Difference between pages "Getting Started with M2 Zero" and "Getting Started with W2"
(Difference between pages)
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→WiFi Client) |
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→Install On SD Card) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Android_6.0_1.jpg|thumb|Overview: BPI-W2 Android 6.0]] | |
| + | [[File:W2_debian.jpg|thumb|[http://forum.banana-pi.org/t/banana-pi-bpi-w2-new-image-debian-9-linux-image-release-2018-09-18/6797 Debian 9 Linux Image Release 2018-09-18]]] | ||
| + | [[File:W2_ubuntu.jpg|thumb|[http://forum.banana-pi.org/t/bananapi-w2-ubuntu-18-04-new-image-release-2018-09-17/6790 BananaPI-W2 Ubuntu 18.04 New Image Release 2018-09-17]]] | ||
| + | [[File:W2_rasbian.jpg|thumb|[http://forum.banana-pi.org/t/banana-pi-bpi-w2-new-image-raspbian-9-4-new-image-release-2018-09-17/6824 BananaPI-W2 Raspbian 9.4 New Image Release 2018-09-17]]] | ||
| + | [[File:Rpitc.jpg|thumb|[http://forum.banana-pi.org/t/bpi-w2-new-iamge-rpitcv3-1-12-demo-bpi-w2-beta-2018-09-03/6686 RPiTCv3_1.12-demo-bpi-w2-beta-2018-09-03]]] | ||
| − | + | Read more: [[Banana Pi BPI-W2]] | |
| − | + | =Development= | |
| + | Let's get start to develop on BPI-W2, see amazing things happen. | ||
| − | + | Old page:[[Getting Started with BPI-W2]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Basic Development== | ==Basic Development== | ||
===Prepare to develop=== | ===Prepare to develop=== | ||
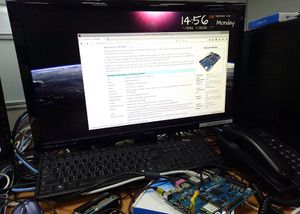
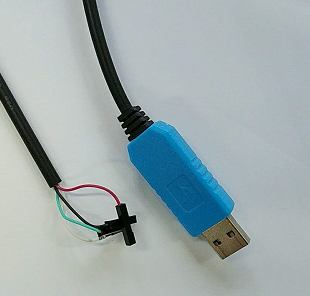
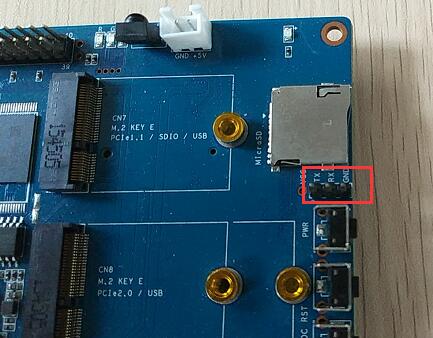
| − | + | * Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Ubuntu System | |
| − | + | * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on W2 | |
| − | + | [[Image:Debug_console_wire.png]] | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:W2_debug_console.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Install Linux Image On W2=== | ||
| + | ====Install On SD Card==== | ||
| + | =====Windows===== | ||
| + | *English: | ||
| + | 1.Format SD card: http://wiki.banana-pi.org/Quick_Start_Banana_pi_SBC#Format_your_SD_under_Windows_os | ||
| − | + | 2.Install Image On SD Card: http://wiki.banana-pi.org/Quick_Start_Banana_pi_SBC#how_to_write_Linux_image | |
| − | + | *Chinese: | |
| − | + | https://www.cnblogs.com/topbin/p/10882992.html | |
| − | + | =====Ubuntu===== | |
| − | + | 1.Install bpi-tools on your system | |
| − | |||
* apt-get install pv | * apt-get install pv | ||
* curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash | * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash | ||
| − | + | 2.After you download the image, insert your TF card into your Ubuntu | |
* Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card. | * Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card. | ||
| − | + | 3.After step 2, then you can insert your TF card into W2, and press power button setup W2. | |
| − | === | + | ====Install On EMMC==== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Load Android image on W2=== | |
| − | + | ====Install On SD Card==== | |
| − | + | ====Install On EMMC==== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Advanced Development== | ==Advanced Development== | ||
| + | ===GPIO=== | ||
| + | ====GPIO Control==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====PWM Control==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===SATA=== | ||
| + | |||
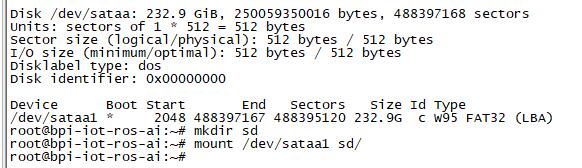
| + | 1. Mount dev on W2 | ||
| + | * After insert sata interface, execute "fdisk -l" | ||
| + | * Then "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx" | ||
| + | [[Image:W2_Sata.jpg]] | ||
| − | + | 2. If you meet some errors when you mount SATA, try these following commands: | |
| − | * | + | * "fdisk /dev/sdx" to create new partition , set your partition numbers and size, after created partitions, input "wq" to save and quit. |
| − | + | * "mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdx" to format the SATA | |
| − | * | + | * "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx" |
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ====SSD==== |
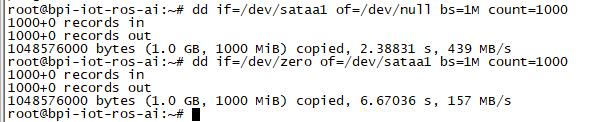
| − | 1. | + | 1. After you success to insert SATA, we could input following commands to test SATA interface: |
| − | * | + | * "time dd if=/dev/xxx of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1000" to test read speed |
| + | * "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed | ||
| + | [[Image:W2_ssd_test.jpg]] | ||
| − | + | ====HDD==== | |
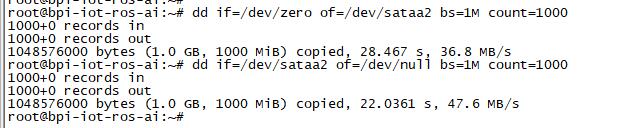
| − | + | 1. After you success to insert SATA, we could input following commands to test SATA interface: | |
| − | * | + | * "time dd if=/dev/xxx of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1000" to test read speed |
| − | * | + | * "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed |
| + | [[Image:W2_hdd_test.jpg]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===NetWork=== |
| − | * | + | ====GMAC==== |
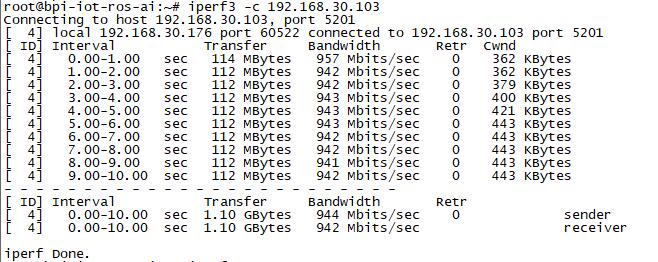
| + | *iperf3 -c [server] | ||
| + | [[Image:w2_iperf3_c.jpg]] | ||
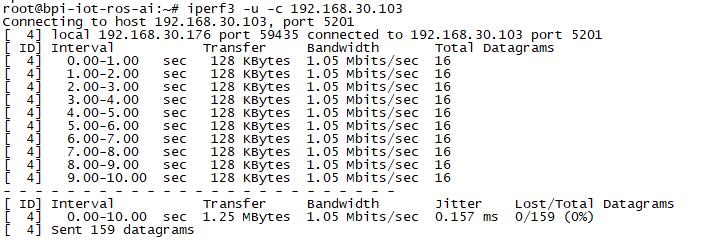
| − | [[Image: | + | *iperf3 -u -c [server] |
| + | [[Image:w2_iperf3_u_c.jpg]] | ||
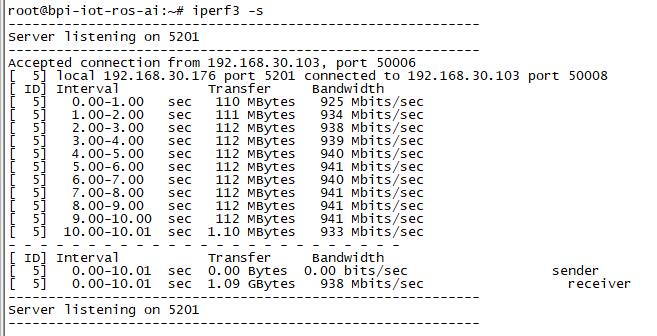
| − | * | + | *iperf3 -s |
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:w2_iperf3_s.jpg]] |
| − | === | + | ====WiFi & BT==== |
| − | + | 1.If you want to use WiFi or BT, you could use RTL8822BE module. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:RTL8822BE.jpg]] | |
| − | |||
| + | =====STA===== | ||
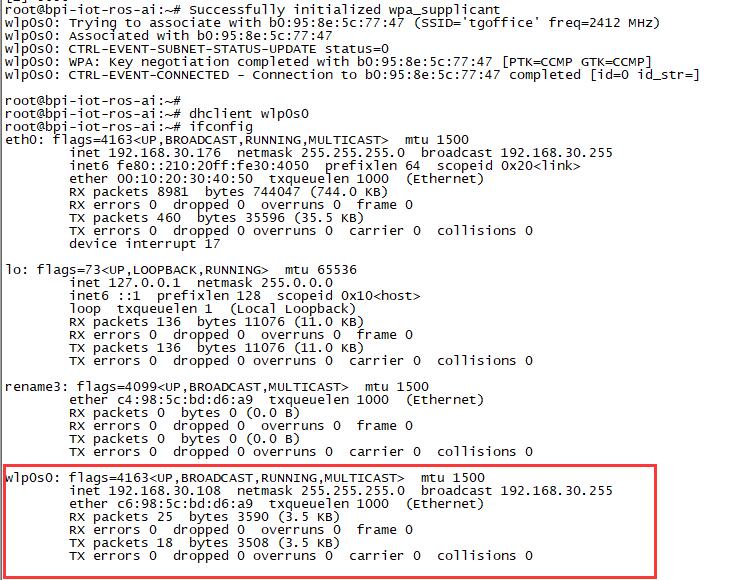
1. Use commands to setup WiFi client | 1. Use commands to setup WiFi client | ||
* ip link set wlan0 up | * ip link set wlan0 up | ||
* iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | * iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID | ||
| − | * vim /etc/ | + | * vim /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf |
network={ | network={ | ||
ssid="ssid" | ssid="ssid" | ||
| Line 101: | Line 113: | ||
2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client | 2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client | ||
| − | + | [[Image:RTL8822BE_STA.jpg]] | |
| − | + | =====AP===== | |
| − | + | Developing | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Image: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Develop 4G module with W2=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===GPU=== |
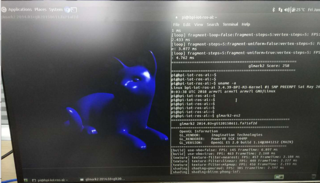
| − | * | + | * Execute "glmark2-es" to start OpenGL test |
| − | [[Image: | + | * glmark2 Score: 30 |
| + | [[Image:M3_GPU_Test.png | 320px]] | ||
| − | + | ===Make your own image=== | |
Revision as of 22:38, 23 May 2019
Introduction
Read more: Banana Pi BPI-W2
Development
Let's get start to develop on BPI-W2, see amazing things happen.
Old page:Getting Started with BPI-W2
Basic Development
Prepare to develop
- Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Ubuntu System
- Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on W2
Install Linux Image On W2
Install On SD Card
Windows
*English: 1.Format SD card: http://wiki.banana-pi.org/Quick_Start_Banana_pi_SBC#Format_your_SD_under_Windows_os
2.Install Image On SD Card: http://wiki.banana-pi.org/Quick_Start_Banana_pi_SBC#how_to_write_Linux_image
*Chinese: https://www.cnblogs.com/topbin/p/10882992.html
Ubuntu
1.Install bpi-tools on your system * apt-get install pv * curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash 2.After you download the image, insert your TF card into your Ubuntu * Execute "bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx" to install image on your TF card. 3.After step 2, then you can insert your TF card into W2, and press power button setup W2.
Install On EMMC
Load Android image on W2
Install On SD Card
Install On EMMC
Advanced Development
GPIO
GPIO Control
PWM Control
SATA
1. Mount dev on W2
- After insert sata interface, execute "fdisk -l"
- Then "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
2. If you meet some errors when you mount SATA, try these following commands:
- "fdisk /dev/sdx" to create new partition , set your partition numbers and size, after created partitions, input "wq" to save and quit.
- "mkfs.ext2 /dev/sdx" to format the SATA
- "mount /dev/sdx /mnt/xxx"
SSD
1. After you success to insert SATA, we could input following commands to test SATA interface:
- "time dd if=/dev/xxx of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1000" to test read speed
- "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed
HDD
1. After you success to insert SATA, we could input following commands to test SATA interface:
- "time dd if=/dev/xxx of=/dev/null bs=1M count=1000" to test read speed
- "time dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdx bs=1M count=1000" to test write speed
NetWork
GMAC
- iperf3 -c [server]
- iperf3 -u -c [server]
- iperf3 -s
WiFi & BT
1.If you want to use WiFi or BT, you could use RTL8822BE module.
STA
1. Use commands to setup WiFi client
- ip link set wlan0 up
- iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID
- vim /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
network={
ssid="ssid"
psk="password"
priority=1
}
- wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
- dhclient wlan0
2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client
AP
Developing
Develop 4G module with W2
GPU
- Execute "glmark2-es" to start OpenGL test
- glmark2 Score: 30