U-bsp.git
- ./build.sh
SATA
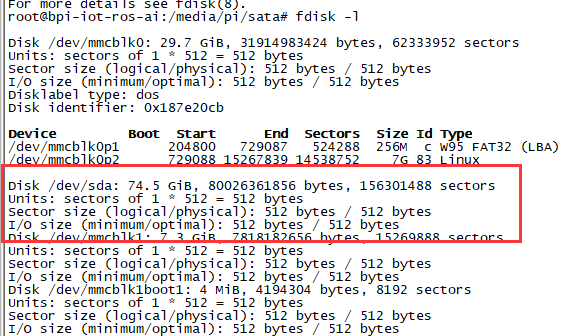
1. Mount SATA on M2U
- After insert sata interface, execute "fdisk -l"
- Then "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
2. If you meet some errors when you mount SATA, try these following commands:
- "fdisk /dev/sdx" to create new partition , set your partition numbers and size, after created partitions, input "wq" to save and quit.
- "mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdx" to format the SATA
- "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
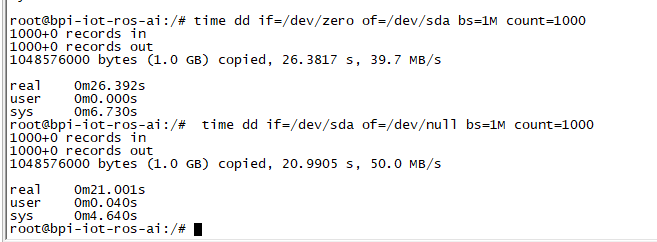
3. After you success to insert SATA, we could input following commands to test SATA interface:
- "time dd if=/dev/xxx of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1000" to test read speed
- "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed
OTG
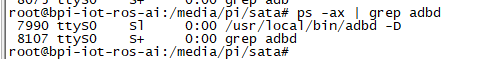
1. On M2U console:
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/adbd.sh", then execute "ps -ax | grep adbd" to see if adbd is set up
2. On PC terminal:
- If adbd was succeed to set up, insert OTG-USB interface to M2U and PC(with Ubuntu system)
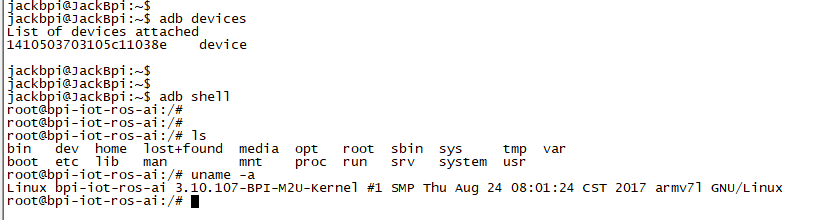
- Execute "adb devices" to see if PC has recognised M2U OTG
- If yes, we could execute "adb shell" to connect M2U by adb now
LCD 5" & LCD 7"
- Execute "bpi-bootsel", you'll see a list of boot files
- Find "BPI_M2U_LCD7.img.gz"
- Then execute "bpi-bootsel /usr/lib/u-boot/bananapi/bpi-m2u/BPI_M2U_LCD7.img.gz"
Touch screen
GMAC
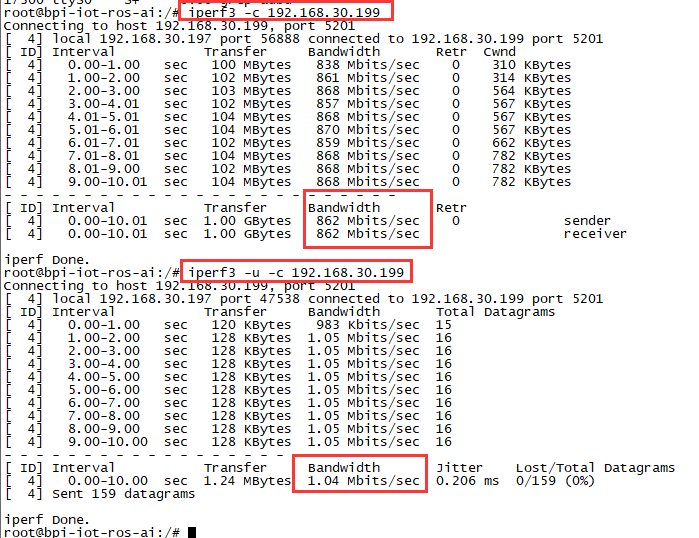
Use iperf3 to test gmac
1. On PC Terminal:
- Execute "iperf3 -s"
2. On M2U console:
- TCP test: "iperf3 -c serverIP"
- UDP test: "iperf3 -u -c serverIP"
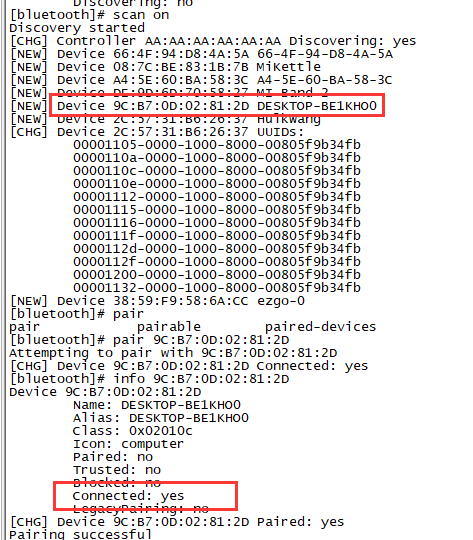
Bluetooth
- Use bluetoothctl tool to operate BT
- Execute "bluetoothctl"
- If you don't know how to use bluetoothctl, type "help", you will see more commands
- Execute these commands:
WiFi on M2U
WiFi Client
You have two ways to setup WiFi Client
1. Use commands to setup WiFi client
- ip link set wlan0 up
- iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID
- vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
network={
ssid="ssid"
psk="password"
priority=1
}
- wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
- dhclient wlan0
2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client
Clear boot
- git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-files/tree/master/SD/100MB
- bpi-bootsel BPI-cleanboot-8k.img.gz /dev/sdX
Camara function
We use HDF5640 camara.
Guvcview
- Use your UI interface to operate camara
- Applications -> Sound & Video -> guvcview
Shell
- We also have built-in command in "/usr/local/bin" to test camara
- "./test_ov5640_image_mode.sh" to test picture taking function
- "./cameratest.sh" to test video recording function
IR function
- Execute "getevent"
- Use your IR device to send information to M2U
RPi.GPIO
Install RPi.GPIO
- Execute "git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/RPi.GPIO"
- after clone the repo, cd RPi,GPIO
- Execute "sudo apt-get update"
- Execute "sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev"
- Execute "sudo python setup.py install" or "sudo python3 setup.py install" to install the module
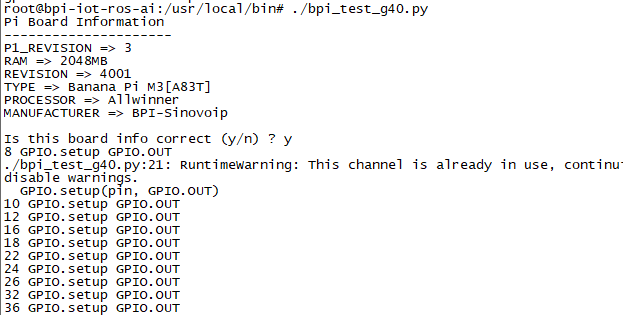
Using RPi.GPIO
- cd /usr/local/bin
- Execute "./bpi_test_g40.py" to test RPi.GPIO
WringPi
- GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git
- We also have built-in test command in "/usr/local/bin"
RGB 1602 LCD
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602.sh"
0.96 Inch OLED Display
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_52pi.sh"
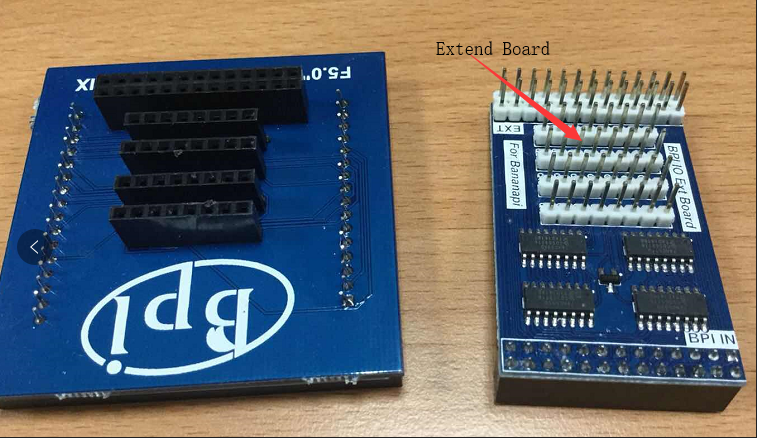
8x8 RGB LED Martix
- Firstly you need a GPIO Extend Board for 8x8 LED Martix
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40.sh"
File System
- read only system change to read & write mode: "mount -o remount,rw /"
Install Qt5.7 & Qtcreator
1.Prepare a 32Gb TF card
2.Use GParted to resize root point '/' as 32Gb
3.apt-get install libxcb*
4.download qt5.7
5.make & make install
6.apt-get install qtcreator
7.Config qtcreator