Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with M5/M2Pro"
(→RPi.GPIO) |
(→Linux Server Image Network Configuration) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 382: | Line 382: | ||
:blinkall, blink all pin header gpios, no extend board. | :blinkall, blink all pin header gpios, no extend board. | ||
| − | :lcd- | + | :lcd-adafruit, [http://wiki.banana-pi.org/BPI_LCD_1602_display_module BPI LCD 1602 display module] example. |
| − | : | + | :oled, [http://wiki.banana-pi.org/BPI_OLED_Display_Module BPI OLED Display Module] example. |
| − | :matrixled | + | :matrixled, [http://wiki.banana-pi.org/BPI_RGB_LED_Matrix_Expansion_Module BPI RGB LED Matrix Expansion Module] example. |
| − | :berryclip | + | :berryclip, [http://wiki.banana-pi.org/BPI_BerryClip_Module BPI BerryClip Module] |
===RPi.GPIO=== | ===RPi.GPIO=== | ||
| Line 406: | Line 406: | ||
: If the package is already installed, it should be uninstalled before installing the new one, or installing the new one with --force-reinstall option. | : If the package is already installed, it should be uninstalled before installing the new one, or installing the new one with --force-reinstall option. | ||
| − | === | + | ===WiringPi-Python=== |
: Build and install, for debian, you must [https://wiki.banana-pi.org/Getting_Started_with_M5/M2Pro#Enable_sudo_for_Debian install sudo] before build | : Build and install, for debian, you must [https://wiki.banana-pi.org/Getting_Started_with_M5/M2Pro#Enable_sudo_for_Debian install sudo] before build | ||
$ sudo apt-get update | $ sudo apt-get update | ||
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools swig git | $ sudo apt-get install build-essential python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools swig git | ||
| − | $ git clone --recursive https://github.com/Dangku/ | + | $ git clone --recursive https://github.com/Dangku/WiringPi-Python.git |
| − | $ cd | + | $ cd WiringPi-Python |
$ sudo python3 setup.py install | $ sudo python3 setup.py install | ||
| Line 422: | Line 422: | ||
$ sudo apt-get update | $ sudo apt-get update | ||
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools git | $ sudo apt-get install build-essential python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools git | ||
| − | $ git clone https://github.com/Dangku/RPi.GPIO | + | $ git clone https://github.com/Dangku/RPi.GPIO.git |
| − | $ cd RPi.GPIO | + | $ cd RPi.GPIO |
$ sudo python3 setup.py clean --all | $ sudo python3 setup.py clean --all | ||
$ sudo python3 setup.py install | $ sudo python3 setup.py install | ||
| Line 860: | Line 860: | ||
:A sample 2.4G wifi ap mode netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-2.4g.yaml | :A sample 2.4G wifi ap mode netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-2.4g.yaml | ||
network: | network: | ||
| − | + | version: 2 | |
| − | + | renderer: NetworkManager | |
| − | + | wifis: | |
| − | + | wlan0: | |
| − | + | dhcp4: no | |
| − | + | access-points: | |
| − | + | "bananapi": | |
| − | + | mode: ap | |
| − | + | band: 2.4GHz | |
| − | + | channel: 6 | |
| − | + | auth: | |
| − | + | key-management: psk | |
| − | + | password: "123456789" | |
:A sample 5G wifi ap mode netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-5g.yaml | :A sample 5G wifi ap mode netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-5g.yaml | ||
network: | network: | ||
| − | + | version: 2 | |
| − | + | renderer: NetworkManager | |
| − | + | wifis: | |
| − | + | wlan0: | |
| − | + | dhcp4: no | |
| − | + | access-points: | |
| − | + | "bananapi": | |
| − | + | mode: ap | |
| − | + | band: 5GHz | |
| − | + | channel: 36 | |
| − | + | auth: | |
| − | + | key-management: psk | |
| − | + | password: "123456789" | |
:4. Manage wifi access point mode with [http://wiki.banana-pi.org/Getting_Started_with_BPI-M5#Linux_Server_Image_Network_Configuration Netplan] and Hostapd. | :4. Manage wifi access point mode with [http://wiki.banana-pi.org/Getting_Started_with_BPI-M5#Linux_Server_Image_Network_Configuration Netplan] and Hostapd. | ||
| Line 894: | Line 894: | ||
:1). Create a netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-hostapd.yaml | :1). Create a netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-hostapd.yaml | ||
network: | network: | ||
| − | + | version: 2 | |
| − | + | renderer: networkd | |
| − | + | ethernets: | |
| − | + | wlan0: | |
| − | + | dhcp4: no | |
| − | + | addresses: | |
| − | + | - 192.168.11.1/24 | |
:2). Install hostapd | :2). Install hostapd | ||
Latest revision as of 01:06, 25 July 2024
Contents
[hide]- 1 Introduction
- 2 specifications
- 3 development
- 3.1 Prepare
- 3.2 Android
- 3.3 Linux
- 3.4 Other Development
- 3.4.1 Custom Linux Boot Logo
- 3.4.2 Custom Android Boot Logo
- 3.4.3 Boot Sequence
- 3.4.4 Erase EMMC for SDcard Bootup
- 3.4.5 Erase Emmc Android by dd command
- 3.4.6 Wifi/BT support
- 3.4.7 Linux Server Image Network Configuration
- 3.4.8 Disable Cloud-init&Snap
- 3.4.9 Enable rc-local
- 3.4.10 Enable sudo for Debian
- 3.4.11 Install Docker Engine
Introduction

Banana Pi M5 is a new generation single board computer design , use Amlogic S905X3 Quad-Core Cortex-A55 (2.0xxGHz) Processor. Mali-G31 MP2 GPU with 4 x Execution Engines (650Mhz). support 4GB LPDDR4 and 16G eMMC flash. it have 4 USB 3.0 port,1GbE LAN port, IR Reciver, Audio Jack, 1 HDMI Out and USB type-c power supply.
Banana Pi M2Pro is the same SOC with M5, but different board layout. 2GB LPDDR4 and 16G eMMC flash, 2 USB 3.0 port,1GbE LAN port, rtl8821cu usb wifi/bt onboard, IR Reciver, 1 HDMI Out, 1 MicroUSB port, DC power supply.
specifications
- SoC – Amlogic S905X3 quad-core Cortex-A55 processor @ up to 2.0 GHz with
- Mali-G31 MP2 GPU @ 650Mhz
- System Memory – 4GB LPDDR4
- Storage – 16GB eMMC flash (option up to 64GB), MicroSD slot up to 2TB
- Video Output – HDMI 2.1 up to 4Kp60 with HDR, CEC, EDID
- Audio – 3.5mm audio jack, digital HDMI audio
- Connectivity – Gigabit Ethernet
- USB – 4x USB 3.0 ports via VL817 hub controller, 1x USB-C port (for power only?)
- Expansion – 40-pin Raspberry Pi header with 28x GPIO, UART, I2C, SPI, PWM, and power signal (+5V, +3.3V, GND).
- Debugging – 3-pin debug header
- Misc – Reset, Power, and U-boot button; power and activity LED’s; IR receiver
- Power Supply – 5V @3A via USB Type-C port
- Dimensions – 92x60mm (Not the same as Raspberry Pi PCB size, but they probably included the connectors during measurement)
- Weight – 48grams
development
Prepare
- 1. Prepare a usb-serial cable(3.3V,Baud: 115200), a 5V/3A adaptor type-c power supply. The serial cable is used for console debug and type-c cable is used for android image download and ADB debug. M2pro is used Micro-usb port for android image download and ADB debug.
- 2. Prepare a SDcard at least 8GB for linux development, android only support emmc boot.
- 3. The SOC rom first boot media is emmc, so board can't bootup from SDcard if the emmc is bootable with any image flashed, more info please refer to board boot sequence.
- 4. In Android SDcard is mmc0, emmc is mmc1, but in Linux SDcard is mmc1, emmc is mmc0.
- 5. User name/password: pi/bananapi ,root/bananapi.
Android
Prepare
- 1. Download and install the AML Usb Burning Tool for android image download via USB type-c on M5 and Micro-usb on M2pro, only support windows.
- 2. Download the latest android image, and confirm that the md5 checksum is correct.
- 3. M5 and M2pro are compatiable with same android image.
Install Image with Usb Burning Tool
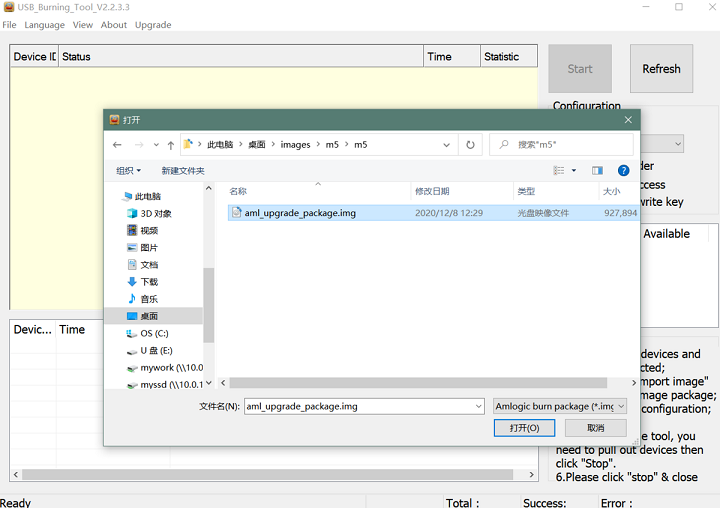
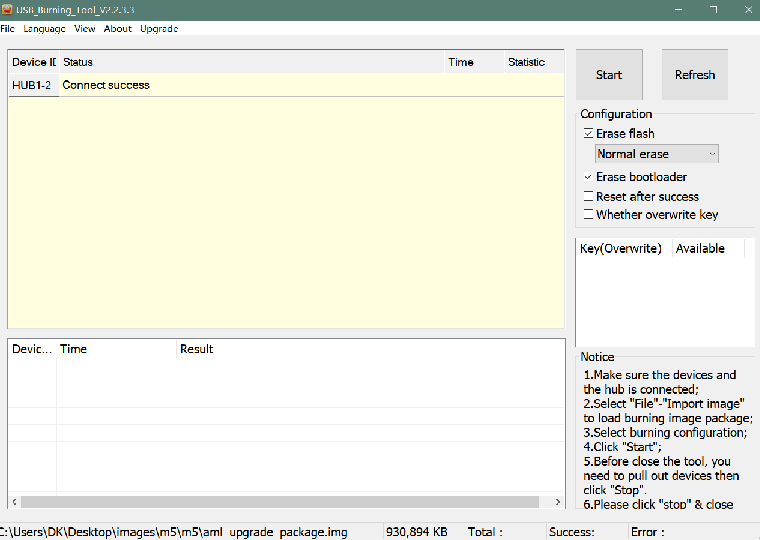
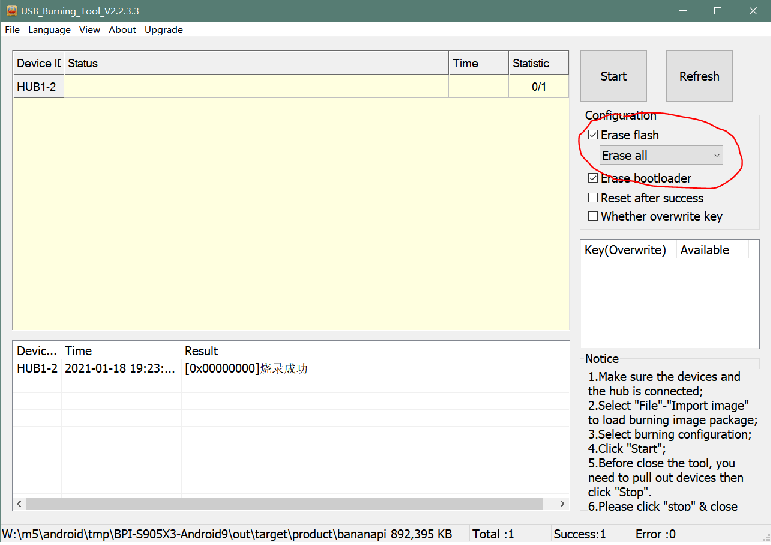
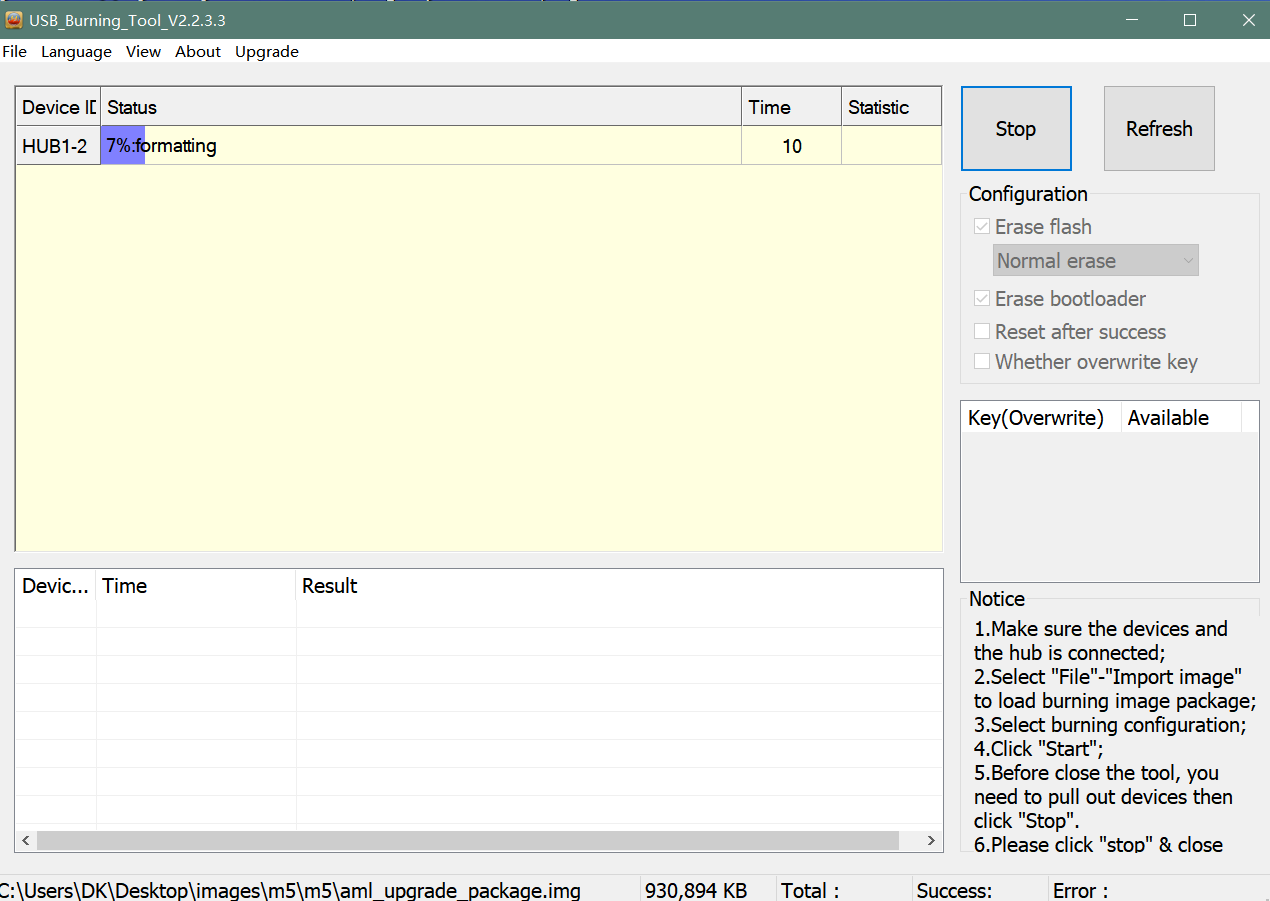
- 1. Open USB_Burning_Tool.exe, select menu File->Import image, choose the android image file aml_upgrade_package.img.
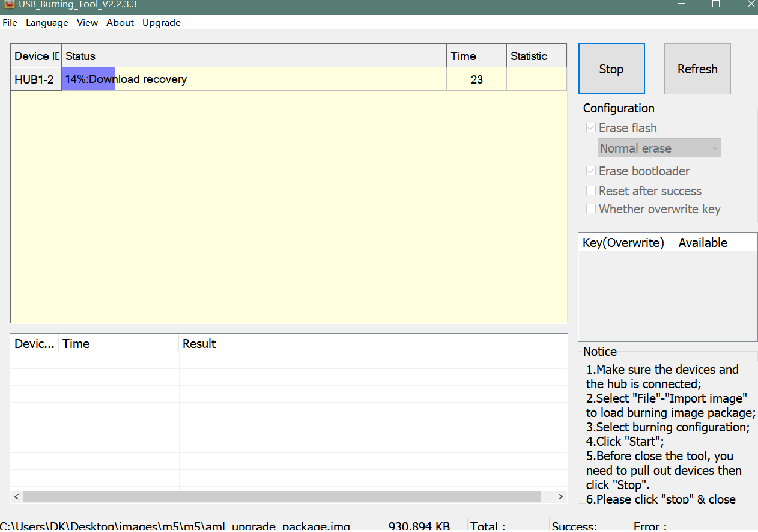
- 2. M5/M2pro board disconnect power, press and hold SW4 button beside 40pin header, plugin type-c usb cable(microUSB on m2pro) to PC
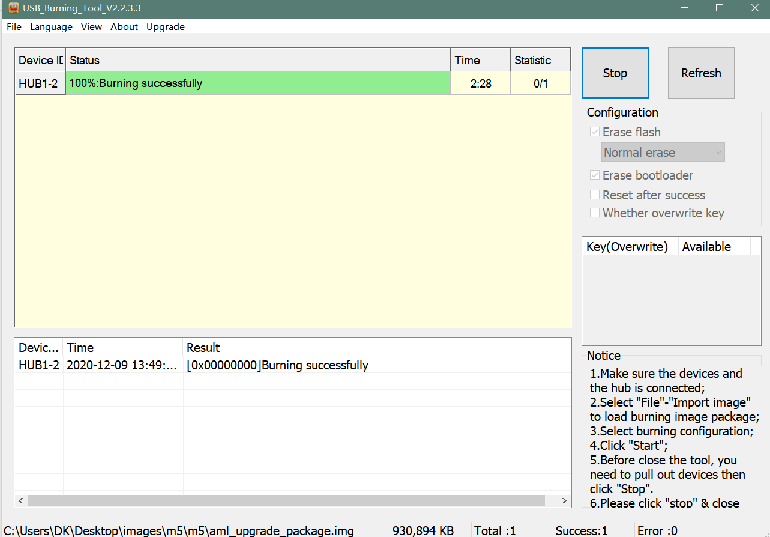
- 3. Click the Start button and wait for upgrade complete.
- 4. After Burning successfull, Unplug the usb and connect to power supply adaptor to startup.
- 5. Click the Stop button to cancel the upgrade process and close the USB Buring Tool.
Install Image with Aml Flash Tool
- aml-flash-tool is a linux platform opensource image flash util for Amlogic android.
$ ./flash-tool.sh --img=/path/to/aml_upgrade_package.img --parts=all --wipe --soc=g12a --reset=y
Build Android Source Code
- 1. Get Android 9.0 source code
$ git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-S905X3-Android9
- or you can get the source code tar archive from Baidu Pan(pincode: 8888) or Google Drive
- 2. Build the Android 9.0 Source code
- Please read the source code README.md
Android DTB overlay
- Bananapi M5/M2Pro DTBO idx value table, default idx value is 0 in release image.
Bananapi M5/M2pro DTBO idx value table idx value device tree overlay description 0 android_p_overlay default dtbo, no use 1 wifi_bt_rtl8822cs enable bpi rtl8822cs wifi/bt module 2 i2c2 enable i2c 2 3 i2c3 enable i2c 3 4 sdio enable sdio 5 uart1 enable 2 pins uart 1 6 uart1_cts_rts enable 4 pins uart 1 7 uart2 enable 2 pins uart 2 8 hifi_pcm5122 enable i2s pcm5122 HiFi DAC
- How to apply a new dtbo
- 1. ADB command via sysfs
root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# adb root restarting adbd as root root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# adb remount remount succeeded root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# adb shell bananapi_m5:/ # echo dtbo > /sys/class/unifykeys/name bananapi_m5:/ # echo "1" > /sys/class/unifykeys/write bananapi_m5:/ # reboot
- 2. Uart console command via sysfs
console:/ $ console:/ $ su console:/ # echo dtbo > /sys/class/unifykeys/name [ 115.702781@0] unifykey: name_store() 1302, name dtbo, 4 [ 115.702856@0] unifykey: name_store() 1311 console:/ # console:/ # echo "1" > /sys/class/unifykeys/write [ 129.262659@0] unifykey: write_store() is a string [ 129.262733@0] unifykey: dtbo, 1, 1 [ 129.265312@0] unifykey: amlkey_write 393 [ 129.292347@1] emmc_key_write:149, write ok console:/ # console:/ # reboot
- 3. Settings App(To-Do)
- Check the bootup uart debug message and confirm which dtbo is loaded actually, here "1" means set idx=1 to apply wifi_bt_rtl8822cs dtbo.
load dtb from 0x1000000 ......
Amlogic multi-dtb tool
Single dtb detected
find 2 dtbos
dtbos to be applied: 1
Apply dtbo 1
- Unifykeys is stored in a specific emmc part, "Normal erase" selected in USB_Burning_Tool will not erase this data for next update, you must select "Erase all" if you want the default dtbo idx to be applied after image download.
- Build Android image with a specific DTBO default.
- 1. Default build-in overlays are defined in device/amlogic/bananapi_m5/Kernel.mk, you can add a new overlay dtbo here.
DTBO_DEVICETREE := android_p_overlay wifi_bt_rtl8822cs i2c2 i2c3 sdio uart1 uart1_cts_rts uart2 hifi_pcm5122
- 2. Default apply DTBO idx is defined in device/amlogic/bananapi_m5/BoardConfig.mk, you can change the idx value to set which overlay dtbo will be applied default.
BOARD_KERNEL_CMDLINE += androidboot.dtbo_idx=0
- 3. DTS files are in common/arch/arm/boot/dts/amlogic/overlay/bananapi_m5/
- More info about android device tree overlays, please refer to google android offical site
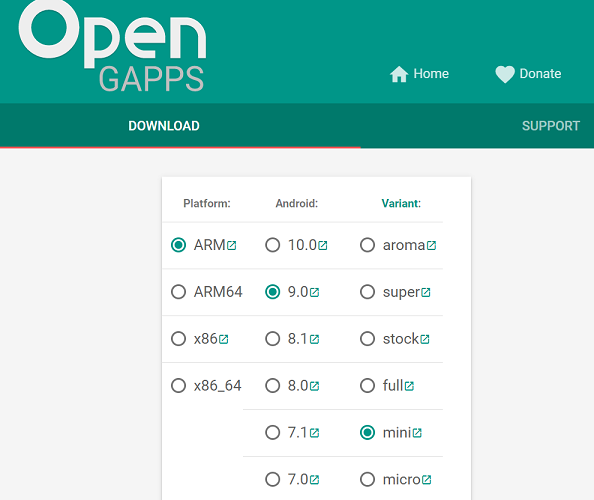
Install OpenGapps
- 1. Download install package from OpenGapps, Android release image is arm/android 9.0 variant.
- 2. Download device_id.apk.
- 3. Copy the OpenGapp package to a udisk or sdcard root directory.
- 4. Create a txt file named factory_update_param.aml in udisk or sdcard root directory with the following android recovery parameter content, and replace the file name with the actual downloaded package.
- udisk:
--wipe_cache --update_package=/udisk/open_gapps-arm-9.0-pico-20210327.zip
- sdcard:
--wipe_cache --update_package=/sdcard/open_gapps-arm-9.0-pico-20210327.zip
- 5. Plugin the udisk or sdcard to the board and poweron.
- 6.OpenGapps install and certify.
- watch this video on bilibili
IR Remote Control Custom
- Before starting this work, some android basic concepts and knowledge need to be known.
- Linux kernel input key event.
- Android keycode.
- Linux keycode map to android keycode.
- Android Adb function work on your PC
- 1. pull the remote files from device
# adb pull /vendor/etc/remote.cfg # adb pull /vendor/etc/remote.tab
- push remote.cfg back
# adb root # adb remount # adb push remote.cfg /vendor/etc/ # adb shell m5_mbox:/ # chmod 644 /vendor/etc/remote.cfg m5_mbox:/ # remotecfg -c /vendor/etc/remote.cfg -d cfgdir = /vendor/etc/remote.cfg work_mode = 1 repeat_enable = 0 debug_enable = 1 max_frame_time = 1000
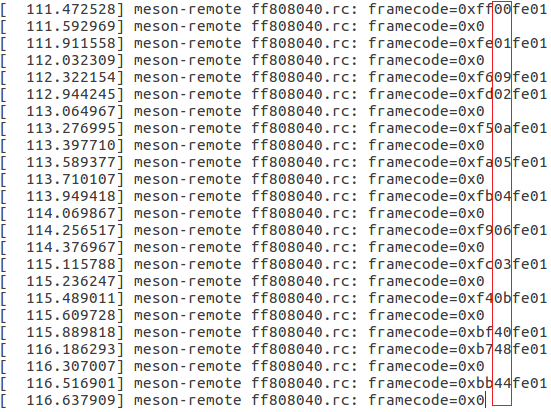
- 3. Get the remote keycode
- Press your remote key one by one and then print the dmesg to get the remote custom_code and each remote key code.
# adb shell dmesg | grep framecode=
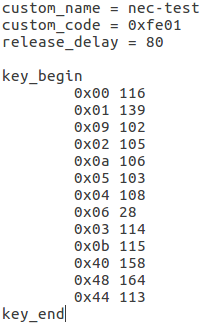
- custom_code = 0xfe01
- keycode = 0x00, 0x01, 0x09, 0x02, 0x0a, 0x05, 0x04 0x06, 0x03, 0x0b, 0x40, 0x48, 0x44
- push remote.tab and test each key whether works
# adb root # adb remount # adb push remote.tab1 /vendor/etc/ # adb shell m5_mbox:/ # chmod 644 /vendor/etc/remote.tab m5_mbox:/ # remotecfg -c /vendor/etc/remote.cfg -t /vendor/etc/remote.tab -d cfgdir = /vendor/etc/remote.cfg work_mode = 1 repeat_enable = 0 debug_enable = 1 max_frame_time = 1000 tabdir = /vendor/etc/remote.tab custom_name = nec-test fn_key_scancode = 0xffff cursor_left_scancode = 0xffff cursor_right_scancode = 0xffff cursor_up_scancode = 0xffff cursor_down_scancode = 0xffff cursor_ok_scancode = 0xffff custom_code = 0xfe01 release_delay = 80 map_size = 13 key[0] = 0x74 key[1] = 0x1008b key[2] = 0x90066 key[3] = 0x20069 key[4] = 0xa006a key[5] = 0x50067 key[6] = 0x4006c key[7] = 0x6001c key[8] = 0x30072 key[9] = 0xb0073 key[10] = 0x40009e key[11] = 0x4800a4 key[12] = 0x440071
- 5. Reboot the board
Linux
Prepare
- 1. Linux image support SDcard or EMMC bootup, but you should read the boot sequence at first.
- 2. It’s recommended to use A1 rated cards, 8GB at least.
- 3. M5 and M2pro are compatiable with same Linux image.
- 4. Make sure bootable EMMC is formatted if you want bootup from SDcard, more info refer to Erase EMMC for SDcard Bootup
- 5. Make sure SDcard is formatted without Linux image flashed if you want bootup from EMMC and use Sdcard as storage.
- 6. Install bpi-tools on your Linux PC(if flash image with other tools, ignore this step). If you can't access this URL or any other install problem, please go to bpi-tools source repo, download and install this tools manually.
$ apt-get install pv $ curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash
- 7. Download latest Linux Image, and confirm that the md5 checksum is correct.
- 8. Default login: pi/bananapi or root/bananapi
- 9. The wiki guide is only for bananapi 4.9 bsp ubuntu/debian images.
Install Image to SDcard
- 1. Install Image with Balena Etcher on Windows, Linux and MacOS.
- Balena Etcher is an opensource GUI flash tool by Balena, Flash OS images to SDcard or USB drive
- 2. Install Image with Balena Cli on Windows, Linux and MacOS.
- Balena CLI is a Command Line Interface for balenaCloud or openBalena. It can be used to flash linux image. Download the installer or standalone package from balena-io and install it correctly to your PC, then you can use the "local flash" command option of balena to flash a linux image to sdcard or usb drive.
$ sudo balena local flash path/to/xxx-bpi-m5-xxx.img.zip $ sudo balena local flash path/to/xxx-bpi-m5-xxx.img.zip --drive /dev/sdX $ sudo balena local flash path/to/xxx-bpi-m5-xxx.img.zip --drive /dev/sdX --yes
- 3. Install Image with dd command on Linux, umount SDcard device /dev/sdX partition if mounted automatically. Actually bpi-copy is the same as this dd command.
$ sudo apt-get install pv unzip $ sudo unzip -p xxx-bpi-m5-xxx.img.zip | pv | dd of=/dev/sdX bs=10M status=noxfer
- 4. Install image with bpi-tools on Linux, plug SDcard to Linux PC and run
$ sudo apt-get install pv unzip $ sudo bpi-copy xxx-bpi-m5-xxx.img.zip /dev/sdX
Install Image to EMMC
- 1. Prepare a SDcard with Linux image flashed and bootup board with this SDcard.
- 2. Copy Linux image to udisk, plug the udisk to board and mount it.
- 3. There are two ways to install the linux image to board.
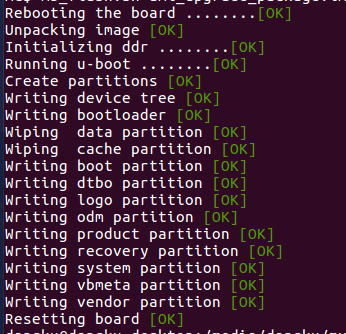
3.1 Install with dd command, umount mmcblk0p1 and mmcblk0p2 partition if mounted automatically. Actually bpi-copy is the same as this dd command. $ sudo apt-get install pv unzip $ sudo unzip -p xxx-bpi-m5-xxx.img.zip | pv | dd of=/dev/mmcblk0 bs=10M status=noxfer
3.2 Install the linux image in udisk with bpi-tools command $ sudo apt-get install pv unzip $ sudo bpi-copy xxx-bpi-m5-xxx.img.zip /dev/mmcblk0
- 4. After download complete, power off safely and eject the SDcard.
Build Linux Source Code
- 1. Get the Linux bsp source code
$ git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-M5-bsp
- 2. Build the bsp source code
- Please read the source code README.md
- 3. If you want build uboot and kernel separately, please download the u-boot the kernel only, get the toolchains, boot script and other configuration files from BPI-M5-bsp
DTB overlay
- 1. DTB overlay is used for 40pin gpios multi-function configuration and install in vfat boot partition, you can check the mount point with mount command.
root@bananapi:~# ls /boot/overlays/ custom_ir.dtbo pwm_b-backlight.dtbo spi0.dtbo ds3231.dtbo pwm_c-beeper.dtbo uart1_cts_rts.dtbo hifi_pcm5102a.dtbo pwm_cd-c.dtbo uart1.dtbo hifi_pcm5122.dtbo pwm_cd.dtbo uart2.dtbo i2c0.dtbo pwm_ef.dtbo waveshare_tft24_lcd.dtbo i2c1.dtbo pwm_ef-f.dtbo waveshare_tft35c_lcd.dtbo pwm_ab.dtbo sdio.dtbo waveshare_tft35c_rtp.dtbo
- 2. Update the overlays env in vfat /boot/boot.ini to enable what you want. Default i2c0, spi0 and uart1 enabled.
# Overlays to load # Example combinations: # spi0 i2c0 i2c1 uart0 # hktft32 # hktft35 setenv overlays "i2c0 spi0 uart1"
- 3. Must be restart the board for overlay dtb loaded.
WiringPi
- Note: This WiringPi only support set 40pin gpio to output, input or software pwm, for io functions as i2c, spi, pwm..., you must enable dtb overlay in boot.ini
- 1. Build and install wiringPi, for debian, you must install sudo before build
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install build-essential git $ git clone https://github.com/Dangku/WiringPi $ cd WiringPi $ chmod a+x build $ sudo ./build
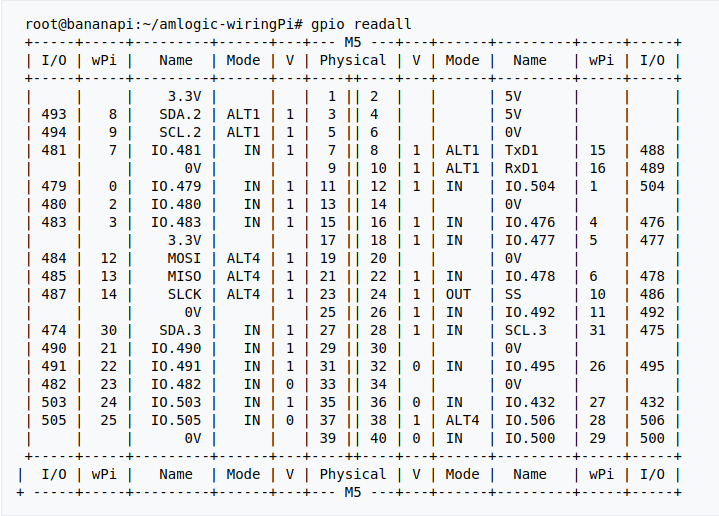
- 2. Run gpio readall to show all 40pins status.
- 3. BPI GPIO Extend board and examples in WiringPi/examples
- blinkall, blink all pin header gpios, no extend board.
- lcd-adafruit, BPI LCD 1602 display module example.
- oled, BPI OLED Display Module example.
- matrixled, BPI RGB LED Matrix Expansion Module example.
- berryclip, BPI BerryClip Module
RPi.GPIO
- Build and install, for debian, you must install sudo before build
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install build-essential python3 python3-pip python3-dev python3-setuptools git $ git clone https://github.com/Dangku/RPi.GPIO.git $ cd RPi.GPIO $ sudo python3 setup.py clean --all $ sudo python3 setup.py install
- Create and install wheel package
$ sudo python3 setup.py bdist_wheel $ sudo pip3 install dist/RPi.GPIO-XXX.whl
- Install from git source directly without development
$ sudo pip3 install git+https://github.com/Dangku/RPi.GPIO.git
- If the package is already installed, it should be uninstalled before installing the new one, or installing the new one with --force-reinstall option.
WiringPi-Python
- Build and install, for debian, you must install sudo before build
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install build-essential python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools swig git $ git clone --recursive https://github.com/Dangku/WiringPi-Python.git $ cd WiringPi-Python $ sudo python3 setup.py install
Luma.Examples
- luma.examples use GPIO.BCM gpio mode default, so you should map 40pin header pins to bcm gpio number and connect the hardware correctly.
- 1. build and install RPi.GPIO
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install build-essential python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools git $ git clone https://github.com/Dangku/RPi.GPIO.git $ cd RPi.GPIO $ sudo python3 setup.py clean --all $ sudo python3 setup.py install
- you can change the bcmledpin variable in test/led.py to your hardware backlight gpio and run it to check RPi.GPIO works well.
$ sudo python3 test/led.py
- hardware backlight will repeat on and off
- 2. luma.examples libs install
$ sudo usermod -a -G i2c,spi,gpio pi
- if group does not exist, the following command will create it:
$ sudo groupadd --system xxx
$ sudo apt-get install python3-dev python3-pip libfreetype6-dev libjpeg-dev build-essential $ sudo apt-get install libsdl-dev libportmidi-dev libsdl-ttf2.0-dev libsdl-mixer1.2-dev libsdl-image1.2-dev $ git clone https://github.com/rm-hull/luma.examples.git $ cd luma.examples
- install luma.core, luma.emulator, luma.lcd, luma.le-matrix, luma.oled pip libs, make sure this step without error or downloading interrupted, try again if get errors
$ sudo -H pip install -e .
- or
$ sudo -H pip3 install -e .
- for debian buster(python 3.7) which does not include /usr/bin/pip in package python3-pip, and will get the following errors when install luma packages with pip3
... WARNING, No "Setup" File Exists, Running "buildconfig/config.py" Using UNIX configuration... /bin/sh: 1: sdl2-config: not found /bin/sh: 1: sdl2-config: not found /bin/sh: 1: sdl2-config: not found ...
- install sdl2 related packages to fix this issue, then install luma libs again with pip3
$ sudo apt-get install libsdl2-dev libsdl2-ttf-dev libsdl2-mixer-dev libsdl2-image-dev $ sudo -H pip3 install -e .
- check installed luma pip libs
$ pip3 list | grep luma luma.core 2.4.0 luma.emulator 1.4.0 luma.lcd 2.10.0 luma.led-matrix 1.7.0 luma.oled 3.11.0
- 3. examples test
- Enable i2c or spi overlays before running test examples
$ cd examples $ sudo python3 bounce.py --config ../conf/ili9341.conf
HDMI LCD
Bananapi M5/M2pro Tested HDMI LCD panel /boot/boot.ini Waveshare 3.5inch 480x320 setenv display_autodetect "false" setenv hdmimode "480x320p60hz"
Waveshare 3.5inch 640x480 Waveshare 4inch 720x720 Waveshare 5inch 960x544 Waveshare 5inch 800x480 Waveshare 5.5inch 1440x2560 setenv display_autodetect "false" setenv hdmimode "1440x2560p60hz"
Waveshare 7inch 800x480 Waveshare 7inch 1024x600 Waveshare 7.9inch 400x1280 Waveshare 8inch 1536x2048 setenv display_autodetect "false" setenv hdmimode "1536x2048p60hz"
Waveshare 8.8inch 480x1920 Waveshare 9inch 2560x1600 setenv display_autodetect "false" setenv hdmimode "2560x1600p60hz"
Waveshare 10.1inch 1024x600 Waveshare 10.1inch 1280x800 Waveshare 11.9inch 320x1480 Waveshare 12.3inch 1920x720 Waveshare 13.3inch 1920x1080 Waveshare 15.6inch 1920x1080
- backlight control
https://github.com/Dangku/Waveshare-USB-Brightness
Boot Linux from USB drive
- S905x3 is not support usb boot in soc rom, so the only way for booting linux from usb drive is create a bootable sdcard or emmc with bootloader flashed, then load boot and rootfs from usb drive. After bootup, everything will run from usb drive.
- 1. The simple way is flash the M5/M2Pro Linux image to sdcard or emmc for bootable and also flash it to the usb drive for loading boot and rootfs.
- 2. Bootup the M5/M2pro board with sdcard or emmc, copy /boot/boot.ini to /boot/boot.ini.org so that bootloader load boot.ini fail and then try to load it from usb drive boot partition.
- 3. Reboot the system, bootscript and rootfs will load from usb drive.
- 4. Test performance
- You can verify the performance of your usb drive on Pi Benchmarks using the following command:
sudo curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TheRemote/PiBenchmarks/master/Storage.sh | sudo bash
- Test results for sd, emmc and usb drive
Category Test Sdcard Test Result Emmc Test Result Usb Drive Test Result HDParm Disk Read 67.91 MB/s 156.64 MB/s 253.40 MB/s HDParm Cached Disk Read 57.39 MB/s 126.53 MB/s 253.52 MB/s DD Disk Write 13.0 MB/s 48.8 MB/s 149 MB/s FIO 4k random read 2456 IOPS (9826 KB/s) 9701 IOPS (38806 KB/s) 5474 IOPS (21897 KB/s) FIO 4k random write 938 IOPS (3753 KB/s) 12888 IOPS (51554 KB/s) 6980 IOPS (27920 KB/s) IOZone 4k read 10615 KB/s 29568 KB/s 23770 KB/s IOZone 4k write 4276 KB/s 33585 KB/s 18598 KB/s IOZone 4k random read 8661 KB/s 29637 KB/s 19982 KB/s IOZone 4k random write 4795 KB/s 38177 KB/s 22134 KB/s Score: 1300 Score: 7811 Score: 5879
Other Development
Custom Linux Boot Logo
- Linux uboot limit boot logo fb size to 1080p60hz/1920x1080 default, so oversize resolution will not be supported by default image, but you can modify uboot source code to support it.
- 1. Prepare a 24bit bmp file and named boot-logo.bmp
- 2. Compress the bmp file to boot-logo.bmp.gz
$ gzip boot-logo.bmp
- 3. copy the target file to BPI-BOOT partition of linux image
$ cp boot-logo.bmp.gz /media/xxx/BPI-BOOT/
Custom Android Boot Logo
- Android bootloader limit boot logo fb display size is 1080p60hz/1920x1080 default, and android kernel dtb partition table limit boot logo partition size to 16MB default .
- 1. Prepare a 24bit bmp file and named boot-logo.bmp
- 2. Compress the bmp file to boot-logo.bmp.gz
$ gzip boot-logo.bmp
- 3. Download m5_android_bootlogo_tool.zip
- 4. Extract this tool
$ unzip m5_android_bootlogo_tool.zip $ cd m5_android_bootlogo_tool/ $ cp -a logo_img_files logo //logo_img_files is the origin bootlogo resource in android source and copy from <android-source-dir>/devices/amlogic/bananapi_m5/log_img_files $ ls -l logo/ -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 525054 Sep 25 16:54 bootup.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 525054 Sep 25 16:54 bootup_X3.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 184 May 19 2020 upgrade_bar.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 180072 May 19 2020 upgrade_error.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 180072 May 19 2020 upgrade_fail.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 180072 May 19 2020 upgrade_logo.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 180072 May 19 2020 upgrade_success.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 184 May 19 2020 upgrade_unfocus.bmp -rwxr--r-- 1 dangku dangku 180072 May 19 2020 upgrade_upgrading.bmp
- 5. Copy the boot-logo.bmp.gz
$ cp boot-logo.bmp.gz logo/bootup.bmp $ cp boot-logo.bmp.gz logo/bootup_X3.bmp
- 6. Create target logo.img with img pack tool, the binary and related libs of m5_android_bootlogo_tool are copy from <android-source-dir>/out/host/linux-x86
$ ./logo_img_packer -r logo logo.img
- 7. Flash boot logo with fastboot
$ adb root $ adb remount $ adb reboot fastboot
- Wait few seconds and check whether fastboot connected
$ fastboot device 1234567890 fastboot $ fastboot flashing unlock_critical $ fastboot flashing unlock $ fastboot flash logo logo.img $ fastboot reboot
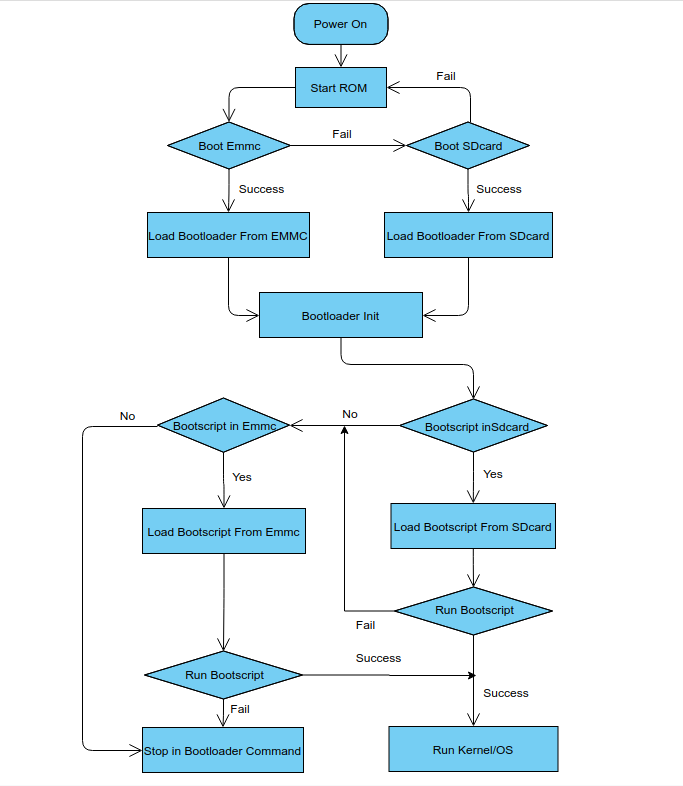
Boot Sequence
- Check bootloader loaded from SDcard or EMMC at the beginning of the console debug messages
- 1. Rom load bootloader from SDcard (Linux log example)
... BL2 Built : 15:21:42, Mar 26 2020. g12a g486bc38 - gongwei.chen@droid11-sz Board ID = 1 Set cpu clk to 24M Set clk81 to 24M Use GP1_pll as DSU clk. DSU clk: 1200 Mhz CPU clk: 1200 MHz Set clk81 to 166.6M board id: 1 Load FIP HDR DDR from SD, src: 0x00010200, des: 0xfffd0000, size: 0x00004000, part: 0 fw parse done PIEI prepare done fastboot data verify result: 255 Cfg max: 12, cur: 1. Board id: 255. Force loop cfg DDR4 probe ...
- 2. Rom load bootloader from EMMC(Android Log example)
... Board ID = 1 Set cpu clk to 24M Set clk81 to 24M Use GP1_pll as DSU clk. DSU clk: 1200 Mhz CPU clk: 1200 MHz Set clk81 to 166.6M eMMC boot @ 0 sw8 s board id: 1 Load FIP HDR DDR from eMMC, src: 0x00010200, des: 0xfffd0000, size: 0x00004000, part: 0 fw parse done PIEI prepare done 00000000 emmc switch 1 ok ddr saved addr:00016000 Load ddr parameter from eMMC, src: 0x02c00000, des: 0xfffd0000, size: 0x00001000, part: 0 00000000 ...
Erase EMMC for SDcard Bootup
- There are four possible scenarios should be pay attention to, EMMC already flashed Android image, EMMC already flashed Linux image, boot process hangup in BL2 and EMMC empty.
- 1. Bootable EMMC with Android image flashed
- a). Using usb burning tool, unplug the download usb cable while the download process at 7% formatting
- b). Using Android Fastboot tool, make sure the adb/fastboot tools is work on your PC before doing this.
root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# adb root adbd is already running as root root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# adb remount remount succeeded root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# adb shell bananapi_m5:/ # reboot fastboot
- Wait a few seconds for board reboot to fastboot mode
root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# fastboot devices 1234567890 fastboot root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# fastboot flashing unlock_critical ... OKAY [ 0.044s] finished. total time: 0.044s root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# fastboot flashing unlock ... OKAY [ 0.047s] finished. total time: 0.047s root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# fastboot erase bootloader erasing 'bootloader'... OKAY [ 0.059s] finished. total time: 0.059s root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# fastboot erase bootloader-boot0 erasing 'bootloader-boot0'... OKAY [ 0.036s] finished. total time: 0.036s root@dangku-desktop:/tmp# fastboot erase bootloader-boot1 erasing 'bootloader-boot1'... OKAY [ 0.035s] finished. total time: 0.035s
- c). Using uboot command, connect a debug console cable and press ESC while power on to enter uboot command line
bananapi_m5_v1#amlmmc erase 1 emmckey_is_protected(): protect start = 0,end = 57343 start = 221184,end = 30535679 Erasing blocks 0 to 8192 @ boot0 start = 0,end = 8191 Erasing blocks 0 to 8192 @ boot1 start = 0,end = 8191 bananapi_m5_v1#reset resetting ... SM1:BL:511f6b:81ca2f;FEAT:A0F83180:20282000;POC:F;RCY:0;EMMC:0;READ:0;CHK:1F;READ:0;CHK:1F;READ:0;CHK;
- These two ways actually erase the bootloader part of EMMC android, After bootup from SDcard Linux, You'd better format the whole EMMC by dd command.
- d). The simplest way is insert the SDcard with Linux image flashed before power on, the Android bootloader will check boot.ini file whether exist in SDcard vfat partition, so that the SDcard Linux will bootup. After bootup, you can format the whole EMMC by dd command and then flash the Linux image to EMMC.
... BPI: try boot from sdcard reading boot.ini 5699 bytes read in 3 ms (1.8 MiB/s) ## Executing script at 01b00000 ... reading Image.gz 9143358 bytes read in 510 ms (17.1 MiB/s) reading meson64_bananapi_m5.dtb 70850 bytes read in 8 ms (8.4 MiB/s) reading uInitrd 11704481 bytes read in 655 ms (17 MiB/s) reading overlays/i2c0.dtbo 223 bytes read in 6 ms (36.1 KiB/s) reading overlays/spi0.dtbo 516 bytes read in 6 ms (84 KiB/s) reading overlays/uart1.dtbo 225 bytes read in 5 ms (43.9 KiB/s)
- 2. Bootable EMMC with Linux image flashed
- a). Using uboot command, connect a debug console cable and press ESC while power on to enter uboot command line
bananapi_m5# mmc erase 0 1000
- b). Linux u-boot also check boot.ini file whether exist in SDcard vfat partition so that the SDcard Linux will bootup. After bootup, you can format the whole EMMC by dd command or flash the Linux image directly to EMMC.
- 3. A extreme situation is bootloader or uboot corrupted, Rom load it from EMMC but hangup in u-boot or BL2, for example the boot process will hangup in BL2 of EMMC if dram init failed, The only way is format the EMMC with usb burning tool, or download the Android image completely and then try other ways to erase EMMC or flash Linux image to EMMC.
- 4. Rom will try to load bootloader from SDcard directly if EMMC is empty.
Erase Emmc Android by dd command
- If the board is flashed android before, the whole emmc must be erased by these commands if you want bootup it with SDcard Linux image.
$ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mmcblk0boot0 bs=1M status=noxfer $ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mmcblk0boot1 bs=1M status=noxfer $ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mmcblk0 bs=1M status=noxfer $ sync
Wifi/BT support
- 1. Android test and support.
rtl8723bu wifi/bt(usb) rtl8188eu wifi(usb) rtl8821cu wifi/bt(usb) rtl8822cs wifi/bt(sdio/uart) rtl8814au wifi(usb), please get the aircrack-ng driver and install.
- How to enable Android Wifi/BT
- USB type: Plug-in the usb dongle to usb host port and reboot the system, After bootup, you can enable or disable wifi and bluetooth in Settings app.
- SDIO/UART type: Connect the hardware module to 40pin header correctly and configure the Android DTB overlay to enable it.
- Note: Android is not support that ethernet and wifi are both connected at the same time, Ethernet have a higher prioprity than wifi, it means wifi can't connect network if ethernet already connected, and wifi will drop connection if ethernet cable plugin.
- 2. Linux test and support.
rtl8188eu wifi(usb) rtl8192eu wifi(usb) rtl8723bu wifi/bt(usb) rtl8811au wifi(usb) rtl8812au wifi(usb) rtl8812bu wifi(usb) rtl8821cu wifi/bt(usb) rtl8822cs wifi/bt(sdio/uart)
- How to enable Linux Wifi
- Wifi module drivers are already prebuild in the release images.
- USB type: Plug-in the usb dongle to usb host port and driver will be loaded automatically.
- SDIO/UART type:
- 1). Connect the hardware module to 40pin header correctly.
- 2). Configure the dtb overlay
# Overlays to load # Example combinations: # spi0 i2c0 i2c1 uart0 # hktft32 # hktft35 setenv overlays "wifi_bt_rtl8822cs"
- 3). Add the wifi module name to /etc/modules for loaded automatically next boot.
# This file contains the names of kernel modules that should be loaded # at boot time, one per line. Lines beginning with "#" are ignored. 88x2cs
- How to enable Linux Bluetooth
- 1). Please download rtk-linux-bt-driver source code, build and install usb or uart rtk linux bluetooth drivers/firmwares to your image.
- 2). For USB type, plug-in the usb dongle to usb host port and driver will be loaded automatically.
- 3). For UART type, Configure the dtb overlay as the same as wifi before install the bluetooth drivers/firmwares. hci_uart driver will be loaded when rtk-hciuart.service start.
Linux Server Image Network Configuration
- Linux Wifi STA mode
- A sample wifi sta mode netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-sta.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
wifis:
wlan0:
dhcp4: true
access-points:
"bananapi":
password: "123456789"
- Linux Wifi AP mode
- 1. Prepare the setup the wifi adater correctly.
- 2. Get the wifi adapter Band, Frequencies, Channel, HT Capability, VHT Capability or other properties
$ iw list
- 3. Manage wifi access point mode with Netplan and Network-Manager.
- Install NetworkManager because ap is only supported with NetworkManager renderer
$ sudo apt install network-manager
- A sample 2.4G wifi ap mode netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-2.4g.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: NetworkManager
wifis:
wlan0:
dhcp4: no
access-points:
"bananapi":
mode: ap
band: 2.4GHz
channel: 6
auth:
key-management: psk
password: "123456789"
- A sample 5G wifi ap mode netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-5g.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: NetworkManager
wifis:
wlan0:
dhcp4: no
access-points:
"bananapi":
mode: ap
band: 5GHz
channel: 36
auth:
key-management: psk
password: "123456789"
- 4. Manage wifi access point mode with Netplan and Hostapd.
- 1). Create a netplan configuration file, 01-wlan0-ap-hostapd.yaml
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
wlan0:
dhcp4: no
addresses:
- 192.168.11.1/24
- 2). Install hostapd
$ sudo apt install hostapd
- Create hostapd configuration file /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf, for example
interface=wlan0 ssid=bananapi driver=nl80211 auth_algs=1 wpa=2 wpa_passphrase=123456789 wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK rsn_pairwise=CCMP #bridge=br0 beacon_int=500 #SSID not hidden ignore_broadcast_ssid=0 hw_mode=a channel=36 max_num_sta=8 ### IEEE 802.11n ieee80211n=1 #require_vht=0 ht_capab=[HT20][HT40+][SHORT-GI-20][SHORT-GI-40][SHORT-GI-80][DSSS_CCK-40] ### IEEE 802.11ac ieee80211ac=1 #require_vht=0 #vht_capab=[MAX-MPDU-3895][SHORT-GI-80][SU-BEAMFORMEE] #vht_oper_chwidth=1 #vht_oper_centr_freq_seg0_idx=42 ### WMM wmm_enabled=1
- 3). To support 80MHz channel width you need load driver with rtw_vht_enable=2 option, Or you can create /etc/modprobe.d/8822cs.conf with content
options 88x2cs rtw_vht_enable=2
- 4). Install and configure dhcp server service, use isc-dhcp-server for example
$ sudo apt install isc-dhcp-server
- Configure dhcp server interface in /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server
# On what interfaces should the DHCP server (dhcpd) serve DHCP requests? # Separate multiple interfaces with spaces, e.g. "eth0 eth1". INTERFACESv4="wlan0"
- Configure dhcp subnet and dns in /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
...
option domain-name "example.org";
option domain-name-servers 8.8.8.8, 114.114.114.114;
...
# No service will be given on this subnet, but declaring it helps the
# DHCP server to understand the network topology.
subnet 192.168.11.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range dynamic-bootp 192.168.11.1 192.168.11.100;
option broadcast-address 192.168.11.255;
option routers 192.168.11.1;
}
- 5). Start Service
$ sudo hostapd /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf -B $ sudo systemctl restart isc-dhcp-server
- 6). Routing configuration.
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.11.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
Disable Cloud-init&Snap
- Cloud-init and Snap service are enabled default, you can disable or remove them.
- 1. disable or remove cloud-init
$ sudo touch /etc/cloud/cloud-init.disabled
- or
$ sudo apt purge cloud-init
- 2. disable or remove snap
$ sudo apt purge snapd
Enable rc-local
- The systemd service rc-local.service already exists in release image, but there is no [Install] part in the unit file. As a result, Systemd is unable to enable it. First, we must update the file.
$ sudo nano /lib/systemd/system/rc-local.service
[Unit] Description=/etc/rc.local Compatibility Documentation=man:systemd-rc-local-generator(8) ConditionFileIsExecutable=/etc/rc.local After=network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/etc/rc.local start TimeoutSec=0 RemainAfterExit=yes GuessMainPID=no [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target Alias=rc-local.service
- Create /etc/rc.local file.
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
#!/bin/sh # # rc.local # # This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel. # Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other # value on error. # # In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution # bits. # # By default this script does nothing. exit 0
- Add executable permission to /etc/rc.local
$ sudo chmod +x /etc/rc.local
- Enable rc-local.service and reboot
$ sudo systemctl enable rc-local.service $ sudo reboot
Enable sudo for Debian
- The release Debian image do not install sudo default, with "su -" command, user can change to root. If you like sudo, you can install it.
$ su root Password:(enter bananapi) # apt-get update # apt-get install sudo # adduser pi sudo
- Then please do logout and login again
Install Docker Engine
- Install Docker Engine on Ubuntu 20.04 Server
- 1. Set up the repository
- Update the apt package index and install packages to allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS:
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
- Add Docker’s official GPG key:
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
- Set up the stable repository
$ echo \
"deb [arch=arm64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
- 2. Install Docker Engine
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
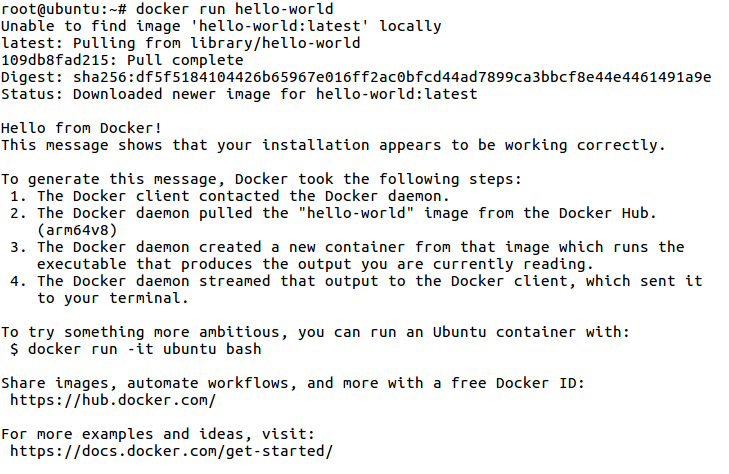
- 3. Verify the Docker Engine is installed correctly by running the hello-world image.
$ sudo docker run hello-world
Install docker with a simple command
$ curl -sSL get.docker.com | sudo sh
Install Docker Engine on other Linux distributions