Difference between revisions of "Getting Started with P2-Zero"
JackZengWiki (talk | contribs) (→Introduction) |
(→Update your image) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[zh:快速上手 香蕉派 BPI-M2 Zero]] | [[zh:快速上手 香蕉派 BPI-M2 Zero]] | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| + | [[File:BPI-F2_zero_1.JPG|thumb|Overview [[Banana Pi BPI-P2 Zero]]]] | ||
[[File:M2Zero_raspbian.png|thumb|Overview: BPI-M2Z raspbian]] | [[File:M2Zero_raspbian.png|thumb|Overview: BPI-M2Z raspbian]] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
=Development= | =Development= | ||
==Basic Development== | ==Basic Development== | ||
| + | ===Load your first Android image on M1=== | ||
| + | 1.You could download latest image from our forum. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2.Put your TF card into a TF-USB adapter, and then plug adapter in your Windows PC usb interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3.Prepare your image, and download image burning tools PhoenixCard.exe. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4.Use "PhoenixCard.exe" to burn android image to TF card. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:M3_Android_Burning.png | 600px]] | ||
===Prepare to develop=== | ===Prepare to develop=== | ||
* Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Ubuntu System | * Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Ubuntu System | ||
| − | * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on | + | * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on P2 Zero |
[[Image:Debug_console_wire.png]] | [[Image:Debug_console_wire.png]] | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:P2_Zero_debug_console.jpg]] |
| + | |||
| + | ===Install Linux Image on P2 Zero=== | ||
| + | Download [http://wiki.banana-pi.org/Banana_Pi_BPI-M2_ZERO#Linux latest Linux image], default login user/password is pi/bananapi or root/bananapi. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Install Image to SDcard on Linux PC with bpi-tools | ||
| + | :1. Install bpi-tools on your system | ||
| + | $ apt-get install pv | ||
| + | $ curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash | ||
| + | :If you can't access this URL or any other problems, please go to [https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools bpi-tools repo] and install this tools manually. | ||
| − | + | :2. Insert your SDcard into your PC | |
| − | + | $ bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Install Image to SDcard with Ether on Windows, Linux and MacOS | |
| − | + | :[https://www.balena.io/etcher/ Balena Etcher] is an open source project by Balena, Flash OS images to SD cards & USB drives | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Install Image to EMMC with SD Ubuntu | |
| − | + | :1.Prepare a sd which is installed ubuntu image and bootup with sdcard | |
| − | + | :2.Copy emmc image to udisk, plug in board, then mount udisk. | |
| − | + | :3.After mount udisk, use command "bpi-copy xxx-emmc-xxx.img" to install image on Emmc. | |
| − | + | :4.After success install, power off the board, eject the sdcard and poweron with emmc boot. | |
===Update your image=== | ===Update your image=== | ||
| − | + | :1. Get the p2 zero bsp source code | |
| − | + | $ git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-M2P-bsp-4.4 | |
| + | |||
| + | :2. Build the source code according to the README.md, and update the packages to the sdcard with bpi image flashed. | ||
| + | ===Install Image to EMMC=== | ||
| + | :1. Prepare a SDcard with Linux image flashed and bootup board with this SDcard. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :2. Copy Linux image to udisk, plug the udisk to OTG Port(via USB-to-MicroUSB) of the board and mount it. | ||
| − | + | :3. Install with dd command, umount mmcblk0p1 and mmcblk0p2 partition if mounted automatically. Actually bpi-copy is the same as this dd command. | |
| − | + | $ sudo apt-get install pv unzip | |
| + | $ sudo unzip -p xxx-bpi-p2zero-xxx.img.zip | pv | dd of=/dev/mmcblk0 bs=10M status=noxfer | ||
| − | + | :4. Install the linux image in udisk with bpi-tools command | |
| − | + | $ sudo apt-get install pv unzip | |
| − | + | $ sudo bpi-copy xxx-bpi-p2zero-xxx.img.zip /dev/mmcblk0 | |
| + | |||
| + | :5. After download complete, power off safely and eject the SDcard. | ||
==Advanced Development== | ==Advanced Development== | ||
| Line 72: | Line 100: | ||
* If yes, we could execute "adb shell" to connect M2 Zero by adb now | * If yes, we could execute "adb shell" to connect M2 Zero by adb now | ||
| − | === | + | ===EMac=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* Use iperf3 to test network | * Use iperf3 to test network | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:P2Zero_network.jpg]] |
===Bluetooth=== | ===Bluetooth=== | ||
Latest revision as of 00:06, 24 November 2022
Contents
Introduction

- Read more about : Banana Pi BPI-P2 Zero
BPI-P2 Zero
Banana Pi BPI-P2 Zero is an ultra compact single board computer measures only 65mm*52.5mm. It uses quad-core Cortex A7 allwinner H2+ processor(Option : H3 and H5), with 512MB RAM memory.8G eMMC flash,100M LAN,add PoE function support , It's ideal for light-weight systems with some space-limited applications. Like other members of Banana Pi, it supports both linux and android operating system.
Key Features
- CPU: Allwinner H2+, Quad-core Cortex-A7
- 512MB DDR 3 SDRAM
- WiFi (AP6212) & Bluetooth onboard
- Mini HDMI
- 40 PIN GPIO, It includes UART, SPI, I2C, IO etc
- 100M LAN
- IEEE 802.3af PoE standard PoE module support
- 8G eMMC flash onboard
Development
Basic Development
Load your first Android image on M1
1.You could download latest image from our forum. 2.Put your TF card into a TF-USB adapter, and then plug adapter in your Windows PC usb interface. 3.Prepare your image, and download image burning tools PhoenixCard.exe. 4.Use "PhoenixCard.exe" to burn android image to TF card.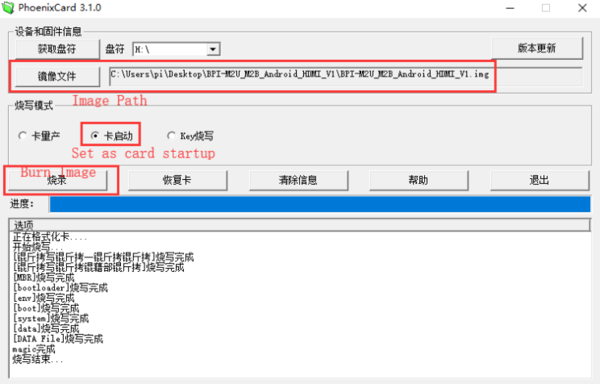
Prepare to develop
* Prepare 8G/above TF card, USB-Serial interface, PC with Ubuntu System * Using your USB-Serial Connect debug console on P2 Zero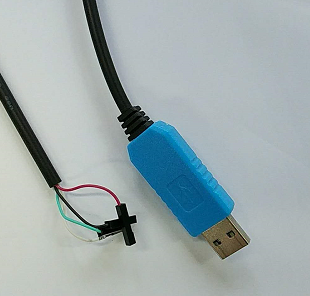
Install Linux Image on P2 Zero
Download latest Linux image, default login user/password is pi/bananapi or root/bananapi.
Install Image to SDcard on Linux PC with bpi-tools
- 1. Install bpi-tools on your system
$ apt-get install pv $ curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash
- If you can't access this URL or any other problems, please go to bpi-tools repo and install this tools manually.
- 2. Insert your SDcard into your PC
$ bpi-copy xxx.img /dev/sdx
Install Image to SDcard with Ether on Windows, Linux and MacOS
- Balena Etcher is an open source project by Balena, Flash OS images to SD cards & USB drives
Install Image to EMMC with SD Ubuntu
- 1.Prepare a sd which is installed ubuntu image and bootup with sdcard
- 2.Copy emmc image to udisk, plug in board, then mount udisk.
- 3.After mount udisk, use command "bpi-copy xxx-emmc-xxx.img" to install image on Emmc.
- 4.After success install, power off the board, eject the sdcard and poweron with emmc boot.
Update your image
- 1. Get the p2 zero bsp source code
$ git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-M2P-bsp-4.4
- 2. Build the source code according to the README.md, and update the packages to the sdcard with bpi image flashed.
Install Image to EMMC
- 1. Prepare a SDcard with Linux image flashed and bootup board with this SDcard.
- 2. Copy Linux image to udisk, plug the udisk to OTG Port(via USB-to-MicroUSB) of the board and mount it.
- 3. Install with dd command, umount mmcblk0p1 and mmcblk0p2 partition if mounted automatically. Actually bpi-copy is the same as this dd command.
$ sudo apt-get install pv unzip $ sudo unzip -p xxx-bpi-p2zero-xxx.img.zip | pv | dd of=/dev/mmcblk0 bs=10M status=noxfer
- 4. Install the linux image in udisk with bpi-tools command
$ sudo apt-get install pv unzip $ sudo bpi-copy xxx-bpi-p2zero-xxx.img.zip /dev/mmcblk0
- 5. After download complete, power off safely and eject the SDcard.
Advanced Development
How to create an image
- Prepare a SD card which have installed system(Ubuntu/Raspbian/..)
- Boot your SD card with M2 Zero, after M2 Zero finish starting, copy your files and config your system, then poweroff M2 Zero. [If you don't want to config your system, you can skip this step]
- Plug your SD card in PC(which is running Linux), "cd /media", then "ln -s <your account> pi"
- Execute "bpi-migrate -c bpi-m2z.conf -c ubuntu-mate-from-sd.conf -d /dev/sdx"
- Then you could get your own image now
OTG
1. On M2 Zero console:
- Execute "./adbd.sh", then execute "ps -ax | grep adbd" to see if adbd is set up
2. On PC terminal:
- If adbd was succeed to set up, insert OTG-USB interface to M2 Zero and PC(with Ubuntu system)
- Execute "adb devices" to see if PC has recognised M2 ZeroP OTG
- If yes, we could execute "adb shell" to connect M2 Zero by adb now
EMac
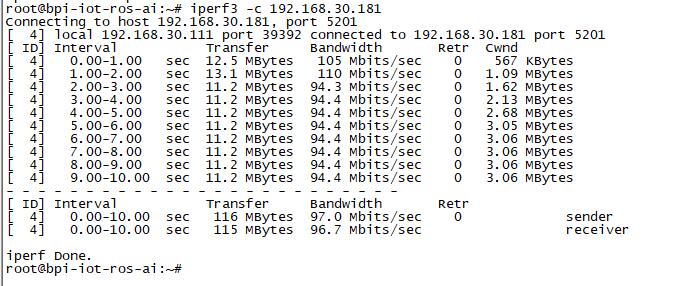
- Use iperf3 to test network
Bluetooth
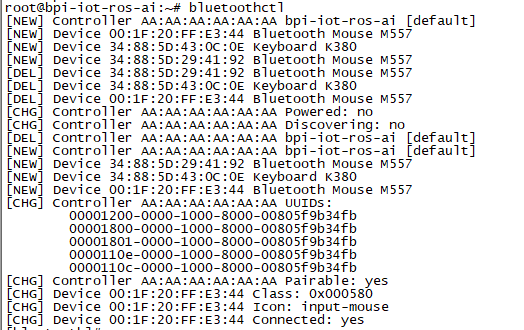
- Use bluetoothctl tool to operate BT
- Execute "bluetoothctl"
- If you don't know how to use bluetoothctl, type "help", you will see more commands
- Execute these commands:
WiFi Client
You have two ways to setup WiFi Client
1. Use commands to setup WiFi client
- ip link set wlan0 up
- iw dev wlan0 scan | grep SSID
- vim /etc/wpasupplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
network={
ssid="ssid"
psk="password"
priority=1
}
- wpa_supplicant -iwlan0 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf
- dhclient wlan0
2. Use UI interface to setup WiFi Client
Clear boot
- git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-files/tree/master/SD/100MB
- bpi-bootsel BPI-cleanboot-8k.img.gz /dev/sdX
Camara function
We use HDF5640 camara.
Guvcview
- Use your UI interface to operate camara
- Applications -> Sound & Video -> guvcview
Shell
- We also have built-in command in /usr/local/bin to test camara
- "./test_ov5640_image_mode.sh" to test picture taking function
- "./cameratest.sh" to test video recording function
Display
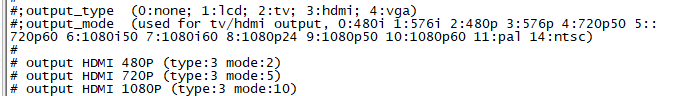
How to change display resolution
For Example: we change M2Z HDMI display 1080P.
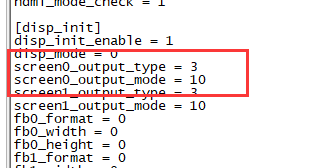
1. First, mount /dev/mmcblk0p1 /mnt, then enter to /mnt/bananapi/bpi-m2z/linux, find "sys_config.fex";
2. "vim sys_config.fex", change "screen0_output_mode = 5" to "screen0_output_mode = 10"
3. After save changed, use "fex2bin" command to transfer sys_config.fex to bin file, "fex2bin sys_config.fex script.bin ", reboot.
parameters meaning:
BPI-Tools
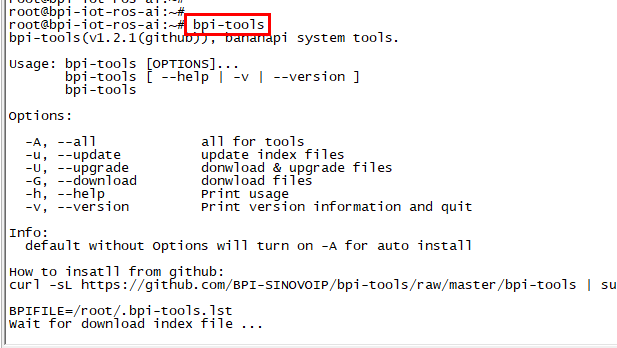
Install Bpi-tools
- Execute "curl -sL https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/bpi-tools/raw/master/bpi-tools | sudo -E bash - "
Update Bpi-tools
- Execute "bpi-tools"
RPi.GPIO
Install RPi.GPIO
- Execute "git clone https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/RPi.GPIO"
- after clone the repo, cd RPi,GPIO
- Execute "sudo apt-get update"
- Execute "sudo apt-get install python-dev python3-dev"
- Execute "sudo python setup.py install" or "sudo python3 setup.py install" to install the module
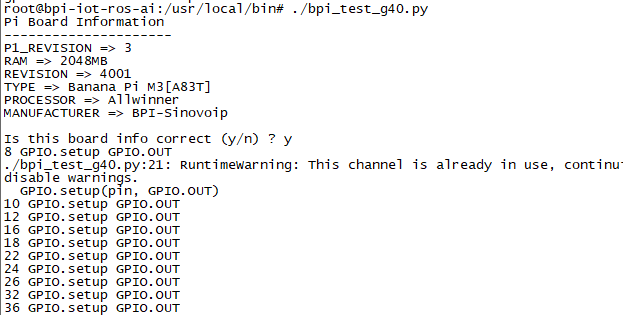
Using RPi.GPIO
- cd /usr/local/bin
- Execute "./bpi_test_g40.py" to test RPi.GPIO
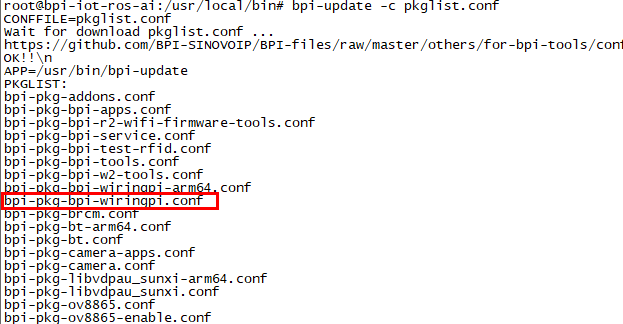
WiringPi
- GitHub: https://github.com/BPI-SINOVOIP/BPI-WiringPi2.git
- We also have built-in test command in "/usr/local/bin"
How to Update WiringPi
- Execute "bpi-update -c pkglist.conf"
- Execute "bpi-update -c bpi-pkg-bpi-wiringpi.conf"
RGB 1602 LCD
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_lcd1602.sh"
0.96 Inch OLED Display
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_52pi.sh"
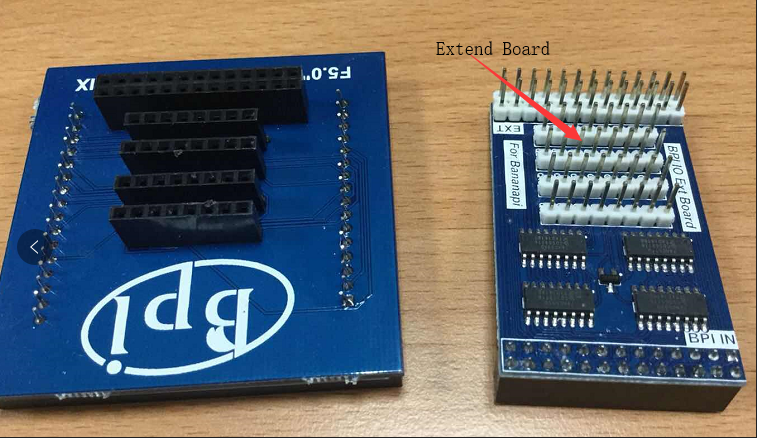
8x8 RGB LED Martix
- Firstly you need a GPIO Extend Board for 8x8 LED Martix
- Execute "/usr/local/bin/bpi_test_gpio40.sh"